Sampling Guide for Air Contaminants in the Workplace - Irsst
Sampling Guide for Air Contaminants in the Workplace - Irsst
Sampling Guide for Air Contaminants in the Workplace - Irsst
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
36 IRSST – <strong>Sampl<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Air</strong> <strong>Contam<strong>in</strong>ants</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Workplace</strong><br />
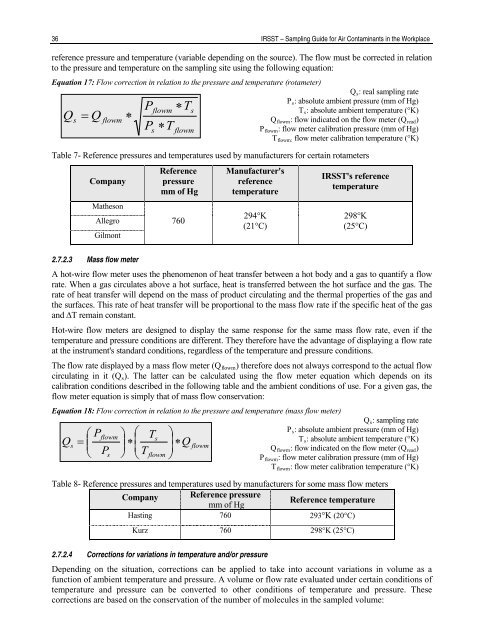
reference pressure and temperature (variable depend<strong>in</strong>g on <strong>the</strong> source). The flow must be corrected <strong>in</strong> relation<br />
to <strong>the</strong> pressure and temperature on <strong>the</strong> sampl<strong>in</strong>g site us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g equation:<br />
Equation 17: Flow correction <strong>in</strong> relation to <strong>the</strong> pressure and temperature (rotameter)<br />
Qs<br />
= Q<br />
flowm<br />
∗<br />
Q s : real sampl<strong>in</strong>g rate<br />
P s : absolute ambient pressure (mm of Hg)<br />
Pflowm<br />
∗Ts<br />
T s : absolute ambient temperature (°K)<br />
Q flowm : flow <strong>in</strong>dicated on <strong>the</strong> flow meter (Q read )<br />
Ps<br />
∗T<br />
flowm<br />
P flowm : flow meter calibration pressure (mm of Hg)<br />
T flowm: flow meter calibration temperature (°K)<br />
Table 7- Reference pressures and temperatures used by manufacturers <strong>for</strong> certa<strong>in</strong> rotameters<br />
Company<br />
Ma<strong>the</strong>son<br />
Allegro<br />
Gilmont<br />
Reference<br />
pressure<br />
mm of Hg<br />
760<br />
Manufacturer's<br />
reference<br />
temperature<br />
294°K<br />
(21°C)<br />
IRSST's reference<br />
temperature<br />
298°K<br />
(25°C)<br />
2.7.2.3 Mass flow meter<br />
A hot-wire flow meter uses <strong>the</strong> phenomenon of heat transfer between a hot body and a gas to quantify a flow<br />
rate. When a gas circulates above a hot surface, heat is transferred between <strong>the</strong> hot surface and <strong>the</strong> gas. The<br />
rate of heat transfer will depend on <strong>the</strong> mass of product circulat<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmal properties of <strong>the</strong> gas and<br />
<strong>the</strong> surfaces. This rate of heat transfer will be proportional to <strong>the</strong> mass flow rate if <strong>the</strong> specific heat of <strong>the</strong> gas<br />
and ∆T rema<strong>in</strong> constant.<br />
Hot-wire flow meters are designed to display <strong>the</strong> same response <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> same mass flow rate, even if <strong>the</strong><br />
temperature and pressure conditions are different. They <strong>the</strong>re<strong>for</strong>e have <strong>the</strong> advantage of display<strong>in</strong>g a flow rate<br />
at <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>strument's standard conditions, regardless of <strong>the</strong> temperature and pressure conditions.<br />
The flow rate displayed by a mass flow meter (Q flowm ) <strong>the</strong>re<strong>for</strong>e does not always correspond to <strong>the</strong> actual flow<br />
circulat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> it (Q s ). The latter can be calculated us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> flow meter equation which depends on its<br />
calibration conditions described <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g table and <strong>the</strong> ambient conditions of use. For a given gas, <strong>the</strong><br />
flow meter equation is simply that of mass flow conservation:<br />
Equation 18: Flow correction <strong>in</strong> relation to <strong>the</strong> pressure and temperature (mass flow meter)<br />
Q s : sampl<strong>in</strong>g rate<br />
P s : absolute ambient pressure (mm of Hg)<br />
⎛ Pflowm<br />
⎞ ⎛ T ⎞<br />
s<br />
Q<br />
T s : absolute ambient temperature (°K)<br />
s<br />
= ⎜ ⎟<br />
⎜<br />
Q<br />
flowm<br />
P<br />
⎟ ∗ ∗<br />
Q flowm : flow <strong>in</strong>dicated on <strong>the</strong> flow meter (Q read )<br />
s<br />
T<br />
⎝ ⎠ ⎝ flowm ⎠<br />
P flowm : flow meter calibration pressure (mm of Hg)<br />
T flowm : flow meter calibration temperature (°K)<br />
Table 8- Reference pressures and temperatures used by manufacturers <strong>for</strong> some mass flow meters<br />
Company Reference pressure<br />
Reference temperature<br />
mm of Hg<br />
Hast<strong>in</strong>g 760 293°K (20°C)<br />
Kurz 760 298°K (25°C)<br />
2.7.2.4 Corrections <strong>for</strong> variations <strong>in</strong> temperature and/or pressure<br />
Depend<strong>in</strong>g on <strong>the</strong> situation, corrections can be applied to take <strong>in</strong>to account variations <strong>in</strong> volume as a<br />
function of ambient temperature and pressure. A volume or flow rate evaluated under certa<strong>in</strong> conditions of<br />
temperature and pressure can be converted to o<strong>the</strong>r conditions of temperature and pressure. These<br />
corrections are based on <strong>the</strong> conservation of <strong>the</strong> number of molecules <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> sampled volume: