Regional Markets
56ec00c44c641_local-markets-book_complete_LR
56ec00c44c641_local-markets-book_complete_LR
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
4 Opportunities for development<br />
Although none of the projects interventions specifically aimed at development of ICT<br />
or mobile phone infrastructure, the emergence of mobile telephones was occasionally<br />
mentioned as contributing to a reduction of transaction costs (and an increase of atthe-gate<br />
prices). In Kenya, for instance, most smallholders can use their mobile phones<br />
to exchange information on prices and production volumes, or to make deals with local<br />
traders – the number of trips that traders make to remotely located suppliers is reduced.<br />
Besides, thanks to mobile telephony, several farmers can now coordinate and bulk their<br />
produce, and can transfer money through M-Pesa.<br />
We have seen that enhancements in the quality of physical infrastructure (roads, processing,<br />
storage and mobile infrastructure development) lead to value chain development<br />
and improve the position of smallholders. Clearly, also for regional market systems,<br />
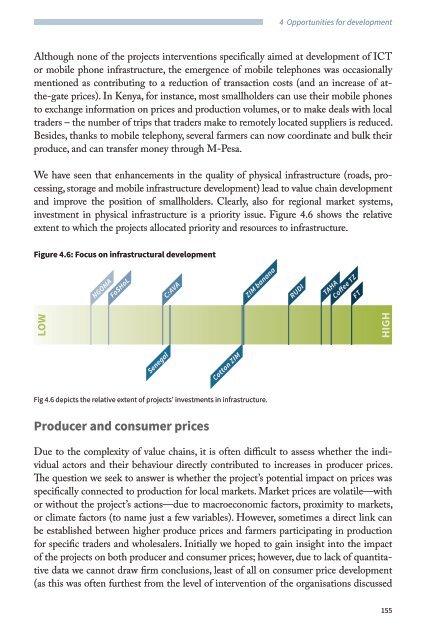
investment in physical infrastructure is a priority issue. Figure 4.6 shows the relative<br />
extent to which the projects allocated priority and resources to infrastructure.<br />
Figure 4.6: Focus on infrastructural development<br />
NGOMA<br />
FoSHoL<br />
C:AVA<br />
ZIM banana<br />
RUDI<br />
TAHA<br />
Coffee TZ<br />
FT<br />
LOW<br />
HIGH<br />
Senegal<br />
Cotton ZIM<br />
Fig 4.6 depicts the relative extent of projects’ investments in infrastructure.<br />
Producer and consumer prices<br />
Due to the complexity of value chains, it is often difficult to assess whether the individual<br />
actors and their behaviour directly contributed to increases in producer prices.<br />
The question we seek to answer is whether the project’s potential impact on prices was<br />
specifically connected to production for local markets. Market prices are volatile—with<br />
or without the project’s actions—due to macroeconomic factors, proximity to markets,<br />
or climate factors (to name just a few variables). However, sometimes a direct link can<br />
be established between higher produce prices and farmers participating in production<br />
for specific traders and wholesalers. Initially we hoped to gain insight into the impact<br />
of the projects on both producer and consumer prices; however, due to lack of quantitative<br />
data we cannot draw firm conclusions, least of all on consumer price development<br />
(as this was often furthest from the level of intervention of the organisations discussed<br />
155