TO 1-1-700 - Robins Air Force Base
TO 1-1-700 - Robins Air Force Base
TO 1-1-700 - Robins Air Force Base
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>TO</strong> 1-1-<strong>700</strong><br />
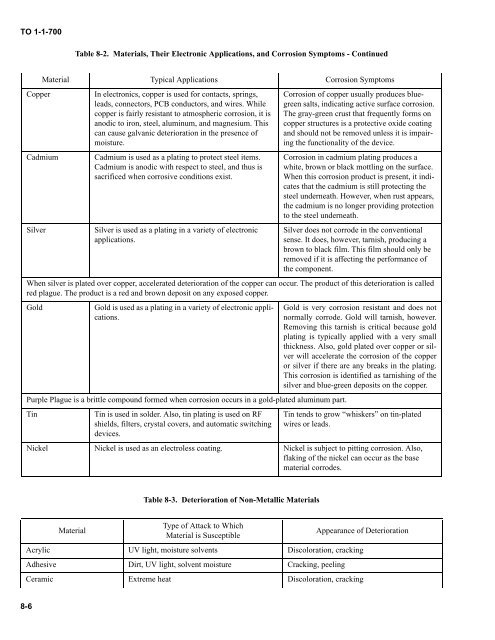
Table 8-2. Materials, Their Electronic Applications, and Corrosion Symptoms - Continued<br />
Copper<br />
Cadmium<br />
Silver<br />
In electronics, copper is used for contacts, springs,<br />
leads, connectors, PCB conductors, and wires. While<br />
copper is fairly resistant to atmospheric corrosion, it is<br />
anodic to iron, steel, aluminum, and magnesium. This<br />
can cause galvanic deterioration in the presence of<br />
moisture.<br />
Cadmium is used as a plating to protect steel items.<br />
Cadmium is anodic with respect to steel, and thus is<br />
sacrificed when corrosive conditions exist.<br />
Silver is used as a plating in a variety of electronic<br />
applications.<br />
Corrosion of copper usually produces bluegreen<br />
salts, indicating active surface corrosion.<br />
The gray-green crust that frequently forms on<br />
copper structures is a protective oxide coating<br />
and should not be removed unless it is impairing<br />
the functionality of the device.<br />
Corrosion in cadmium plating produces a<br />
white, brown or black mottling on the surface.<br />
When this corrosion product is present, it indicates<br />
that the cadmium is still protecting the<br />
steel underneath. However, when rust appears,<br />
the cadmium is no longer providing protection<br />
to the steel underneath.<br />
Silver does not corrode in the conventional<br />
sense. It does, however, tarnish, producing a<br />
brown to black film. This film should only be<br />
removed if it is affecting the performance of<br />
the component.<br />
When silver is plated over copper, accelerated deterioration of the copper can occur. The product of this deterioration is called<br />
red plague. The product is a red and brown deposit on any exposed copper.<br />
Gold<br />
Gold is used as a plating in a variety of electronic applications.<br />
Purple Plague is a brittle compound formed when corrosion occurs in a gold-plated aluminum part.<br />
Tin<br />
Material Typical Applications Corrosion Symptoms<br />
Tin is used in solder. Also, tin plating is used on RF<br />
shields, filters, crystal covers, and automatic switching<br />
devices.<br />
Gold is very corrosion resistant and does not<br />
normally corrode. Gold will tarnish, however.<br />
Removing this tarnish is critical because gold<br />
plating is typically applied with a very small<br />
thickness. Also, gold plated over copper or silver<br />
will accelerate the corrosion of the copper<br />
or silver if there are any breaks in the plating.<br />
This corrosion is identified as tarnishing of the<br />
silver and blue-green deposits on the copper.<br />
Tin tends to grow “whiskers” on tin-plated<br />
wires or leads.<br />
Nickel Nickel is used as an electroless coating. Nickel is subject to pitting corrosion. Also,<br />
flaking of the nickel can occur as the base<br />
material corrodes.<br />
Table 8-3. Deterioration of Non-Metallic Materials<br />
Material<br />
Type of Attack to Which<br />
Material is Susceptible<br />
Appearance of Deterioration<br />
Acrylic UV light, moisture solvents Discoloration, cracking<br />
Adhesive Dirt, UV light, solvent moisture Cracking, peeling<br />
Ceramic Extreme heat Discoloration, cracking<br />
8-6