Elephants Elephants - Wildpro - Twycross Zoo
Elephants Elephants - Wildpro - Twycross Zoo
Elephants Elephants - Wildpro - Twycross Zoo
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
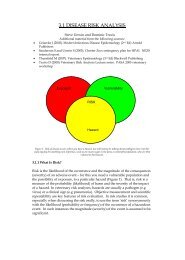
measure of improvement in early cases. Severe degenerative joint disease is<br />
an indication for euathansia.<br />
Dislocations generally carry a poor prognosis.<br />
Foot disorders, see under ‘foot care and problems’.<br />
Fractures of the long bones. In juveniles, domestic large animal techniques<br />
can be successful, but the prognosis in adult elephants is very poor. Fractures<br />
and dislocations of the femur/hip can result from awkward falls during<br />
anaesthetic induction or recovery.<br />
Trunk injuries. The trunk has a massive blood supply and thus severe<br />
haemorrhage may result following trauma. Paralysis of the trunk can arise<br />
from motor nerve damage. Loss of part of the trunk can be a serious problem<br />
for an elephant, but some animals adapt better than others.<br />
Trunk paralysis. Partial or complete paralysis of the trunk with consequent<br />
muscle atrophy is occasionally seen in Asian elephants. The cause is<br />
unknown, but cranial nerve trauma or infection and arteriosclerosis have all<br />
been suggested.<br />
Nutritional Problems<br />
Few nutritional problems have been well documented in elephant, but the<br />
following should be borne in mind (and see Section 3.4):<br />
Metabolic bone disease can be seen in handreared juvenile elephants with<br />
characteristic bowing of the long bones of the hind limbs.<br />
Hypocalcaemic tetany has been reported in elephants housed exclusively<br />
indoors with no access to sunlight. Animals that have marginal calcium<br />
reserves may also develop tetany when stressed.<br />
Iron deficiency anaemia is especially likely to occur in young, growing<br />
animals particularly if inadequately supplemented or without access to earth.<br />
Young African elephants fed alfalfa as the major dietary constituent can<br />
develop inward buckling of the tibio-tarsal joints, probably arising from too<br />
rapid a growth rate. This is treated by reducing dietary protein intake<br />
(Schmidt 1986).<br />
Parasitic Disease<br />
Parasitic disease does not play a major role in the veterinary management of<br />
captive elephants in the UK. Intestinal infestations rarely lead to clinical<br />
diarrhoea in the long-term captive animal, although parasite-related disease<br />
may be seen in newly imported stock. <strong>Elephants</strong> are host to a wide range of<br />
parasites in the wild, and therefore vigilance is necessary especially in newly<br />
imported animals. For a comprehensive list of the helminths of elephants and<br />
their significance, see (Mikota et al 1994) (Basson et al 1971).(Chowdhury and<br />
Aguirre 2001)<br />
Parasitic infestations of elephants include:<br />
• Ascarids, oxyurids, strongylids, paramphistomes, ancylostomes,<br />
sygamids and filarids.<br />
121