Mirror-touch synaesthesia: the role of shared ... - UCL Discovery
Mirror-touch synaesthesia: the role of shared ... - UCL Discovery
Mirror-touch synaesthesia: the role of shared ... - UCL Discovery
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 7<br />
135<br />
Identity Discrimination<br />
b<br />
Emotion Discrimination<br />
a<br />
300<br />
*<br />
300<br />
250<br />
250<br />
200<br />
200<br />
150<br />
150<br />
100<br />
100<br />
50<br />
50<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-50<br />
Baseline minus cTBS RT (msec)<br />
-50<br />
Baseline minus cTBS RT (msec)<br />
-100<br />
-100<br />
-150<br />
-150<br />
rSI rPM Vertex<br />
-200<br />
rSI rPM Vertex<br />
-200<br />
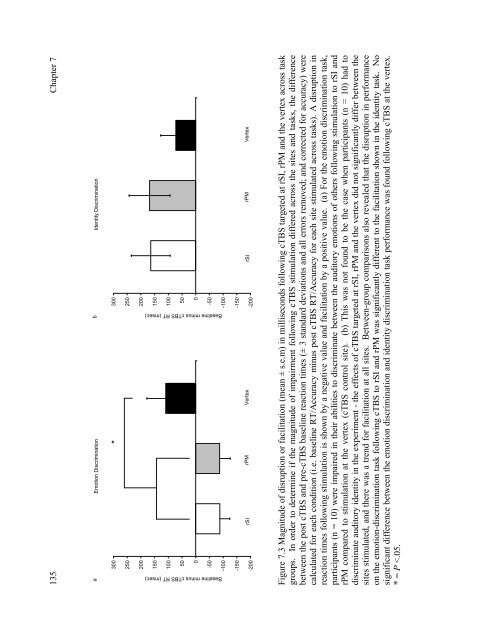
Figure 7.3 Magnitude <strong>of</strong> disruption or facilitation (mean ± s.e.m) in milliseconds following cTBS targeted at rSI, rPM and <strong>the</strong> vertex across task<br />
groups. In order to determine if <strong>the</strong> magnitude <strong>of</strong> impairment following cTBS stimulation differed across <strong>the</strong> sites and tasks, <strong>the</strong> difference<br />
between <strong>the</strong> post cTBS and pre-cTBS baseline reaction times (± 3 standard deviations and all errors removed; and corrected for accuracy) were<br />
calculated for each condition (i.e. baseline RT/Accuracy minus post cTBS RT/Accuracy for each site stimulated across tasks). A disruption in<br />
reaction times following stimulation is shown by a negative value and facilitation by a positive value. (a) For <strong>the</strong> emotion discrimination task,<br />
participants (n = 10) were impaired in <strong>the</strong>ir abilities to discriminate between <strong>the</strong> auditory emotions <strong>of</strong> o<strong>the</strong>rs following stimulation to rSI and<br />
rPM compared to stimulation at <strong>the</strong> vertex (cTBS control site). (b) This was not found to be <strong>the</strong> case when participants (n = 10) had to<br />
discriminate auditory identity in <strong>the</strong> experiment - <strong>the</strong> effects <strong>of</strong> cTBS targeted at rSI, rPM and <strong>the</strong> vertex did not significantly differ between <strong>the</strong><br />
sites stimulated, and <strong>the</strong>re was a trend for facilitation at all sites. Between-group comparisons also revealed that <strong>the</strong> disruption in performance<br />
on <strong>the</strong> emotion-discrimination task following cTBS to rSI and rPM was significantly different to <strong>the</strong> facilitation shown in <strong>the</strong> identity task. No<br />
significant difference between <strong>the</strong> emotion discrimination and identity discrimination task performance was found following cTBS at <strong>the</strong> vertex.<br />
* = P