- Page 1: Iron sedimentation and the neodymiu
- Page 4 and 5: The process(es) by which IFs were d
- Page 7: This thesis represents original and
- Page 10 and 11: viii
- Page 12 and 13: goal of the research is to discern
- Page 14 and 15: Figure 1. Map of southern Africa sh
- Page 16 and 17: appropriate to briefly discuss: 1)
- Page 18 and 19: 100 10 MORB 1 0.1 raw data (mg/kg)
- Page 20 and 21: 10 -2 hydrothermal fluid 10 -3 10 -
- Page 24 and 25: 100 MCO + 3 + M(CO 3 )- 2 rare eart
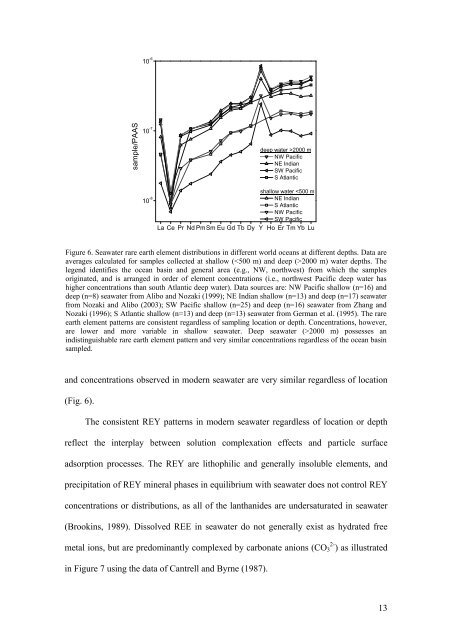
- Page 26 and 27: net effect of carbonate complexatio
- Page 28 and 29: feature was not recognized in early
- Page 30 and 31: sound geochemical basis for anomalo
- Page 32 and 33: deviation of the 143 Nd/ 144 Nd rat
- Page 34 and 35: available, it should be possible to
- Page 36 and 37: modern and Archean oceans, as well
- Page 38 and 39: Bau M., Möller P., and Dulski P. (
- Page 40 and 41: Elderfield H. and Greaves M.J. (198
- Page 42 and 43: Haley B.A., Klinkhammer G.P. (2003)
- Page 44 and 45: Lee J.H. and Byrne R.H. (1993) Comp
- Page 46 and 47: Piepgras D.J. and Wasserburg G.J. (
- Page 48 and 49: Tosiani T., Loubet M., Viers J., Va
- Page 50 and 51: THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 52 and 53: Abstract The benefits of inductivel
- Page 54 and 55: List of Figures Figure 1. Sample de
- Page 56 and 57: 1. Introduction The advent of induc
- Page 58 and 59: Figure 1. Flow-chart diagram of the
- Page 60 and 61: during decomposition (SiF 4 and CO
- Page 62 and 63: Fractionation between the three iso
- Page 64 and 65: cps, then 3000 cps must be subtract
- Page 66 and 67: variety of ways. These range from r
- Page 68 and 69: Table 3. Change in HFSE concentrati
- Page 70 and 71: 0.90, corresponding to an anomalous
- Page 72 and 73:
10 2 JDo-1 reference values 10 1 IF
- Page 74 and 75:
Figure 5. Diagram depicting various
- Page 76 and 77:
20 18 basalt BHVO-2 (n=5) run preci
- Page 78 and 79:
The method precision for elements p
- Page 80 and 81:
Two approaches may be utilized to d
- Page 82 and 83:
For the more recent, full 32 elemen
- Page 84 and 85:
isotopic data for geologic CRMs, av
- Page 86 and 87:
Table 4. Interferences observed for
- Page 88 and 89:
value uncertainty (as %RSD) is repr
- Page 90 and 91:
1.50 FeR-4 (n=2) 1.25 JUB / referen
- Page 92 and 93:
1 IF-G/shale 0.1 0.01 La Ce Pr Nd P
- Page 94 and 95:
consistent (App. 1), and similar to
- Page 96 and 97:
1.50 SGR-1b (n=3) 1.25 JUB / refere
- Page 98 and 99:
1.50 JCh-1 (n=3) 1.25 JUB / referen
- Page 100 and 101:
1.50 JDo-1 (n=5) 1.25 JUB / referen
- Page 102 and 103:
determinations in carbonate rocks r
- Page 104 and 105:
1.50 JMn-1 (n=4) 1.25 JUB / referen
- Page 106 and 107:
eference value. The result is that
- Page 108 and 109:
eference value and the measured JUB
- Page 110 and 111:
the 32 analyzed elements, with Ti b
- Page 112 and 113:
Govindaraju K. (1995) 1995 working
- Page 114 and 115:
Appendix 1. Analytical data Appendi
- Page 116 and 117:
Appendix 1. Literature reference va
- Page 118 and 119:
Appendix 1 continued. Data in mg/kg
- Page 120 and 121:
the concentration of the major elem
- Page 122 and 123:
Potential interferences on monoisot
- Page 124 and 125:
1500 0.5 M HCl 4.0 interference on
- Page 126 and 127:
4000 0.40 0.20 3500 0.17 mg/kg 0.18
- Page 128 and 129:
interference on 95 Mo in sample sol
- Page 130 and 131:
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 132 and 133:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 134 and 135:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 136 and 137:
Table 2 Trace element concentration
- Page 138 and 139:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 140 and 141:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 142 and 143:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 144 and 145:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 146 and 147:
Nd isotopes in 2.9 Ga Archean surfa
- Page 148 and 149:
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 150 and 151:
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 152 and 153:
Author's personal copy B.W. Alexand
- Page 154 and 155:
Author's personal copy B.W. Alexand
- Page 156 and 157:
Author's personal copy B.W. Alexand
- Page 158 and 159:
Author's personal copy B.W. Alexand
- Page 160 and 161:
Author's personal copy B.W. Alexand
- Page 162 and 163:
Author's personal copy B.W. Alexand
- Page 164 and 165:
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 166 and 167:
and preservation of oxide-facies IF
- Page 168 and 169:
TOP relative stratigraphic position
- Page 170 and 171:
The mechanism by which the alkali m
- Page 172 and 173:
6. Widdel, F. et al. Ferrous iron o
- Page 174 and 175:
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 176 and 177:
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
- Page 178 and 179:
82 PRESERVATION OF PRIMARY REE PATT
- Page 180 and 181:
84 PRESERVATION OF PRIMARY REE PATT
- Page 182 and 183:
86 PRESERVATION OF PRIMARY REE PATT
- Page 184:
ulk, open ocean seawater tended to