1. First steps in Reaktor Core - Native Instruments
1. First steps in Reaktor Core - Native Instruments
1. First steps in Reaktor Core - Native Instruments
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4.2. Object Bus Connections<br />
Object Bus Connections (OBC) are a special type of connection between<br />
modules. An OBC connection between two modules declares that they share<br />
some <strong>in</strong>ternal object. The most typical case of modules us<strong>in</strong>g OBC connections<br />
are memory Read and Write modules, which would share a common memory<br />
if connected by an OBC.<br />
The functionality of the Write module is to write a value that is <strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g at its<br />
<strong>in</strong>put, to the OBC-shared memory. The functionality of the Read module is to<br />
read a value from the OBC-shared memory <strong>in</strong> response to an <strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g clock<br />
signal (C <strong>in</strong>put). The read value is sent to the output of the Read module.<br />
�<br />
����� �<br />
�� ��<br />
��<br />
�����<br />
�� ��<br />
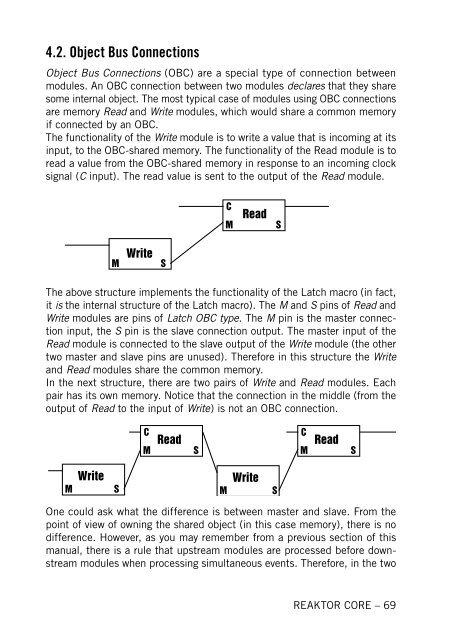
The above structure implements the functionality of the Latch macro (<strong>in</strong> fact,<br />
it is the <strong>in</strong>ternal structure of the Latch macro). The M and S p<strong>in</strong>s of Read and<br />
Write modules are p<strong>in</strong>s of Latch OBC type. The M p<strong>in</strong> is the master connection<br />
<strong>in</strong>put, the S p<strong>in</strong> is the slave connection output. The master <strong>in</strong>put of the<br />
Read module is connected to the slave output of the Write module (the other<br />
two master and slave p<strong>in</strong>s are unused). Therefore <strong>in</strong> this structure the Write<br />
and Read modules share the common memory.<br />
In the next structure, there are two pairs of Write and Read modules. Each<br />
pair has its own memory. Notice that the connection <strong>in</strong> the middle (from the<br />
output of Read to the <strong>in</strong>put of Write) is not an OBC connection.<br />
�<br />
����� �<br />
�� ��<br />
��<br />
���� �<br />
�� ��<br />
����� �<br />
�� ��<br />
��<br />
���� �<br />
�� ��<br />
One could ask what the difference is between master and slave. From the<br />
po<strong>in</strong>t of view of own<strong>in</strong>g the shared object (<strong>in</strong> this case memory), there is no<br />
difference. However, as you may remember from a previous section of this<br />
manual, there is a rule that upstream modules are processed before downstream<br />
modules when process<strong>in</strong>g simultaneous events. Therefore, <strong>in</strong> the two<br />
REAKTOR CORE – 69