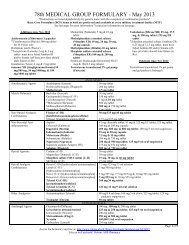
TO 1-1-700 - Robins Air Force Base
TO 1-1-700 - Robins Air Force Base
TO 1-1-700 - Robins Air Force Base
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>TO</strong> 1-1-<strong>700</strong><br />
f. Devices with permanently lubricated components (primarily<br />
bearings) can experience lubricant removal in the<br />
presence of MIL-D-16791 and shall not be cleaned in<br />
the aqueous ultrasonic cleaner. Equipment containing<br />
these components may be cleaned in the aqueous ultrasonic<br />
cleaner provided the lubricated components are<br />
securely sealed in a plastic bag.<br />
g. Sealed components may trap water. After cleaning, all<br />
sealed components shall be opened to eliminate water<br />
traps and to facilitate drying.<br />
8.6.2.3.1 Solvent Ultrasonic Cleaner. The solvent ultrasonic<br />
cleaner works similarly to the aqueous ultrasonic<br />
cleaner, except that it uses a solvent solution instead of a<br />
detergent solution for the bath. It is used to remove light to<br />
heavy oil, grease, and hydraulic fluid contamination by ultrasonic<br />
scrubbing in a solvent solution. The following guidelines<br />
shall be observed while operating the solvent ultrasonic<br />
cleaner:<br />
a. The solvent ultrasonic cleaner may be operated at any<br />
temperature up to the solvent's boiling point. The maximum<br />
operating frequency is 40 kHz. The solvent shall<br />
be specified by the manufacturer or maintenance authority.<br />
b. Neoprene materials (particularly coaxial connector gaskets)<br />
are vulnerable to damage from the solvent and<br />
shall not be cleaned in the solvent ultrasonic cleaner<br />
unless all vulnerable areas are sealed in a plastic bag.<br />
c. Devices with permanently lubricated components (primarily<br />
bearings) can experience lubricant removal in the<br />
presence of solvents and shall not be cleaned in the<br />
solvent ultrasonic cleaner. Equipment containing these<br />
components may be cleaned provided the lubricated<br />
components are securely sealed in a plastic bag.<br />
d. The solvent ultrasonic cleaner may be used as a solvent<br />
degreaser. When used as a degreaser, the solvent ultrasonic<br />
cleaner does not use the ultrasonic vibration function.<br />
Therefore, the cleaner may be used to rinse and dry<br />
PCBs provided that all other restrictions in this paragraph<br />
are followed.<br />
e. Sealed components may trap the solvent solution. After<br />
cleaning, all sealed components shall be opened to eliminate<br />
water traps and to facilitate drying.<br />
8.6.2.3.2 Water <strong>Base</strong> Solvent Spray Booth.<br />
MIL-D-16791, DETERGENT, NON-IONIC 22<br />
The water base solvent spray booth removes dirt, dust, salt<br />
spray deposits, and light corrosion products. This is achieved<br />
by spraying the components with a detergent and water solution.<br />
The detergent solution is composed of 1 ounce of MIL-<br />
D-16791 for 1 gallon of water. In addition, it can spray water<br />
for rinsing purposes or compressed air for drying. The following<br />
guidelines shall be observed while operating the water<br />
base solvent spray booth:<br />
a. The water base solvent spray booth can be used as a<br />
precleaner to remove contaminants before the component<br />
is cleaned using another method.<br />
b. Devices with permanently lubricated components (primarily<br />
bearings) can experience lubricant removal in the<br />
presence of the detergent solution and shall not be<br />
cleaned in the water base solvent spray booth. Equipment<br />
containing these components may be cleaned provided<br />
the lubricated components are securely sealed in a<br />
plastic bag.<br />
c. Sealed components may trap the solvent solution. After<br />
cleaning, all sealed components shall be opened to eliminate<br />
water traps and to facilitate drying.<br />
8.6.2.3.3 Abrasive Tools. Abrasive tools are commonly<br />
used for corrosion removal in a variety of circumstances. The<br />
following guidelines provide some instructions and restrictions<br />
regarding the use of abrasive tools on electronic equipment.<br />
a. Mono-basic sodium phosphate or glass beads used in<br />
abrasive tools can become trapped in miniature and<br />
micro miniature female edge connectors. When using a<br />
blast cabinet on components using these connectors is<br />
necessary, they shall be sealed with SAE-AMS-T-<br />
21595, Type I Pressure Sensitive Tape. The tape shall be<br />
removed and any adhesive residue removed immediately<br />
after cleaning.<br />
b. Delicate metal surfaces are extremely vulnerable to<br />
damage if abrasive tools are used improperly. Operators<br />
shall exercise extreme care when using abrasive tools on<br />
electronic equipment.<br />
c. Abrasive blast cabinets shall not be used on equipment<br />
that is sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD) in any<br />
circumstance.<br />
8-26