Mécanismes d'évolution de texture au cours du recuit d'alliages de ...
Mécanismes d'évolution de texture au cours du recuit d'alliages de ...
Mécanismes d'évolution de texture au cours du recuit d'alliages de ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
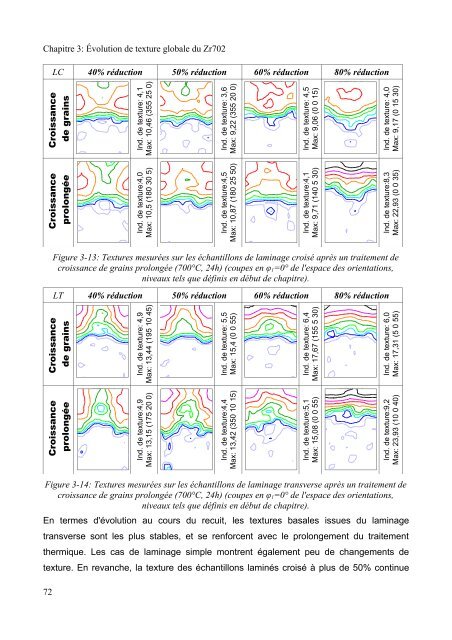
Chapitre 3: Évolution <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong> globale <strong>du</strong> Zr702<br />
LC 40% ré<strong>du</strong>ction 50% ré<strong>du</strong>ction 60% ré<strong>du</strong>ction 80% ré<strong>du</strong>ction<br />
Croissance<br />
<strong>de</strong> grains<br />
Croissance<br />
prolongée<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 4,1<br />
Max: 10,46 (355 25 0)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:4,0<br />
Max: 10,5 (180 30 5)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 3,6<br />
Max: 9,22 (355 20 0)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:4,5<br />
Max: 10,87 (180 25 50)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 4,5<br />
Max: 9,06 (0 0 15)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:4,1<br />
Max: 9,71 (140 5 30)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 4,0<br />
Max: 9,17 (0 15 30)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:8,3<br />
Max: 22,93 (0 0 35)<br />
Figure 3-13: Textures mesurées sur les échantillons <strong>de</strong> laminage croisé après un traitement <strong>de</strong><br />
croissance <strong>de</strong> grains prolongée (700°C, 24h) (coupes en φ1=0° <strong>de</strong> l'espace <strong>de</strong>s orientations,<br />
nive<strong>au</strong>x tels que définis en début <strong>de</strong> chapitre).<br />
LT 40% ré<strong>du</strong>ction 50% ré<strong>du</strong>ction 60% ré<strong>du</strong>ction 80% ré<strong>du</strong>ction<br />
Croissance<br />
<strong>de</strong> grains<br />
Croissance<br />
prolongée<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 4,9<br />
Max: 13,44 (195 10 45)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:4,9<br />
Max: 13,15 (175 20 0)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 5,5<br />
Max: 15,4 (0 0 55)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:4,4<br />
Max: 13,42 (350 10 15)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 6,4<br />
Max: 17,67 (155 5 30)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:5,1<br />
Max: 15,08 (0 0 55)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>: 6,0<br />
Max: 17,31 (5 0 55)<br />
Ind. <strong>de</strong> <strong>texture</strong>:9,2<br />
Max: 23,93 (10 0 40)<br />
Figure 3-14: Textures mesurées sur les échantillons <strong>de</strong> laminage transverse après un traitement <strong>de</strong><br />
croissance <strong>de</strong> grains prolongée (700°C, 24h) (coupes en φ1=0° <strong>de</strong> l'espace <strong>de</strong>s orientations,<br />
nive<strong>au</strong>x tels que définis en début <strong>de</strong> chapitre).<br />
En termes <strong>d'évolution</strong> <strong>au</strong> <strong>cours</strong> <strong>du</strong> <strong>recuit</strong>, les <strong>texture</strong>s basales issues <strong>du</strong> laminage<br />
transverse sont les plus stables, et se renforcent avec le prolongement <strong>du</strong> traitement<br />
thermique. Les cas <strong>de</strong> laminage simple montrent également peu <strong>de</strong> changements <strong>de</strong><br />
<strong>texture</strong>. En revanche, la <strong>texture</strong> <strong>de</strong>s échantillons laminés croisé à plus <strong>de</strong> 50% continue<br />
72<br />
Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0<br />
Constant Phi1 = 0<br />
Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0<br />
Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0<br />
Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0 Constant Phi1 = 0