Medium Voltage Application Guide
Medium Voltage Application Guide
Medium Voltage Application Guide
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Time (s)<br />
SWITCHGEAR<br />
Protection Devices<br />
Protection devices are used in medium voltage distribution systems to protect line and cable feeders, busbar<br />
systems, transformers, motors, generators and power factor correction banks. Abnormal conditions can be<br />
detected based on secondary current and voltage measurement, or temperature monitoring using thermal devices.<br />
When an abnormal condition is detected, correct coordination of the protection devices will rapidly isolate the fault<br />
to a specific zone in the system.<br />
Older protection devices relied on electromechanical relays to measure system parameters. Modern protection<br />
devices are exclusively low consumption, digital, and microprocessor based, with many communication options<br />
available. Modern high-end protection devices incorporate many parameter settings along with programmable<br />
logic control which provides not only protection functions, but switchgear control and interlocking.<br />
Protection devices are primarily covered by IEC 60255-1.<br />
Protection functions<br />
Overcurrent<br />
This is the most widely used form of protection. In a 3-phase power system, all three line currents are measured<br />
using current transformers. The secondary output of a 1 A or 5 A current transformer is connected to the current<br />
input of a protection device. Within the protection device, analog signals are filtered and sampled before being<br />
converted to digital signals for processing. A trip condition occurs if a preset current level is exceeded for a specific<br />
time.<br />
There are two basic methods of overcurrent protection:<br />
<br />
<br />
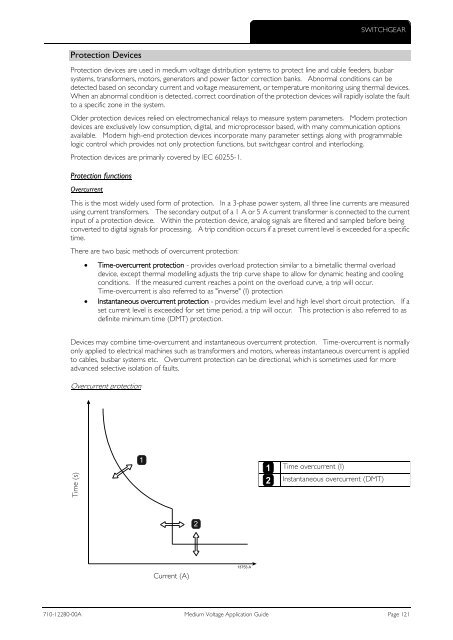
Time-overcurrent protection - provides overload protection similar to a bimetallic thermal overload<br />
device, except thermal modelling adjusts the trip curve shape to allow for dynamic heating and cooling<br />
conditions. If the measured current reaches a point on the overload curve, a trip will occur.<br />
Time-overcurrent is also referred to as "inverse" (I) protection<br />
Instantaneous overcurrent protection - provides medium level and high level short circuit protection. If a<br />
set current level is exceeded for set time period, a trip will occur. This protection is also referred to as<br />
definite minimum time (DMT) protection.<br />
Devices may combine time-overcurrent and instantaneous overcurrent protection. Time-overcurrent is normally<br />
only applied to electrical machines such as transformers and motors, whereas instantaneous overcurrent is applied<br />
to cables, busbar systems etc. Overcurrent protection can be directional, which is sometimes used for more<br />
advanced selective isolation of faults.<br />
Overcurrent protection<br />
1<br />
Time overcurrent (I)<br />
Instantaneous overcurrent (DMT)<br />
2<br />
Current (A)<br />
13753.A<br />
710-12280-00A <strong>Medium</strong> <strong>Voltage</strong> <strong>Application</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> Page 121