- Page 1 and 2:
Beyond Time: Temporal and Extra-tem
- Page 3 and 4:
Abstract Beyond Time: Temporal and
- Page 5 and 6:
To Kelvin and Mboshela i
- Page 7 and 8:
and have continued in their support
- Page 9 and 10:
from Veritas Graduate Student Fello
- Page 11 and 12:
2.2.3 Comparison with Proto-BB . .
- Page 13 and 14:
6.5 Summary of analysis of -ite as
- Page 15 and 16:
Glosses Used Gloss Meaning 1 First
- Page 17 and 18:
1.2 Theoretical background and moti
- Page 19 and 20:
Following this general direction, I
- Page 21 and 22:
The first major twentieth-century a
- Page 23 and 24:
To make the fuzzy theories more pre
- Page 25 and 26:
Multiple degrees of past/future ref
- Page 27 and 28:
1.2.3 Approaches to extra-temporal
- Page 29 and 30:
1.2.3.3 Primary temporal meaning fo
- Page 31 and 32:
In their framework, time-based tens
- Page 33 and 34:
. fortalééza y-a-cek-íw-a n’aa
- Page 35 and 36:
an in-depth diachronic study of Tot
- Page 37 and 38:
1.2.3) may develop at any stage. Th
- Page 39 and 40:
within the narrative, “set apart
- Page 41 and 42:
without affecting its temporal stru
- Page 43 and 44:
Fleisch (2000), and Seidel (2008) d
- Page 45 and 46:
. “Indicate episode ends” (Seid
- Page 47 and 48:
imperfective, progressive, habitual
- Page 49 and 50:
cluding activities, accomplishments
- Page 51 and 52:
Some examples of the major categori
- Page 53 and 54:
y the speaker’s perception of whe
- Page 55 and 56:
P-Domain: D-Domain: Association Dis
- Page 57 and 58:
Figure 1.15: Representation without
- Page 59 and 60:
1.3.8 Other conventions Following C
- Page 61 and 62:
Translations into Lozi were also pr
- Page 63 and 64:
1.4.3 Limitations Although I carrie
- Page 65 and 66:
Chapter 5 describes two major marke
- Page 67 and 68:
(17) Innovations common to Bantu Bo
- Page 69 and 70:
Totela data in de Luna (2008, 2010)
- Page 71 and 72:
For more on the historical movement
- Page 73 and 74:
may be an overrepresentation, since
- Page 75 and 76:
2. “Endangered languages”: a.
- Page 77 and 78:
officially recognized on a national
- Page 79 and 80:
(19) Observed NT dialect continuum:
- Page 81 and 82:
ilabial labio- dent. alveolar post-
- Page 83 and 84:
à Only occurs in NC sequences (see
- Page 85 and 86:
ilabial labio- dent. alveolar post-
- Page 87 and 88:
2.2.4.1 Vowel length As noted above
- Page 89 and 90:
2.2.6 Proto-Bantu Correspondences T
- Page 91 and 92:
c. *t > s (before *u) *-túmÙ > ò
- Page 93 and 94:
(32) *j a. *j > ∅ *-jìtìd > òk
- Page 95 and 96:
Although data are not available for
- Page 97 and 98:
morphemes typically grammaticalize
- Page 99 and 100:
tive. Because the distal can co-occ
- Page 101 and 102:
Noun Subject Class Marker 1(a) -mu-
- Page 103 and 104:
c. Following u òkùwùlìlà òkù
- Page 105 and 106:
òkù-yèndà ‘to walk’ → òk
- Page 107 and 108:
(62) a. òkùsàmbìlìlà òkù-s
- Page 109 and 110:
(66) Iterative extensions òkùtyò
- Page 111 and 112:
(72) Tentive extension òkúkwààt
- Page 113 and 114:
c. Negatives with -saka ‘want, li
- Page 115 and 116:
c. As source Nòkùlòngàwô kús
- Page 117 and 118:
Although all non-verb-final orderin
- Page 119 and 120:
(89) abanakazi (aba) bena nabachech
- Page 121 and 122:
Sounds Examples PB ZT NT PB ZT NT G
- Page 123 and 124:
disappearance. In most cases, vowel
- Page 125 and 126:
2.4.2 NT and ZT: differences in TAM
- Page 127 and 128:
2.4.2.4 Negation FV NT ZT -a indica
- Page 129 and 130:
e studied to evaluate claims about
- Page 131 and 132:
in the prehodiernal past. Similarly
- Page 133 and 134:
maintains the current discourse dom
- Page 135 and 136:
NC Bare Cmpl 1/1a a- a- 2/2a ba- a-
- Page 137 and 138:
(109) a. Atelic durative: ndanenga
- Page 139 and 140:
. Past reading: ndákòmòkwà nda-
- Page 141 and 142:
perception stative -suwa behaves li
- Page 143 and 144:
With activity verbs such as -yenda
- Page 145 and 146:
Totela data than other proposed sol
- Page 147 and 148:
Botne’s description of -ire, in i
- Page 149 and 150:
is formal. As Dahl (1985:129) notes
- Page 151 and 152:
P-Domain: D-Domain: Association Dis
- Page 153 and 154:
(137) a. [Context: the person descr
- Page 155 and 156:
a “path of least effort” in whi
- Page 157 and 158:
ecause the consequences of the past
- Page 159 and 160:
(145) Sunu, twabuuka! Twabuuka ndet
- Page 161 and 162:
3.3.2 -a- with motion verbs in narr
- Page 163 and 164:
(152) Âwò, kàlì mùntù. Ii! N
- Page 165 and 166:
3.3.5 -a- in narrative: summary The
- Page 167 and 168:
verbs, the pathways of development
- Page 169 and 170:
4. With a slight change in accent,
- Page 171 and 172:
Chapter 4 Semantics and Pragmatics
- Page 173 and 174:
These are discussed in section 4.4,
- Page 175 and 176:
. Non-stative predicate: Was macht
- Page 177 and 178:
all require a virtual, fictive read
- Page 179 and 180:
Others (e.g Bybee et al. 1994), in
- Page 181 and 182:
two-state situations, which are mad
- Page 183 and 184:
The choice of modal base and orderi
- Page 185 and 186:
adjacent syllable (to the right) is
- Page 187 and 188:
(189) ìjìlò ndìyá kùmpìlì i
- Page 189 and 190:
(199) chìyùnì (ndìsákà) chiyu
- Page 191 and 192:
Because this chapter deals with the
- Page 193 and 194:
In summary, analysis of the “pres
- Page 195 and 196:
(212) a. ndilabon-a ≈ ndilibwene
- Page 197 and 198:
The -la- marker is also compatible
- Page 199 and 200:
4.3.6 Interactions with situation t
- Page 201 and 202:
4.3.6.3 Duratives With durative (no
- Page 203 and 204:
(232) a. àbá bàyîmbà bàtàbà
- Page 205 and 206:
equirement, situations can either o
- Page 207 and 208:
the [present] is used not so much b
- Page 209 and 210:
In many languages, including Totela
- Page 211 and 212:
otherwise reveal. Non-completive fo
- Page 213 and 214:
are unmarked, as well as presents w
- Page 215 and 216:
the head of his murdered child, fra
- Page 217 and 218:
D.60 (e.g. Ha), and in some M langu
- Page 219 and 220:
-la- lost its disjunctive flavor an
- Page 221 and 222:
(251) tu-la-cita 1pl-pres-do ‘we
- Page 223 and 224:
(253) a. Durative verbs: a-Ø-fik-i
- Page 225 and 226:
Chapter 5 Past and Future: Dissocia
- Page 227 and 228: groups. While no languages had zero
- Page 229 and 230: . chìlìmò chàmánà chilimo cha
- Page 231 and 232: English, for example, future tense
- Page 233 and 234: differences - both concrete and sub
- Page 235 and 236: (270) Prehodiernal -ka-: ndàkàsà
- Page 237 and 238: c. ìjìlò chì-nzí ! ná-mù-li-
- Page 239 and 240: . ìjìlò nándìlà yá kùmpìl
- Page 241 and 242: not on the day of perspective time.
- Page 243 and 244: With both na- and -ka-, the time sp
- Page 245 and 246: with negation. The lack of -a- mark
- Page 247 and 248: . ísè19 nándìsíkè nándìlè
- Page 249 and 250: (303) Iñolo lyenu twakalibona ijil
- Page 251 and 252: would be similar, but the dissociat
- Page 253 and 254: 5.4 Dissociativity in narrative Bot
- Page 255 and 256: (310) âwo kàlì mú ! kwáámè n
- Page 257 and 258: 1. In narrator “commentary” abo
- Page 259 and 260: [In the Guaymí case] the immediate
- Page 261 and 262: proclitic is still extremely produc
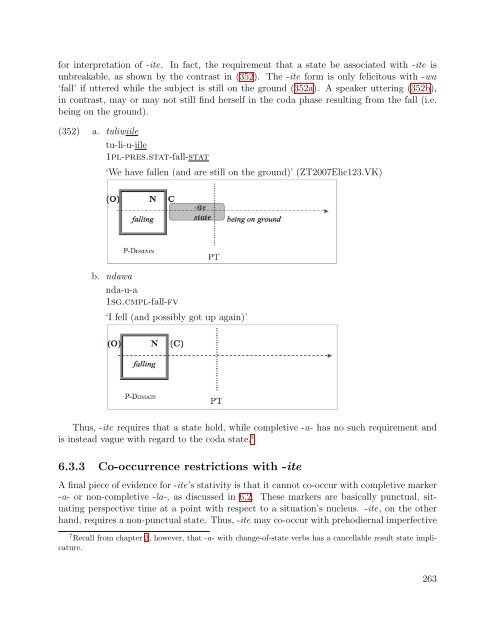
- Page 263 and 264: (319) hasina bawane amali. . . hasi
- Page 265 and 266: (321) Progressive uses a. ndìlìy
- Page 267 and 268: -it-. . . -e. A handful of forms ar
- Page 269 and 270: (331) chìnzí mwíndìtè? chinzi
- Page 271 and 272: will be seen below, comparing the u
- Page 273 and 274: Kratzer (2000) for German stativize
- Page 275 and 276: . balinunite ba-li-nun-ite 1sg-pres
- Page 277: Thus, the distribution of -ite sugg
- Page 281 and 282: A question raised by the characteri
- Page 283 and 284: Such clashing interpretations arose
- Page 285 and 286: poses that information structuring
- Page 287 and 288: 6.4.3 -ite’s relevance presupposi
- Page 289 and 290: Another example is given in (364).
- Page 291 and 292: (368) handilahupwile bamayo hanu ma
- Page 293 and 294: . kámbè ndàkàyá ! kwáSàmís
- Page 295 and 296: . [Context set 1: I am busy. I don
- Page 297 and 298: 6.6.1 -ite’s narrative distributi
- Page 299 and 300: . Nabo basikuchela shombo nokubona
- Page 301 and 302: immediate question under discussion
- Page 303 and 304: (386) Durative root (only perfectiv
- Page 305 and 306: (389) a. mbá-a-c-éte ‘they came
- Page 307 and 308: -ile variants for verbs that normal
- Page 309 and 310: Resultative, especially with COS ve
- Page 311 and 312: 6.7.3.1 Tonga Tonga (M64) has an -i
- Page 313 and 314: offer him food because he is full (
- Page 315 and 316: Describes Describes past situation
- Page 317 and 318: suffixes across Bantu, suggest that
- Page 319 and 320: 7.2 Completion, Tense, and Tenor To
- Page 321 and 322: espectively. (409c) shows that -na-
- Page 323 and 324: The intended meaning in (413) can b
- Page 325 and 326: Figure 7.2: Contentful phase of -sa
- Page 327 and 328: In short, according to Botne & Kers
- Page 329 and 330:
(426) àwà kándìlàwúkà ndàk
- Page 331 and 332:
. tàkándìtwâ ta-ka-ndi-tu-a neg
- Page 333 and 334:
(440) yùmwí èná òkùlé nèñ
- Page 335 and 336:
7.3.4 “Perfect” meanings Totela
- Page 337 and 338:
. ndìlìnèngètè ndi-li-neng-ete
- Page 339 and 340:
(459) ijilo liizite nandilayenda na
- Page 341 and 342:
Rather than presupposing that a sit
- Page 343 and 344:
This construction appears to treat
- Page 345 and 346:
(483) tàlí mwàyá kwàKàìwàl
- Page 347 and 348:
7.4.3 Hortatives and subjunctives H
- Page 349 and 350:
In general, counterfactual completi
- Page 351 and 352:
(504) buti muponena twali kumisiya
- Page 353 and 354:
(512) Kùyá bùmínà àbántù. K
- Page 355 and 356:
Sometimes, when distal -ka- occurs
- Page 357 and 358:
More likely Less likely to be infle
- Page 359 and 360:
Chapter 8 Conclusion and future res
- Page 361 and 362:
8.2 Directions for future research
- Page 363 and 364:
——. 2007. Stem tone melodies in
- Page 365 and 366:
——, 2010. High-tone anticipatio
- Page 367 and 368:
Glasbey, Sheila. 1998. Progressives
- Page 369 and 370:
Jacottet, Émile. 1896-1901. Étude
- Page 371 and 372:
Morris, Charles W. 1938. Foundation
- Page 373 and 374:
Shirai, Yasuhiro. 1998. Where the p
- Page 375 and 376:
Appendix A Definitions This appendi
- Page 377 and 378:
Information Structure (IS) (followi
- Page 379 and 380:
Time of Situation (TSit) the time f
- Page 381 and 382:
B.2 Consonant mutation: t ¿ s Alth
- Page 383 and 384:
B.5 -ile forms In Totela, only a fe
- Page 385 and 386:
Figure C.1: Downdrift in máyìwíy
- Page 387 and 388:
C.2.1 HTA within words HTA may be s
- Page 389 and 390:
o ku ba hu pu la H H H MR o ku ba h
- Page 391 and 392:
nánkala ‘crab’ echí-fuwa ‘b
- Page 393 and 394:
Syll Ø Root Pattern H Root Pattern
- Page 395 and 396:
Syll Ø Root Pattern H Root Pattern
- Page 397 and 398:
C.33 Persistive -chi- ‘still’ +
- Page 399 and 400:
384 Syll Ø Root Ø Root H Root H R
- Page 401 and 402:
C.7.2 Posited input H on second roo
- Page 403 and 404:
Syll Ø Root H Root 1 ta-ndi-nâ-lw
- Page 405 and 406:
390 Syll Ø Root Ø Root H Root H R
- Page 407 and 408:
C.7.3 Posited input H on final vowe
- Page 409 and 410:
Syll Ø Root H Root 1 ndi-chi-lwâ
- Page 411 and 412:
396 Syll Ø Root Ø Root H Root H R
- Page 413 and 414:
C.7.4 Other patterns Other patterns
- Page 415 and 416:
Appendix D Agreement forms Bantu la
- Page 417 and 418:
Figure D.1 indicates attested singu
- Page 419 and 420:
. bàchìkwàngálà bàlàùlùkà
- Page 421 and 422:
406 NC Prefix SM OM Poss Poss Num A
- Page 423:
Clement Tubusenge, Tiyebulyo Jenika