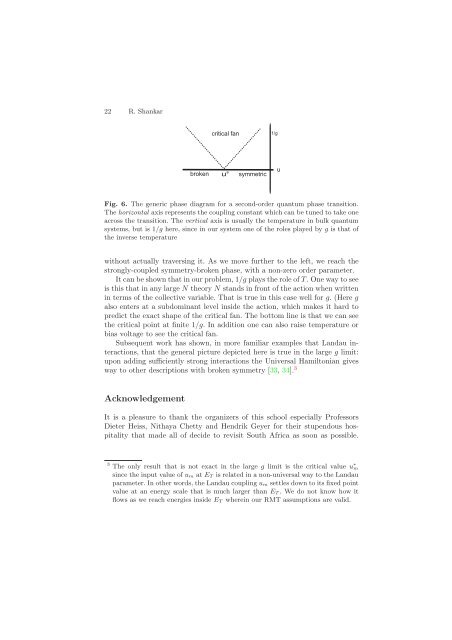
22 R. Shankar broken critical fan u∗ symmetric Fig. 6. The generic phase diagram for a second-order quantum phase transition. The horizontal axis represents the coupling constant which can be tun<strong>ed</strong> <strong>to</strong> take one across the transition. The vertical axis is usually the temperature in bulk quantum systems, but is 1/g here, since in our system one of the roles play<strong>ed</strong> by g is that of the inverse temperature without actually traversing it. As we move further <strong>to</strong> the left, we reach the strongly-coupl<strong>ed</strong> symmetry-broken phase, with a non-zero order parameter. It can be shown that in our problem, 1/g plays the role of T . One way <strong>to</strong> see is this that in any large N theory N stands in front of the action when written in terms of the collective variable. That is t<strong>ru</strong>e in this case well for g. (Hereg also enters at a subdominant level inside the action, which makes it hard <strong>to</strong> pr<strong>ed</strong>ict the exact shape of the critical fan. The bot<strong>to</strong>m line is that we can see the critical point at finite 1/g. In addition one can also raise temperature or bias voltage <strong>to</strong> see the critical fan. Subsequent work has shown, in more familiar examples that Landau interactions, that the general picture depict<strong>ed</strong> here is t<strong>ru</strong>e in the large g limit: upon adding sufficiently strong interactions the Universal Hamil<strong>to</strong>nian gives way <strong>to</strong> other descriptions with broken symmetry [33, 34]. 3 Acknowl<strong>ed</strong>gement It is a pleasure <strong>to</strong> thank the organizers of this school especially Professors Dieter <strong>Heiss</strong>, Nithaya Chetty and Hendrik Geyer for their stupendous hospitality that made all of decide <strong>to</strong> revisit South Africa as soon as possible. 3 The only result that is not exact in the large g limit is the critical value u ∗ m since the input value of um at ET is relat<strong>ed</strong> in a non-universal way <strong>to</strong> the Landau parameter. In other words, the Landau coupling um settles down <strong>to</strong> its fix<strong>ed</strong> point value at an energy scale that is much larger than ET .W<strong>ed</strong>onotknowhowit flows as we reach energies inside ET wherein our RMT assumptions are valid. 1/g u
References RG for Interacting Fermions 23 1. M. E. Fisher Critical Phenomena, F.W.J.Hahne,Edi<strong>to</strong>r,LectureNotesNumber 186, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, (1983). These notes are from the Engelbrecht Summer School of 1983! 4 2. R. Shankar, Physica A177, 530 (1991); R.Shankar, Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 129 (1994). 5, 6, 11, 12, 14 3. L. D. Landau, Sov. Phys. JETP 3, 920 (1956); Sov. Phys. JETP 5, 101 (1957). 8 4. A. A. Abrikosov, L. P. Gorkov, and I. E. Dzyaloshinski, Methods of <strong>Quantum</strong> Field Theory in Statistical Physics, Dover Publications, New York, 1963. 8 5. D. J. Gross and A. Neveu, Phys. Rev.D10, 3235 (1974). 10 6. P. Polchinski In: TASI Elementary Particle Physics, <strong>ed</strong>byJ.Polchinskiand J.Harvey (World Scientific, 1992.) 12 7. For recent reviews, see, T. Guhr, A. Müller-Groeling, and H. A. Weidenmüller, Phys. Rep. 299, 189 (1998); Y. Alhassid, Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 895 (2000); A. D. Mirlin, Phys. Rep. 326, 259 (2000). 12, 13 8. M. L. Mehta, Random Matrices, Academic Press, San Diego, 1991. K. B. Efe<strong>to</strong>v, Adv. Phys. 32, 53 (1983); B. L. Al’tshuler ad B. I. Shklovskii, Sov. Phys. JETP 64, 127 (1986). 13 9. I. L. Aleiner, P. W. Brouwer, and L. I. Glazman, Phys. Rep. 358, 309 (2002), and references therein; Y. Oreg, P. W. Brouwer, X. Waintal, and B. I. Halperin, condmat/0109541, “Spin, spin-orbit, and electron-electron interactions in mesoscopic systems”. 12, 13, 14 10. R. A. Jalabert, A. D. S<strong>to</strong>ne, and Y. Alhassid, Phys. Rev. Lett.68, 3468 (1992). 13 11. A. M. Chang, H. U. Baranger, L. N. Pfeiffer, K. W. West, and T. Y. Chang, Phys. Rev. Lett.76, 1695 (1996); J. A. Folk, S. R. Patel, S. F. Godjin, A. G. Huibers,S.M.Cronenwett,andC.M.Marcus,Phys.Rev.Lett.76, 1699 (1996). 13 12. S. R. Patel, D. R. Stewart, C. M. Marcus, M. Gokc<strong>ed</strong>ag, Y. Alhassid, A. D. S<strong>to</strong>ne, C. I. Du<strong>ru</strong>roz, and J. S. Harris, Phys. Rev. Lett.81, 5900 (1998). 13 13. D. V. Averin and K. K. Likharev, in Mesoscopic Phenomena in Solids, <strong>ed</strong>it<strong>ed</strong> by B. L. Altshuler, P. A. Lee, and R. Webb (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1991); C. W. J. Beenakker, Phys. Rev. B44, 1646 (1991). 13 14. A. V. Andreev and A. Kamenev, Phys. Rev. Lett.81, 3199 (1998), P. W. Brouwer, Y. Oreg, and B. I. Halperin, Phys. Rev. B60, R13977 (1999), H. U. Baranger, D. Ullmo, and L. I. Glazman, Phys. Rev. B61, R2425 (2000). 13, 14 15. I. L. Kurland, I. L. Aleiner, and B. L. Al’tshuler, Phys. Rev. B62, 14886 (2000). 13, 14 16. O. P<strong>ru</strong>s, A. Auerbach, Y. Aloni, U. Sivan, and R. Berkovits, Phys. Rev. B54, R14289 (1996), R. Berkovits, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2128 (1998), A. Cohen, K. Richter, and R. Berkovits, Phys. Rev. B60, 2536 (1999), P. N. Walker, G. Montambaux, and Y. Gefen, ibid, 2541 (1999), S. Levit and D. Orgad, Phys. Rev. B60, 5549 (1999), D. Ullmo and H. U. Baranger, Phys. Rev. B64, 245324 (2001), V. Belinicher, E. Ginossar, and S. Levit, cond-mat/0109005, Y. Alhassid and S. Malhotra, cond-mat/0202453. 13, 14 17. U. Sivan et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1123 (1996); S. R. Patel et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4522 (1998). 13 18. F. Simmel et al, Phys. Rev. B59, 10441 (1999); D. Abusch-Magder et al,Physica E 6, 382 (2000). 13, 14 19. Y. M. Blanter, A. D. Mirlin, and B. A. Muzykantskii, Phys. Rev. Lett.78, 2449 (1997), R. O. Vallejos, C. H. Lewenkopf, and E. R. Mucciolo, Phys. Rev. Lett.81, 677 (1998). 14