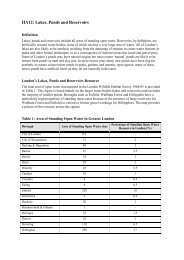
- Page 1 and 2:
Managment Guidelines for the Welfar
- Page 3 and 4:
MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR THE WELFA
- Page 5 and 6:
Table of Contents Management Guidel
- Page 7 and 8:
SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION 1.1 The Pur
- Page 9 and 10:
5. Elephants are large and intellig
- Page 11 and 12:
Section 2: BIOLOGY AND FIELD DATA A
- Page 13 and 14:
The woolly mammoth (M. primigenius)
- Page 15 and 16:
jaw but no more than two teeth are
- Page 17 and 18:
Features of the elephant’s reprod
- Page 19 and 20: Fig. 2. Map showing current and for
- Page 21 and 22: Table IV. AFRICAN ELEPHANT NUMBERS
- Page 23 and 24: populations using this method; the
- Page 25 and 26: obtained from the wildlife resource
- Page 27 and 28: and bots. For a comprehensive list
- Page 29 and 30: condition and increase the likeliho
- Page 31 and 32: animals in Sri Lanka as well as dir
- Page 33 and 34: COMMUNICATION Elephants, being larg
- Page 35 and 36: Section 3: MANAGEMENT IN CAPTIVITY
- Page 37 and 38: to North America in 1796 and the fi
- Page 39 and 40: and a lack of foraging opportunitie
- Page 41 and 42: protected contact until a full revi
- Page 43 and 44: enrichment and access to food (see
- Page 45 and 46: Adequate food storage areas MUST be
- Page 47 and 48: Fig 7a. Example of a good outside a
- Page 49 and 50: Most facilities in the British Isle
- Page 51 and 52: Table V. SUMMARY OF DIET COMPOSITIO
- Page 53 and 54: prevent obesity and associated heal
- Page 55 and 56: than the average zinc content of th
- Page 57 and 58: RECOMMENDATIONS Based on (Ullrey et
- Page 59 and 60: Stereotypies may be a mechanism whe
- Page 61 and 62: � Control/predictability. Ideally
- Page 63 and 64: Fig. 8b A waterfall in an enriched
- Page 65 and 66: institutions MUST exchange keepers
- Page 67 and 68: Reproductive Biology Department at
- Page 69: eadily available and the results ta
- Page 73 and 74: within an individual, thus a partic
- Page 75 and 76: 130 kg, the last having a survival
- Page 77 and 78: The goal should be to give cows exp
- Page 79 and 80: i r t h s 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Fig. 1
- Page 81 and 82: Mason report are never used. Method
- Page 83 and 84: incidents as appropriate. To facili
- Page 85 and 86: einforcer. Classical conditioning t
- Page 87 and 88: process. More than one handler may
- Page 89 and 90: 1 Must added • An opportunity to
- Page 91 and 92: c MANAGEMENT d Fig. 11. Elephants i
- Page 93 and 94: or operant conditioning. Only posit
- Page 95 and 96: • In FC positive and negative rei
- Page 97 and 98: the ERD, it should be used daily an
- Page 99 and 100: Training captive born elephants Whe
- Page 101 and 102: processed, written out and implemen
- Page 103 and 104: There are some acceptable justifica
- Page 105 and 106: 3.12 Standard Operating Procedure:
- Page 107 and 108: Fig. 13. Three sizes of ankus, show
- Page 109 and 110: Storage: when not carried by an aut
- Page 111 and 112: • Current equipment should be ass
- Page 113 and 114: Firearms When elephants are being m
- Page 115 and 116: • Alpha-2-agonists � Xylazine i
- Page 117 and 118: Pre-shipment Screening Prior to tra
- Page 119 and 120: observation for an hour after vacci
- Page 121 and 122:
Clostridial enterotoxaemia, see und
- Page 123 and 124:
measure of improvement in early cas
- Page 125 and 126:
metritis have all been described (M
- Page 127 and 128:
Fractures and longitudinal splits.
- Page 129 and 130:
management in zoos, their conservat
- Page 131 and 132:
After 1 the publication of the firs
- Page 133 and 134:
Some of the more unfortunate events
- Page 135 and 136:
� Is a further SOP required? �
- Page 137 and 138:
Broughton of HSE and Robert Landrid
- Page 139 and 140:
Barina, A., Reidl, M., Schmid, L.,
- Page 141 and 142:
Carlstead, K. & Kleiman, D. 1998. B
- Page 143 and 144:
Dineley, J. 1984. Operant condition
- Page 145 and 146:
Fraser, D., Phillips, P.A. & Thomps
- Page 147 and 148:
Hildebrandt, T., Göritz, F., Schno
- Page 149 and 150:
Khyne U Mar 2001. The studbook of t
- Page 151 and 152:
Leong, K.M., Burks, K., Rizkalla, C
- Page 153 and 154:
Moss, C. & Poole, J.H. 1983. Relati
- Page 155 and 156:
Olson, D. & Wiese, R.J. 2000. State
- Page 157 and 158:
Rasmussen, L.E. & Schulte, B.A. 199
- Page 159 and 160:
Schmid, J. 1995. Keeping circus ele
- Page 161 and 162:
Stewart, D.R., Stabenfeldt, G.H. &
- Page 163 and 164:
Wallace, C., Ingram, K. & Dierenfel
- Page 165 and 166:
Section 6: Appendices 6.1 Appendix
- Page 167 and 168:
Trunk (up) - curl trunk up to touch
- Page 169 and 170:
6.1.2 Appendix 1.1: Calf Training 1
- Page 171 and 172:
this time be used to the sight and
- Page 173 and 174:
These commands allow routine good h
- Page 175 and 176:
6.2 Appendix 2: Correct Application
- Page 177 and 178:
6.3 Appendix 3: Risk Assessments 1
- Page 179 and 180:
6.4 Appendix 4: Elephant Profiles 6
- Page 181 and 182:
6.5 Appendix 5: Staff training 1 A
- Page 183 and 184:
March 2003 Example from Woburn Safa
- Page 185 and 186:
(a.) Please indicate (tick) the typ
- Page 187 and 188:
6.6.2 Table of results of nutrition
- Page 189 and 190:
6.6.3 Table List of plant species u
- Page 191 and 192:
Vitamin E conversion factors Vitami
- Page 193 and 194:
Table 2. Doses for individual suppl
- Page 195 and 196:
uilding a new enclosure that will b
- Page 197 and 198:
exception of one female Asian that
- Page 199 and 200:
non-Fed members) that do not operat
- Page 201 and 202:
4 3 2 1 0 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000
- Page 203 and 204:
Three calves out of 17 live births
- Page 205 and 206:
Females - Only one collection that
- Page 207 and 208:
ELEPHANT TAG SURVEY (Please continu
- Page 209 and 210:
23 Are enrichments assessed in any
- Page 211 and 212:
etc? 8 How often has general anaest
- Page 213 and 214:
FEMALE ELEPHANT Please photocopy as
- Page 215 and 216:
213
- Page 217 and 218:
ody weight of dams, the age at whic
- Page 219:
Intra-specific aggression: incidenc