- Page 1 and 2:
1 Title of PhD Thesis: Mirror-touch
- Page 3 and 4:
3 LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES Figure
- Page 5 and 6:
5 ABSTRACT Synaesthesia is a condit
- Page 7 and 8:
7 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Firstly, I would
- Page 9 and 10:
9 Chapter 1 aroused some interest,
- Page 11 and 12:
11 Chapter 1 can skip generations (
- Page 13 and 14:
13 Chapter 1 to incongruent conditi
- Page 15 and 16:
15 Chapter 1 word/grapheme-colour s
- Page 17 and 18:
17 Chapter 1 the outside world (com
- Page 19 and 20:
19 Chapter 1 interacts with process
- Page 21 and 22:
21 Chapter 1 experience is due to a
- Page 23 and 24:
23 1.4.1 Synaesthesia involving tac
- Page 25 and 26:
25 Chapter 1 synaesthesia reported
- Page 27 and 28:
27 Chapter 1 if tactile stimulation
- Page 29 and 30:
29 Chapter 1 and colleagues (2005)
- Page 31 and 32:
31 Chapter 1 facial cheeks or hands
- Page 33 and 34:
33 1.5 Synaesthesia and models of t
- Page 35 and 36:
35 Chapter 1 the tactile mirror sys
- Page 37 and 38:
37 Chapter 2 over inflated female t
- Page 39 and 40:
39 Chapter 2 another person (or pos
- Page 41 and 42:
41 Chapter 2 Participants were aske
- Page 43 and 44:
43 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 (a) Summary
- Page 45 and 46:
45 Chapter 2 previously reported ca
- Page 47 and 48:
47 Chapter 2 the previously assumed
- Page 49 and 50:
Chapter 2 49 a. b. * 30 * * 1150 25
- Page 51 and 52:
51 Chapter 2 observing touch to the
- Page 53 and 54:
53 Results and Discussion Chapter 2
- Page 55 and 56:
55 Chapter 2 good evidence for a vi
- Page 57 and 58:
57 Chapter 2 via the dorsal stream
- Page 59 and 60:
59 Chapter 2 synaesthetes, touch to
- Page 61 and 62:
61 Chapter 2 This distinction is si
- Page 63 and 64:
63 CHAPTER 3: SENSORY PROCESSING IN
- Page 65 and 66:
65 Chapter 3 there is good evidence
- Page 67 and 68:
67 Chapter 3 Two coloured caps rema
- Page 69 and 70:
69 Chapter 3 colour perception task
- Page 71 and 72:
71 Chapter 3 p = trials correct / n
- Page 73 and 74:
73 Chapter 3 discrimination of colo
- Page 75 and 76:
75 Chapter 3 Leone, 2002) - further
- Page 77 and 78:
77 Chapter 3 (e.g. Cohen Kadosh et
- Page 79 and 80:
79 Chapter 4 Recent research has su
- Page 81 and 82: 81 Chapter 4 study. All cases of mi
- Page 83 and 84: 83 Chapter 4 that empathy is multi-
- Page 85 and 86: 85 Chapter 4 Hlushchuk, Williams, S
- Page 87 and 88: 87 Chapter 4 The BFI is a 44-item s
- Page 89 and 90: 89 IRI Score 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 1
- Page 91 and 92: 91 Chapter 4 extraversion [n = 120,
- Page 93 and 94: 93 Chapter 4 experience by contacti
- Page 95 and 96: 95 CHAPTER 5: FACIAL EXPRESSION REC
- Page 97 and 98: 97 Chapter 5 others (the mirror-tou
- Page 99 and 100: 99 Chapter 5 actors. Target and dis
- Page 101 and 102: 101 Chapter 5 effect for face perce
- Page 103 and 104: 103 5.3 Results Films Facial Expres
- Page 105 and 106: Chapter 5 105 75 b 85 a Synaesthete
- Page 107 and 108: Chapter 5 107 80 b 45 a Synaesthete
- Page 109 and 110: 109 Same-Different Expression and I
- Page 111 and 112: 111 Chapter 5 heightened emotion se
- Page 113 and 114: 113 Chapter 6 There are also import
- Page 115 and 116: 115 Chapter 6 overall duration of r
- Page 117 and 118: 117 Chapter 6 Figure 6.2 The effect
- Page 119 and 120: 119 Chapter 6 is infinite (with the
- Page 121 and 122: 121 Chapter 6 Figure 6.5 Functional
- Page 123 and 124: 123 Chapter 6 Huang et al., 2009; S
- Page 125 and 126: 125 Chapter 7 CHAPTER 7: THE ROLE O
- Page 127 and 128: 127 Chapter 7 right hemisphere soma
- Page 129 and 130: 129 Chapter 7 University College Lo
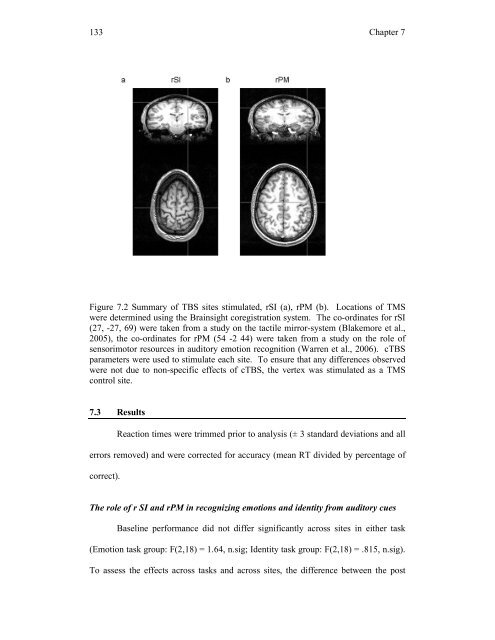
- Page 131: 131 Chapter 7 Figure 7.1 Summary of
- Page 135 and 136: Chapter 7 135 Identity Discriminati
- Page 137 and 138: 137 Chapter 7 2000; Pitcher et al.,
- Page 139 and 140: 139 Chapter 7 Eimer, in press). The
- Page 141 and 142: 141 Chapter 8 subliminal exposure t
- Page 143 and 144: 143 Chapter 8 necessary for all or
- Page 145 and 146: 145 Chapter 8 stimulated: rSI, rIFG
- Page 147 and 148: 147 TMS Protocol and Site Localisat
- Page 149 and 150: 149 Baseline minus cTBS RT (msec) 2
- Page 151 and 152: 151 Chapter 8 recognition, but not
- Page 153 and 154: 153 Chapter 8 The findings that cTB
- Page 155 and 156: 155 CHAPTER 9: CONCLUSIONS Chapter
- Page 157 and 158: 157 Chapter 9 the mirror-touch syna
- Page 159 and 160: 159 Chapter 9 Ramachandran, 2005; R
- Page 161 and 162: 161 Chapter 9 close proximity to th
- Page 163 and 164: 163 Chapter 9 for the specular-anat
- Page 165 and 166: 165 Chapter 9 non-synaesthetes, lin
- Page 167 and 168: 167 Chapter 9 cortical inhibition (
- Page 169 and 170: 169 Chapter 9 which underpin it). I
- Page 171 and 172: 171 Chapter 9 separate from a ‘sp
- Page 173 and 174: 173 Chapter 9 system (Rizzolatti an
- Page 175 and 176: 175 REFERENCES References Adolphs,
- Page 177 and 178: 177 References Avenanti, A., Bueti,
- Page 179 and 180: 179 References Batson, C. D. (1991)
- Page 181 and 182: 181 Bryant, G., and Barrett, H. C.
- Page 183 and 184:
183 References Coslett, B. (1998).
- Page 185 and 186:
185 References Donner, T. H., Kette
- Page 187 and 188:
187 References Fink, G. R., Markowi
- Page 189 and 190:
189 Grossenbacher, P.G., and Lovela
- Page 191 and 192:
191 References Iriki, A., Tanaka, M
- Page 193 and 194:
193 References Kipps, C. M., Duggin
- Page 195 and 196:
195 References Marks, L. E. (1975).
- Page 197 and 198:
197 References Oberman, L. M., Hubb
- Page 199 and 200:
199 References Pitcher, D., Walsh,
- Page 201 and 202:
201 References Russell, R., Duchain
- Page 203 and 204:
203 References Seron, X., Pesenti,
- Page 205 and 206:
205 Spiller, M. J., and Jansari, A.
- Page 207 and 208:
207 Treisman, A. (2004). In: L. Rob
- Page 209 and 210:
209 Walsh, V., and Pascual-Leone, A
- Page 211 and 212:
211 Wildgruber, D., Riecker, A., He
- Page 213 and 214:
213 Appendix (4) Do you experience