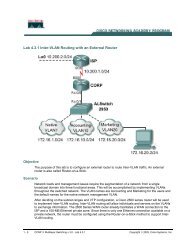
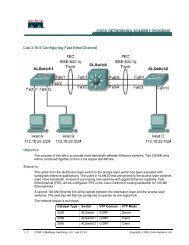
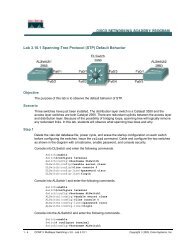
- Page 2 and 3:
Chemistry for the Utterly Confused
- Page 4 and 5:
Chemistry for the Utterly Confused
- Page 6 and 7:
We would like to dedicate this book
- Page 8 and 9:
◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 10 and 11:
Contents ix Chapter 5 Gases 79 Do I
- Page 12 and 13:
Contents xi Get Started 146 10-1 Mo
- Page 14 and 15:
Contents xiii 15-4 pH 222 15-5 Acid
- Page 16 and 17:
Contents xv Chapter 20 Nuclear Chem
- Page 18 and 19:
◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 20 and 21:
◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 22 and 23:
Chemistry for the Utterly Confused
- Page 24 and 25:
CHAPTER 1 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 26 and 27:
Chemistry: First Steps 3 compound b
- Page 28 and 29:
Chemistry: First Steps 5 exact norm
- Page 30 and 31:
Chemistry: First Steps 7 We now nee
- Page 32 and 33:
Chemistry: First Steps 9 mathematic
- Page 34 and 35:
Chemistry: First Steps 11 we do not
- Page 36 and 37:
Chemistry: First Steps 13 19. How m
- Page 38 and 39:
CHAPTER 2 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 40 and 41:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 17 Caref
- Page 42 and 43:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 19 table
- Page 44 and 45:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 21 If a
- Page 46 and 47:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 23 Once
- Page 48 and 49:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 25 and n
- Page 50 and 51:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 27 1. Th
- Page 52 and 53:
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules 29 20. N
- Page 54 and 55:
CHAPTER 3 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 56 and 57:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 33 Caref
- Page 58 and 59:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 35 Quick
- Page 60 and 61:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 37 Quick
- Page 62 and 63:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 39 Quick
- Page 64 and 65:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 41 Caref
- Page 66 and 67:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 43 the b
- Page 68 and 69:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 45 7. Th
- Page 70 and 71:
Mass, Moles, and Equations 47 17. a
- Page 72 and 73:
CHAPTER 4 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 74 and 75:
Aqueous Solutions 51 4-2 Solubility
- Page 76 and 77:
Aqueous Solutions 53 Don’t Forget
- Page 78 and 79:
Aqueous Solutions 55 Quick Tip Cert
- Page 80 and 81:
Aqueous Solutions 57 Quick Tip Quic
- Page 82 and 83:
Aqueous Solutions 59 Don’t Forget
- Page 84 and 85:
Aqueous Solutions 61 Don’t Forget
- Page 86 and 87:
Aqueous Solutions 63 Quick Tip Mg(N
- Page 88 and 89:
Aqueous Solutions 65 All the separa
- Page 90 and 91:
Aqueous Solutions 67 Don’t Forget
- Page 92 and 93:
Aqueous Solutions 69 There will be
- Page 94 and 95:
Aqueous Solutions 71 Don’t Forget
- Page 96 and 97:
Aqueous Solutions 73 Don’t Forget
- Page 98 and 99:
Aqueous Solutions 75 The calculatio
- Page 100 and 101:
Aqueous Solutions 77 25. The titrat
- Page 102 and 103:
CHAPTER 5 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 104 and 105:
Gases 81 Quick Tip Don’t Forget!
- Page 106 and 107:
Gases 83 Quick Tip Let’s see how
- Page 108 and 109:
Gases 85 Don’t Forget! Quick Tip
- Page 110 and 111:
Gases 87 Second, the KMT relates th
- Page 112 and 113:
Gases 89 The larger the gas particl
- Page 114 and 115:
Gases 91 Note that the mandatory co
- Page 116 and 117:
Gases 93 If it was not clear before
- Page 118 and 119:
Gases 95 ANSWER KEY 1. PTotal PA
- Page 120 and 121:
CHAPTER 6 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 122 and 123:
Thermochemistry 99 Quick Tip Don’
- Page 124 and 125:
Thermochemistry 101 Don’t Forget!
- Page 126 and 127:
Thermochemistry 103 C2H2(g) (5/2) O
- Page 128 and 129:
Thermochemistry 105 Quick Tip Some
- Page 130 and 131:
CHAPTER 7 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 132 and 133:
Quantum Theory and Electrons 109 Al
- Page 134 and 135:
Quantum Theory and Electrons 111 Th
- Page 136 and 137:
Quantum Theory and Electrons 113 Do
- Page 138 and 139:
Quantum Theory and Electrons 115 Do
- Page 140 and 141:
Quantum Theory and Electrons 117 AN
- Page 142 and 143:
CHAPTER 8 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 144 and 145:
Periodic Trends 121 8-2 Ionization
- Page 146 and 147:
Periodic Trends 123 The general tre
- Page 148 and 149:
Periodic Trends 125 in its ground s
- Page 150 and 151:
CHAPTER 9 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 152 and 153:
Chemical Bonding 129 Quick Tip In S
- Page 154 and 155:
Chemical Bonding 131 9-3 Ionic Bond
- Page 156 and 157:
Chemical Bonding 133 Quick Tip Neve
- Page 158 and 159:
Chemical Bonding 135 Don’t Forget
- Page 160 and 161:
Chemical Bonding 137 9-6 Bond Energ
- Page 162 and 163:
Chemical Bonding 139 Quick Tip invo
- Page 164 and 165:
Chemical Bonding 141 Quick Tip Elem
- Page 166 and 167:
Chemical Bonding 143 11. a 12. b 13
- Page 168 and 169:
CHAPTER 10 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 170 and 171:
Molecular Geometry and Hybridizatio
- Page 172 and 173:
Molecular Geometry and Hybridizatio
- Page 174 and 175: Molecular Geometry and Hybridizatio
- Page 176 and 177: Molecular Geometry and Hybridizatio
- Page 178 and 179: Molecular Geometry and Hybridizatio
- Page 180 and 181: CHAPTER 11 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 182 and 183: Intermolecular Forces, Solids and L
- Page 184 and 185: Intermolecular Forces, Solids and L
- Page 186 and 187: Intermolecular Forces, Solids and L
- Page 188 and 189: Intermolecular Forces, Solids and L
- Page 190 and 191: Intermolecular Forces, Solids and L
- Page 192 and 193: Intermolecular Forces, Solids and L
- Page 194 and 195: CHAPTER 12 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 196 and 197: Solutions 173 ways of expressing th
- Page 198 and 199: Solutions 175 Don’t Forget! Don
- Page 200 and 201: Solutions 177 12-3 Colligative Prop
- Page 202 and 203: Solutions 179 Just as the freezing
- Page 204 and 205: Solutions 181 Don’t Forget! Using
- Page 206 and 207: Solutions 183 Quick Tip A molar mas
- Page 208 and 209: Solutions 185 3. All methods of num
- Page 210 and 211: CHAPTER 13 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 212 and 213: Kinetics 189 4. Physical state of r
- Page 214 and 215: Kinetics 191 Don’t Forget! consta
- Page 216 and 217: Kinetics 193 Don’t Forget! the co
- Page 218 and 219: Kinetics 195 Quick Tip Careful! Rem
- Page 220 and 221: Kinetics 197 The decomposition of h
- Page 222 and 223: Kinetics 199 reaction is first orde
- Page 226 and 227: CHAPTER 14 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 228 and 229: Chemical Equilibria 205 Quick Tip D
- Page 230 and 231: Chemical Equilibria 207 14-3 Le Ch
- Page 232 and 233: Chemical Equilibria 209 Given the f
- Page 234 and 235: Chemical Equilibria 211 Careful! Do
- Page 236 and 237: Chemical Equilibria 213 Quick Tip F
- Page 238 and 239: Chemical Equilibria 215 Quick Tip I
- Page 240 and 241: Chemical Equilibria 217 10. Write K
- Page 242 and 243: CHAPTER 15 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 244 and 245: Acids and Bases 221 Don’t Forget!
- Page 246 and 247: Acids and Bases 223 The pH of pure
- Page 248 and 249: Acids and Bases 225 Quick Tip Quick
- Page 250 and 251: Acids and Bases 227 15-7 Lewis Acid
- Page 252 and 253: Acids and Bases 229 We do not have
- Page 254 and 255: Acids and Bases 231 Quick Tip We ne
- Page 256 and 257: Acids and Bases 233 2. Alkali metal
- Page 258 and 259: CHAPTER 16 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 260 and 261: Buffers and Other Equilibria 237 we
- Page 262 and 263: Buffers and Other Equilibria 239 Do
- Page 264 and 265: Buffers and Other Equilibria 241 16
- Page 266 and 267: Buffers and Other Equilibria 243 Qu
- Page 268 and 269: Buffers and Other Equilibria 245 Qu
- Page 270 and 271: Buffers and Other Equilibria 247 pK
- Page 272 and 273: Buffers and Other Equilibria 249 Th
- Page 274 and 275:
CHAPTER 17 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 276 and 277:
Entropy and Free Energy 253 17-2 En
- Page 278 and 279:
Entropy and Free Energy 255 17-5 Ut
- Page 280 and 281:
Entropy and Free Energy 257 Quick T
- Page 282 and 283:
Entropy and Free Energy 259 Be Care
- Page 284 and 285:
Entropy and Free Energy 261 Before
- Page 286 and 287:
Entropy and Free Energy 263 ANSWER
- Page 288 and 289:
CHAPTER 18 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 290 and 291:
Electrochemistry 267 Quick Tip Some
- Page 292 and 293:
Electrochemistry 269 Don’t Forget
- Page 294 and 295:
Electrochemistry 271 We can use thi
- Page 296 and 297:
Electrochemistry 273 do is reverse
- Page 298 and 299:
Electrochemistry 275 Don’t Forget
- Page 300 and 301:
Electrochemistry 277 Be Careful! Th
- Page 302 and 303:
Electrochemistry 279 ANSWER KEY 1.
- Page 304 and 305:
CHAPTER 19 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 306 and 307:
Chemistry of the Elements 283 19-2
- Page 308 and 309:
Chemistry of the Elements 285 Be Ca
- Page 310 and 311:
Chemistry of the Elements 287 Don
- Page 312 and 313:
Chemistry of the Elements 289 6. Wh
- Page 314 and 315:
CHAPTER 20 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 316 and 317:
Nuclear Chemistry 293 The sum of th
- Page 318 and 319:
Nuclear Chemistry 295 Don’t Forge
- Page 320 and 321:
Nuclear Chemistry 297 that is not a
- Page 322 and 323:
Nuclear Chemistry 299 Don’t Forge
- Page 324 and 325:
Nuclear Chemistry 301 t 1/2 (ln 2)
- Page 326 and 327:
Nuclear Chemistry 303 1. A typical
- Page 328 and 329:
CHAPTER 21 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 330 and 331:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 332 and 333:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 334 and 335:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 336 and 337:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 338 and 339:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 340 and 341:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 342 and 343:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 344 and 345:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 346 and 347:
Organic, Biochemistry, and Polymers
- Page 348 and 349:
◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆
- Page 350 and 351:
Index 327 chemical formulas, 19-21
- Page 352 and 353:
Index 329 Gibbs free energy (G), 25
- Page 354 and 355:
Index 331 octet rule, 128, 135, 140
- Page 356 and 357:
Index 333 viscosity, 161 voltaic ce
- Page 358 and 359:
◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆