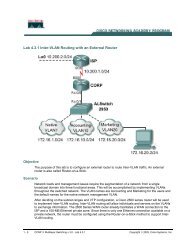
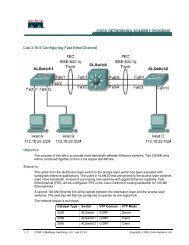
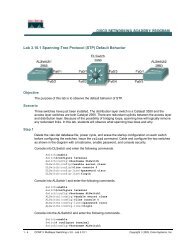
Untitled - Kelly Walsh High School
Untitled - Kelly Walsh High School
Untitled - Kelly Walsh High School
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
326 INDEX<br />
atoms (Cont.):<br />
nomenclature, 21–26<br />
overview, 15–16<br />
periodic table, 17–19<br />
Aufbau principle, 111–113<br />
Avogadro’s number, 34–35, 40–42<br />
balanced chemical equations, 32–36, 41<br />
band theory of conductivity, 283–284<br />
base anhydrides, 284<br />
base dissociation constant (K b), 225–226<br />
bases, 219–233<br />
acid-base equilibrium, 223–226<br />
Brønsted-Lowery theory, 220<br />
Lewis theory, 227<br />
overview, 53–55, 219–220<br />
pH scale, 222–223<br />
properties of salts and oxides, 226<br />
strength of, 220–221<br />
water dissociation constant, 221–222<br />
weak, 227–233<br />
beta emission, 293, 295<br />
bimolecular reactions, 198<br />
binary acids, 26<br />
biochemistry (see Organic chemistry)<br />
Bohr, Niels, 109<br />
boiling-point elevation, 178–179<br />
bonds<br />
chemical, 127–144<br />
bond energy and length, 137<br />
covalent bonds, 132–135<br />
electronegativity, 130<br />
Lewis structures, 137–144<br />
Lewis symbols, 128–130<br />
overview, 127–128<br />
resonance, 136<br />
hydrogen bonding, 160<br />
valence bond theory, 149–151<br />
(See also Ionic bonds)<br />
Born-Haber cycle, 132<br />
branches, 309<br />
Brønsted-Lowery acid-base theory, 220, 232<br />
buffers, 236–237, 249<br />
C (molar heat capacity), 99–101<br />
c (specific heat capacity), 99–101<br />
cal (calories), 98<br />
calories (cal), 98<br />
calorimetry, 98–100, 103–105<br />
capillary action, 161–162<br />
carbohydrates, 314–315, 322<br />
carboxylic acid groups, 314, 318–320<br />
catalysis:<br />
condensation reactions, 319<br />
hydrogenation, 317<br />
kinetics, 196–197, 201<br />
and reaction rate, 189<br />
saponification, 321<br />
cathodes, 269, 274–276<br />
cations:<br />
aqueous solutions, 53, 61<br />
ionic bonding, 131<br />
ionization energy, 121–122<br />
Lewis structures for, 135<br />
metals as, 24, 283<br />
overview, 20<br />
salt, 55<br />
transition metals as, 287<br />
cell notation, 269–270<br />
cells:<br />
actual potential, 272–273<br />
electrolytic, 273–274<br />
galvanic (voltaic), 268–270<br />
and nucleic acids, 315–316<br />
standard reduction potentials of,<br />
270–271<br />
unit, 162<br />
chelating ligands, 287<br />
chemical bonds, 127–144<br />
bond energy and bond length, 137<br />
covalent bonds, 132–135<br />
electronegativity, 130<br />
ionic bonds and lattice energy,<br />
131–132<br />
Lewis structures, 137–141<br />
Lewis symbols, 128–130<br />
overview, 127–128<br />
resonance, 136<br />
chemical equilibria, 203–218, 235–250<br />
acid-base equilibrium, 223–226<br />
buffers and pH, 236–237<br />
calculating, 209–216<br />
common-ion effect, 236<br />
complex ion formation constant, 241<br />
equilibrium constants, 205–206<br />
Le Châtelier’s principle, 207–209<br />
overview, 203–205, 235–236<br />
pH and titrations, 241–248<br />
solubility product constant, 238–240<br />
titrations and indicators, 237–238