2013–2014 UNIVERSITY CATALOG - Florida Institute of Technology
2013–2014 UNIVERSITY CATALOG - Florida Institute of Technology
2013–2014 UNIVERSITY CATALOG - Florida Institute of Technology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
simulation and analysis. In the senior year, students design, build and<br />
test complete systems as part <strong>of</strong> their senior design course.<br />
The educational objectives for electrical engineering are to produce<br />
graduates who will establish themselves as practicing pr<strong>of</strong>essionals<br />
who will engage in advanced studies in engineering or a related field;<br />
display awareness <strong>of</strong> the importance <strong>of</strong> an opportunities for lifelong<br />
learning; excel in the global marketplace; and demonstrate the ability<br />
to work successfully as members <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>essional teams and function<br />
effectively as responsible pr<strong>of</strong>essionals.<br />
A major component <strong>of</strong> the electrical engineering program at <strong>Florida</strong><br />
Tech involves hands-on learning. The electrical engineering student<br />
begins taking electrical engineering courses during his/her freshman<br />
year. The freshman-level courses include programming and interfacing<br />
an embedded microcontroller. Laboratory experience and computerbased<br />
analysis are integrated into most classes and all laboratories.<br />
In electrical engineering, a strong emphasis is on the mastery principle.<br />
It is assured that electrical engineering students not only know the<br />
material critical to engineering, but also can demonstrate mastery <strong>of</strong><br />
the material, which is the goal <strong>of</strong> everyone in the program.<br />
During the freshman and sophomore years, students learn the basics<br />
<strong>of</strong> electrical engineering along with college-level mathematics and<br />
physics. In addition, courses in computer design with hands-on lab<br />
experiences are taken both terms <strong>of</strong> the freshman year.<br />
Throughout the sophomore and junior years, students learn the basic<br />
analytical techniques <strong>of</strong> engineering—ways in which the engineer<br />
views physical situations and uses mathematical techniques to design<br />
basic subsystems. Many <strong>of</strong> the courses taken by students at this level<br />
<strong>of</strong>fer integrated lab experiences. In this way, students can visualize<br />
the practical aspects <strong>of</strong> various electronic theories they encounter.<br />
During the senior year, students continue to build their knowledge<br />
base to develop a systems approach to engineering design. They gain a<br />
deeper knowledge in at least two specializations through combination<br />
lecture/lab courses, followed by advanced courses in related areas.<br />
Through electives, students may explore various topics within electrical<br />
engineering for which they have developed specific interests.<br />
Degree Requirements<br />
Candidates for the Bachelor <strong>of</strong> Science in Electrical Engineering<br />
must complete the minimum course requirements as outlined in the<br />
following full-time curriculum. Deviations from the recommended<br />
program may be made only with the approval <strong>of</strong> the student’s advisor<br />
and concurrence <strong>of</strong> the department head, in accordance with the<br />
Accreditation Board for Engineering and <strong>Technology</strong> (ABET) criteria.<br />
Students may complete these requirements on a part-time basis.<br />
Pr<strong>of</strong>iciency in certain key areas is <strong>of</strong> primary importance to success<br />
as electrical engineers. For this reason, a student who receives a<br />
grade <strong>of</strong> D in any <strong>of</strong> the following courses is strongly urged to repeat<br />
the course to attain a grade <strong>of</strong> at least C: ECE 2111, ECE 2112,<br />
ECE 3111, ECE 3222, ECE 3442; MTH 1001, MTH 1002,<br />
MTH 2001, MTH 2201; PHY 1001, PHY 2002, PHY 2003.<br />
Students must successfully complete a minimum <strong>of</strong> 90 percent <strong>of</strong> all<br />
the courses listed below under the freshman and sophomore years<br />
before being allowed to register for upper-level (3000/4000) courses.<br />
Students who have completed 24 credit hours and have not passed<br />
COM 1101 will register for this course in the next available semester.<br />
118 <strong>Florida</strong> Tech <strong>2013–2014</strong><br />
Students who have completed 48 credit hours and have not passed<br />
COM 1102 will register for this course in the next available semester.<br />
Courses that are acceptable as humanities/social science electives<br />
are identified as such in the Course Descriptions section. Definitions<br />
<strong>of</strong> electives for engineering programs are presented in the Academic<br />
Overview section.<br />
Additional policies and procedures governing degree requirements<br />
may be found in the program’s student handbook and online in the<br />
learning management system (ANGEL).<br />
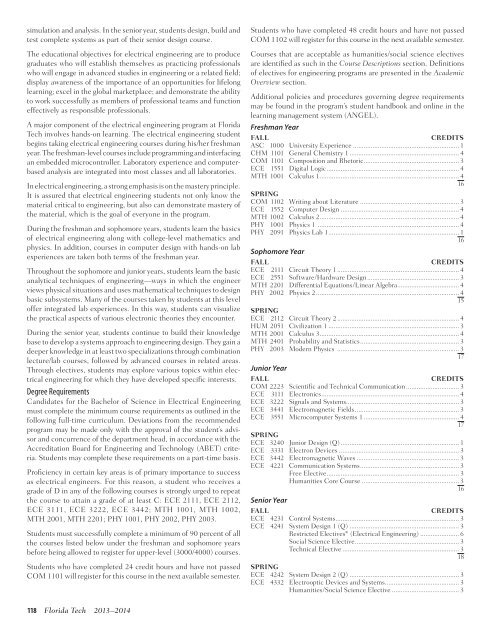
Freshman Year<br />
FALL CREDITS<br />
ASC 1000 University Experience ............................................................ 1<br />
CHM 1101 General Chemistry 1 .............................................................. 4<br />
COM 1101 Composition and Rhetoric ...................................................... 3<br />
ECE 1551 Digital Logic ........................................................................... 4<br />
MTH 1001 Calculus 1 ............................................................................... 4<br />
16<br />
SPRING<br />
COM 1102 Writing about Literature ........................................................ 3<br />
ECE 1552 Computer Design ................................................................... 4<br />
MTH 1002 Calculus 2 ............................................................................... 4<br />
PHY 1001 Physics 1 ................................................................................ 4<br />
PHY 2091 Physics Lab 1 .......................................................................... 1<br />
16<br />
Sophomore Year<br />
FALL CREDITS<br />
ECE 2111 Circuit Theory 1 ..................................................................... 4<br />
ECE 2551 S<strong>of</strong>tware/Hardware Design .................................................... 3<br />
MTH 2201 Differential Equations/Linear Algebra ................................... 4<br />
PHY 2002 Physics 2 ................................................................................. 4<br />
15<br />
SPRING<br />
ECE 2112 Circuit Theory 2 ..................................................................... 4<br />
HUM 2051 Civilization 1 .......................................................................... 3<br />
MTH 2001 Calculus 3 ............................................................................... 4<br />
MTH 2401 Probability and Statistics ........................................................ 3<br />
PHY 2003 Modern Physics ..................................................................... 3<br />
17<br />
Junior Year<br />
FALL CREDITS<br />
COM 2223 Scientific and Technical Communication .............................. 3<br />
ECE 3111 Electronics .............................................................................. 4<br />
ECE 3222 Signals and Systems................................................................ 3<br />
ECE 3441 Electromagnetic Fields ........................................................... 3<br />
ECE 3551 Microcomputer Systems 1 ...................................................... 4<br />
17<br />
SPRING<br />
ECE 3240 Junior Design (Q) ................................................................... 1<br />
ECE 3331 Electron Devices .................................................................... 3<br />
ECE 3442 Electromagnetic Waves .......................................................... 3<br />
ECE 4221 Communication Systems ........................................................ 3<br />
Free Elective ........................................................................... 3<br />
Humanities Core Course ....................................................... 3<br />
16<br />
Senior Year<br />
FALL CREDITS<br />
ECE 4231 Control Systems ...................................................................... 3<br />
ECE 4241 System Design 1 (Q) .............................................................. 3<br />
Restricted Electives* (Electrical Engineering) ...................... 6<br />
Social Science Elective ........................................................... 3<br />
Technical Elective .................................................................. 3<br />
18<br />
SPRING<br />
ECE 4242 System Design 2 (Q) .............................................................. 3<br />
ECE 4332 Electrooptic Devices and Systems .......................................... 3<br />
Humanities/Social Science Elective ...................................... 3