Growing Together: Economic Integration for an Inclusive and - escap
Growing Together: Economic Integration for an Inclusive and - escap
Growing Together: Economic Integration for an Inclusive and - escap
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
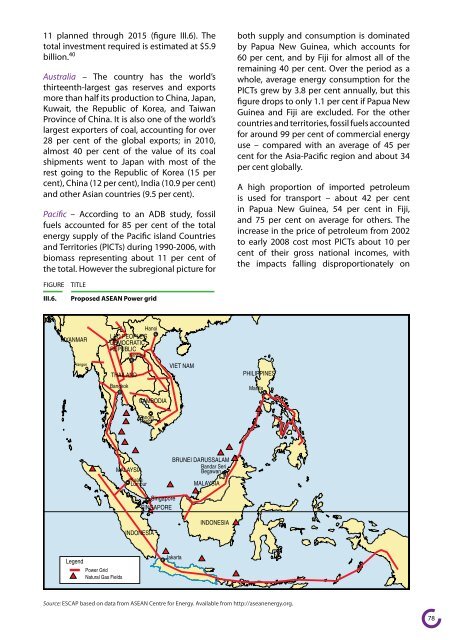
11 pl<strong>an</strong>ned through 2015 (figure III.6). The<br />
total investment required is estimated at $5.9<br />
billion. 40<br />
Australia – The country has the world’s<br />
thirteenth-largest gas reserves <strong>an</strong>d exports<br />
more th<strong>an</strong> half its production to China, Jap<strong>an</strong>,<br />
Kuwait, the Republic of Korea, <strong>an</strong>d Taiw<strong>an</strong><br />
Province of China. It is also one of the world’s<br />
largest exporters of coal, accounting <strong>for</strong> over<br />
28 per cent of the global exports; in 2010,<br />
almost 40 per cent of the value of its coal<br />
shipments went to Jap<strong>an</strong> with most of the<br />
rest going to the Republic of Korea (15 per<br />
cent), China (12 per cent), India (10.9 per cent)<br />
<strong>an</strong>d other Asi<strong>an</strong> countries (9.5 per cent).<br />
Pacific – According to <strong>an</strong> ADB study, fossil<br />
fuels accounted <strong>for</strong> 85 per cent of the total<br />
energy supply of the Pacific isl<strong>an</strong>d Countries<br />
<strong>an</strong>d Territories (PICTs) during 1990-2006, with<br />
biomass representing about 11 per cent of<br />
the total. However the subregional picture <strong>for</strong><br />
FIGURE TITLE<br />
III.6. Proposed ASEAN Power grid<br />
MYANMAR<br />
Y<strong>an</strong>gon<br />
H<strong>an</strong>oi<br />
LAO PEOPLE'S<br />
DEMOCRATIC<br />
REPUBLIC<br />
Vienti<strong>an</strong>e<br />
THAILAND<br />
B<strong>an</strong>gkok<br />
Legend<br />
Power Grid<br />
Natural Gas Fields<br />
Phnom<br />
Penh<br />
MALAYSIA<br />
Kuala<br />
Lumpur<br />
CAMBODIA<br />
Singapore<br />
SINGAPORE<br />
INDONESIA<br />
VIET NAM<br />
BRUNEI DARUSSALAM<br />
B<strong>an</strong>dar Seri<br />
Begaw<strong>an</strong><br />
Jakarta<br />
MALAYSIA<br />
INDONESIA<br />
both supply <strong>an</strong>d consumption is dominated<br />
by Papua New Guinea, which accounts <strong>for</strong><br />
60 per cent, <strong>an</strong>d by Fiji <strong>for</strong> almost all of the<br />
remaining 40 per cent. Over the period as a<br />
whole, average energy consumption <strong>for</strong> the<br />
PICTs grew by 3.8 per cent <strong>an</strong>nually, but this<br />
figure drops to only 1.1 per cent if Papua New<br />
Guinea <strong>an</strong>d Fiji are excluded. For the other<br />
countries <strong>an</strong>d territories, fossil fuels accounted<br />
<strong>for</strong> around 99 per cent of commercial energy<br />
use – compared with <strong>an</strong> average of 45 per<br />
cent <strong>for</strong> the Asia-Pacific region <strong>an</strong>d about 34<br />
per cent globally.<br />
A high proportion of imported petroleum<br />
is used <strong>for</strong> tr<strong>an</strong>sport – about 42 per cent<br />
in Papua New Guinea, 54 per cent in Fiji,<br />
<strong>an</strong>d 75 per cent on average <strong>for</strong> others. The<br />
increase in the price of petroleum from 2002<br />
to early 2008 cost most PICTs about 10 per<br />
cent of their gross national incomes, with<br />
the impacts falling disproportionately on<br />
PHILIPPINES<br />
TIMOR-LESTE<br />
Source: ESCAP based on data from ASEAN Centre <strong>for</strong> Energy. Available from http://ase<strong>an</strong>energy.org.<br />
M<strong>an</strong>ila<br />
PAPUA<br />
NEW GUINEA<br />
78