AstraZeneca Annual Report and Form 20-F Information 2011
AstraZeneca Annual Report and Form 20-F Information 2011
AstraZeneca Annual Report and Form 20-F Information 2011
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
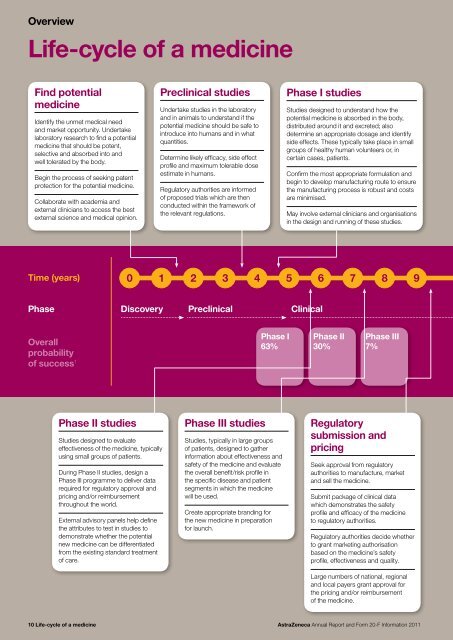
OverviewLife-cycle of a medicineFind potentialmedicineIdentify the unmet medical need<strong>and</strong> market opportunity. Undertakelaboratory research to find a potentialmedicine that should be potent,selective <strong>and</strong> absorbed into <strong>and</strong>well tolerated by the body.Begin the process of seeking patentprotection for the potential medicine.Collaborate with academia <strong>and</strong>external clinicians to access the bestexternal science <strong>and</strong> medical opinion.Preclinical studiesUndertake studies in the laboratory<strong>and</strong> in animals to underst<strong>and</strong> if thepotential medicine should be safe tointroduce into humans <strong>and</strong> in whatquantities.Determine likely efficacy, side effectprofile <strong>and</strong> maximum tolerable doseestimate in humans.Regulatory authorities are informedof proposed trials which are thenconducted within the framework ofthe relevant regulations.Phase I studiesStudies designed to underst<strong>and</strong> how thepotential medicine is absorbed in the body,distributed around it <strong>and</strong> excreted; alsodetermine an appropriate dosage <strong>and</strong> identifyside effects. These typically take place in smallgroups of healthy human volunteers or, incertain cases, patients.Confirm the most appropriate formulation <strong>and</strong>begin to develop manufacturing route to ensurethe manufacturing process is robust <strong>and</strong> costsare minimised.May involve external clinicians <strong>and</strong> organisationsin the design <strong>and</strong> running of these studies.Time (years)0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Phase Discovery Preclinical ClinicalOverallprobabilityof success 1Phase I63%Phase II30%Phase III7%Phase II studiesStudies designed to evaluateeffectiveness of the medicine, typicallyusing small groups of patients.During Phase II studies, design aPhase III programme to deliver datarequired for regulatory approval <strong>and</strong>pricing <strong>and</strong>/or reimbursementthroughout the world.External advisory panels help definethe attributes to test in studies todemonstrate whether the potentialnew medicine can be differentiatedfrom the existing st<strong>and</strong>ard treatmentof care.Phase III studiesStudies, typically in large groupsof patients, designed to gatherinformation about effectiveness <strong>and</strong>safety of the medicine <strong>and</strong> evaluatethe overall benefit/risk profile inthe specific disease <strong>and</strong> patientsegments in which the medicinewill be used.Create appropriate br<strong>and</strong>ing forthe new medicine in preparationfor launch.Regulatorysubmission <strong>and</strong>pricingSeek approval from regulatoryauthorities to manufacture, market<strong>and</strong> sell the medicine.Submit package of clinical datawhich demonstrates the safetyprofile <strong>and</strong> efficacy of the medicineto regulatory authorities.Regulatory authorities decide whetherto grant marketing authorisationbased on the medicine’s safetyprofile, effectiveness <strong>and</strong> quality.Large numbers of national, regional<strong>and</strong> local payers grant approval forthe pricing <strong>and</strong>/or reimbursementof the medicine.10 Life-cycle of a medicine<strong>AstraZeneca</strong> <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Report</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Form</strong> <strong>20</strong>-F <strong>Information</strong> <strong>20</strong>11