Ghidul privind diagnosticul şi managementul sincopei - Romanian ...
Ghidul privind diagnosticul şi managementul sincopei - Romanian ...
Ghidul privind diagnosticul şi managementul sincopei - Romanian ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Romanian</strong> Journal of Cardiology<br />
Vol. 26(21), No. 2, 2011<br />
Cornelia Cãlinescu et al<br />
Risk factors for sudden death<br />
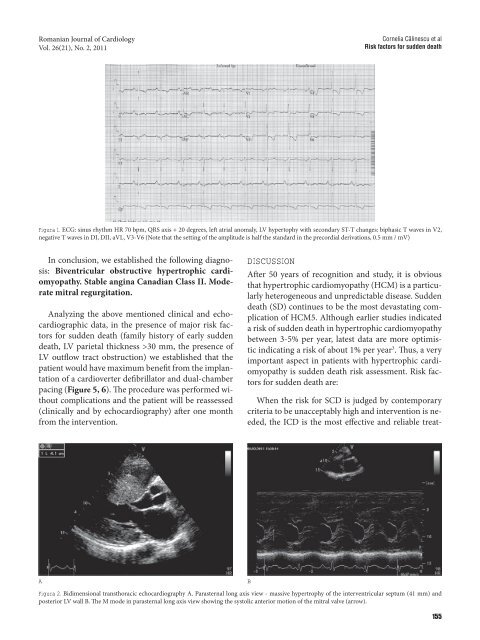
Figura 1. ECG: sinus rhythm HR 70 bpm, QRS axis + 20 degrees, left atrial anomaly, LV hypertophy with secondary ST-T changes: biphasic T waves in V2,<br />
negative T waves in DI, DII, aVL, V3-V6 (Note that the setting of the amplitude is half the standard in the precordial derivations, 0.5 mm / mV)<br />
In conclusion, we established the following diagnosis:<br />
Biventricular obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.<br />
Stable angina Canadian Class II. Moderate<br />
mitral regurgitation.<br />
Analyzing the above mentioned clinical and echocardiographic<br />
data, in the presence of major risk factors<br />
for sudden death (family history of early sudden<br />
death, LV parietal thickness >30 mm, the presence of<br />
LV outfl ow tract obstruction) we established that the<br />
patient would have maximum benefi t from the implantation<br />
of a cardioverter defi brillator and dual-chamber<br />
pacing (Figure 5, 6). Th e procedure was performed without<br />
complications and the patient will be reassessed<br />
(clinically and by echocardiography) aft er one month<br />
from the intervention.<br />
A B<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
Aft er 50 years of recognition and study, it is obvious<br />
that hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a particularly<br />
heterogeneous and unpredictable disease. Sudden<br />
death (SD) continues to be the most devastating complication<br />
of HCM5. Although earlier studies indicated<br />
a risk of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy<br />
between 3-5% per year, latest data are more optimistic<br />
indicating a risk of about 1% per year3 . Th us, a very<br />
important aspect in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy<br />
is sudden death risk assessment. Risk factors<br />
for sudden death are:<br />
When the risk for SCD is judged by contemporary<br />
criteria to be unacceptably high and intervention is needed,<br />
the ICD is the most eff ective and reliable treat-<br />
Figura 2. Bidimensional transthoracic echocardiography A. Parasternal long axis view - massive hypertrophy of the interventricular septum (41 mm) and<br />
posterior LV wall B. Th e M mode in parasternal long axis view showing the systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve (arrow).