Student Project Abstracts 2005 - Pluto - University of Washington
Student Project Abstracts 2005 - Pluto - University of Washington
Student Project Abstracts 2005 - Pluto - University of Washington
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
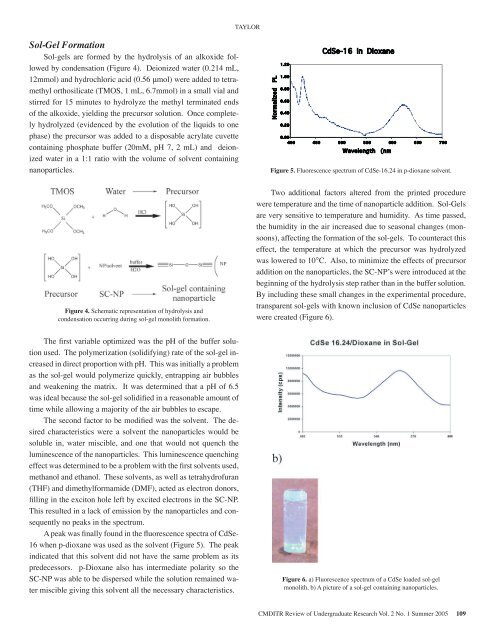
easonable the solvent. amount The <strong>of</strong> desired time while characteristics allowing amajority were a solvent <strong>of</strong> the air the bubbles nanoparticles to escape. would besoluble The second in, water factor miscible, to be and modified one that wasthe would solvent. not quench The the desired luminescence characteristics <strong>of</strong> theSol-Gel werenanoparticles.a Formation solvent the nanoparticlesThis luminescencewould besolublequenching Sol-gels arein,formed effectwaterby was themiscible,hydrolysis determinedand<strong>of</strong> an alkoxideoneto bethatfollowedproblem by condensation with (Figure the 4). first Deionized solvents water (0.214 used, mL,awould12mmol) methanolnotand hydrochloric andquenchethanol.the luminescenceacid (0.56 These μmol) were solvents,<strong>of</strong>added to tetramethylwell orthosilicate as tetrahydr<strong>of</strong>uran Thisasthenanoparticles.(TMOS, 1 mL, 6.7mmol) (THF) luminescencea small vial and andquenchingstirred dimethylformamide effect was 15 minutes to hydrolyze (DMF), determinedthe methyl terminated acted to be as aendsproblem<strong>of</strong> the electron alkoxide, donors, with theyielding the filling firstprecursor in solution. the solvents exciton used,Once completelyhydrolyzed left by (evidenced excited and ethanol.holemethanolby electrons Thesethe evolution in <strong>of</strong> the solvents, liquids SC-NP. asto onewellphase) This the resulted as tetrahydr<strong>of</strong>uranprecursor was in added a lack to a disposable emission (THF)acrylate by cuvette the anddimethylformamidecontaining nanoparticles phosphate and buffer consequently (DMF),(20mM, pH 7, 2 no actedmL) peaks and deionizedin aselectron thewaterspectrum. donors, filling in the exciton holein a 1:1 ratio with the volume <strong>of</strong> solvent containingnanoparticles.left by A excited peak was electrons finally in found the SC-NP. in theThis fluorescence resulted spectra in a lack <strong>of</strong> <strong>of</strong> CdSe-16 emission when by p- thenanoparticles dioxane was used and consequently as the solvent no (Figure peaks 5). inthe The spectrum. peak indicated that this solvent did nothave the A same peak problem was finally as its predecessors. found in thefluorescence p-Dioxane also spectra has intermediate <strong>of</strong> CdSe-16 polarity when so p-dioxane the SC-NP was was used able as the to be solvent dispersed (Figure while 5).The the peak solution indicated remained that water this miscible solvent did giving notthis solvent all the necessary characteristics.have the same problem as its predecessors.p-Dioxane also has intermediate polarity sothe SC-NP was able to be dispersed whilethe solution remained water miscible givingFigure 5: Fluorescence spectrum <strong>of</strong> CdSe-16.24in p-dioxane solvent.this solvent all the necessary characteristics.Figure 4. Schematic representation <strong>of</strong> hydrolysis andcondensation occurring during sol-gel monolith formation.Two additional factors altered from theprinted procedure were temperature and theCdSe-16 in Dioxane0.20Figure 5. Fluorescence spectrum <strong>of</strong> CdSe-16.24 in p-dioxane solvent.Two additional factors altered from the printed procedureWavelength (nmwere temperature and the time <strong>of</strong> nanoparticle addition. Sol-Gelsare very sensitive to temperature and humidity. As time passed,the humidity in the air increased due to seasonal changes (monsoons),affecting the formation <strong>of</strong> the sol-gels. To counteract thiseffect, the temperature at which the precursor was hydrolyzedwas lowered to 10°C. Also, to minimize the effects <strong>of</strong> precursoraddition on the nanoparticles, the SC-NP’s were introduced at thebeginning <strong>of</strong> the hydrolysis step rather than in the buffer solution.By including these small changes in the experimental procedure,transparent sol-gels with known inclusion <strong>of</strong> CdSe nanoparticleswere created (Figure 6).The first variable optimized was the pH <strong>of</strong> the buffer solutionFigure timeused.<strong>of</strong>The 5: nanoparticlepolymerization Fluorescence (solidifying)addition. spectrum rate <strong>of</strong> Sol-Gels<strong>of</strong> CdSe-16.24 the sol-gelareincreasedvery in sensitive direct proportion in p-dioxane to temperature with pH. solvent. This was and initially humidity. a problemas the As sol-gel time would passed, polymerize the quickly, humidity entrapping the air bubbles airand increased weakening Two additional the matrix. due It to factors was determined seasonal altered that changes from a pH <strong>of</strong> the 6.5was printed (monsoons), ideal because procedure the affecting sol-gel were solidified the temperature in formation a reasonable and <strong>of</strong> amount the <strong>of</strong>time sol-gels. while <strong>of</strong> allowing nanoparticle To a majority counteract addition. <strong>of</strong> the air bubbles this Sol-Gels effect, to escape. the arevery temperature Thesensitivesecond factor at to which betemperaturemodified the was precursor theandsolvent.humidity.The was desiredAscharacteristics were a solvent the nanoparticles would behydrolyzed time passed, was lowered the humidity to 10 C. in Also, the to airsoluble in, water miscible, and one that would not quench theincreased minimize the due effects to <strong>of</strong> seasonal precursor addition changesluminescence <strong>of</strong> the nanoparticles. This luminescence quenching(monsoons), the nanoparticles, affecting the formation SC-NP’s <strong>of</strong> were theeffect was determined to be a problem with the first solvents used,sol-gels. introduced To at counteract the beginning this effect, <strong>of</strong> themethanol and ethanol. These solvents, as well as tetrahydr<strong>of</strong>urantemperature hydrolysis step at which rather the than precursor in the buffer was(THF) and dimethylformamide (DMF), acted as electron donors,filling hydrolyzed solution. Byin exciton was includinghole lowered theseleft by excited to electrons 10 small C. changesin Also, the SC-NP. toThis minimizein the experimentalresulted in the a lack effectsprocedure,<strong>of</strong> emission <strong>of</strong> by precursortransparentthe nanoparticles additionsol-gels with known inclusion <strong>of</strong> CdSeand consequentlyonnanoparticlesthe no peaks nanoparticles, inwerethe spectrum.createdthe(FigureSC-NP’s6).wereintroduced A peak was finally at found the in the beginning fluorescence spectra <strong>of</strong> <strong>of</strong> CdSe- the16 hydrolysis when p-dioxane step was used rather as solvent than (Figure in the 5). buffer The peakindicated solution. that this By solvent including did not have these small same problem changes as itspredecessors. in the experimental p-Dioxane also has procedure, intermediate transparentpolarity so theSC-NP sol-gels was able with to be dispersed known while inclusion the solution <strong>of</strong> remained CdSe watermiscible 4 CMDITR giving Review this solvent <strong>of</strong> Undergraduate all the necessary Research characteristics. Vol. 1 No. 1 Summer 2004Figure 6. a) Fluorescence spectrum <strong>of</strong> a CdSe loaded sol-gelmonolith, b) A picture <strong>of</strong> a sol-gel containing nanoparticles.nanoparticles were created (Figure 6).TAYLORNormalized PL1.201.000.800.601.200.40Normalized PL0.200.001.000.80CdSe-16 in Dioxane4 0 0 450 500 5 5 0 6 0 0 6 5 0 7000.600.400.00Wavelength(nm4 0 0 4 5 0 5 00 5 5 0 6 0 0 6 5 0 7 0 0Figure 6: a) Fluorescence spectrum <strong>of</strong> a CdSeloaded sol-gel monolith, b) A picture <strong>of</strong> a sol-gelcontaining nanoparticles.Figure 6: a) Fluorescence spectrum <strong>of</strong> a CdSeloaded sol-gel monolith, b) A picture <strong>of</strong> a sol-gelcontaining nanoparticles.CMDITR Review <strong>of</strong> Undergraduate Research Vol. 2 No. 1 Summer <strong>2005</strong> 109