The Development of Neural Network Based System Identification ...
The Development of Neural Network Based System Identification ...
The Development of Neural Network Based System Identification ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
7.3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS 199<br />
20<br />
100<br />
20<br />
100<br />
Collective Pitch (Degree)<br />
Pitch Curve<br />
0<br />
50<br />
Throttle Curve<br />
−20<br />
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 0<br />
Collective Stick Input<br />
Throttle Value (%)<br />
Collective Pitch (Degree)<br />
10<br />
50<br />
Pitch Curve<br />
Throttle Curve<br />
0<br />
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 0<br />
Collective Stick Input<br />
Throttle Value (%)<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
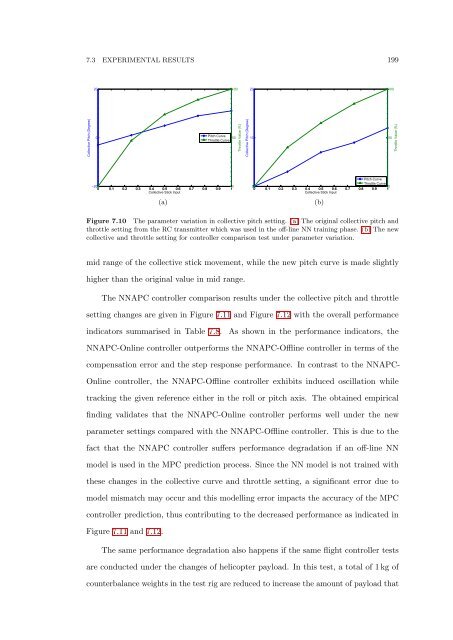
Figure 7.10 <strong>The</strong> parameter variation in collective pitch setting. (a) <strong>The</strong> original collective pitch and<br />
throttle setting from the RC transmitter which was used in the <strong>of</strong>f-line NN training phase. (b) <strong>The</strong> new<br />
collective and throttle setting for controller comparison test under parameter variation.<br />
mid range <strong>of</strong> the collective stick movement, while the new pitch curve is made slightly<br />
higher than the original value in mid range.<br />
<strong>The</strong> NNAPC controller comparison results under the collective pitch and throttle<br />
setting changes are given in Figure 7.11 and Figure 7.12 with the overall performance<br />
indicators summarised in Table 7.8.<br />
As shown in the performance indicators, the<br />
NNAPC-Online controller outperforms the NNAPC-Offline controller in terms <strong>of</strong> the<br />
compensation error and the step response performance. In contrast to the NNAPC-<br />
Online controller, the NNAPC-Offline controller exhibits induced oscillation while<br />
tracking the given reference either in the roll or pitch axis. <strong>The</strong> obtained empirical<br />
finding validates that the NNAPC-Online controller performs well under the new<br />
parameter settings compared with the NNAPC-Offline controller. This is due to the<br />
fact that the NNAPC controller suffers performance degradation if an <strong>of</strong>f-line NN<br />
model is used in the MPC prediction process. Since the NN model is not trained with<br />
these changes in the collective curve and throttle setting, a significant error due to<br />
model mismatch may occur and this modelling error impacts the accuracy <strong>of</strong> the MPC<br />
controller prediction, thus contributing to the decreased performance as indicated in<br />
Figure 7.11 and 7.12.<br />
<strong>The</strong> same performance degradation also happens if the same flight controller tests<br />
are conducted under the changes <strong>of</strong> helicopter payload. In this test, a total <strong>of</strong> 1 kg <strong>of</strong><br />
counterbalance weights in the test rig are reduced to increase the amount <strong>of</strong> payload that