Hand hygiene.pdf
Hand hygiene.pdf
Hand hygiene.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
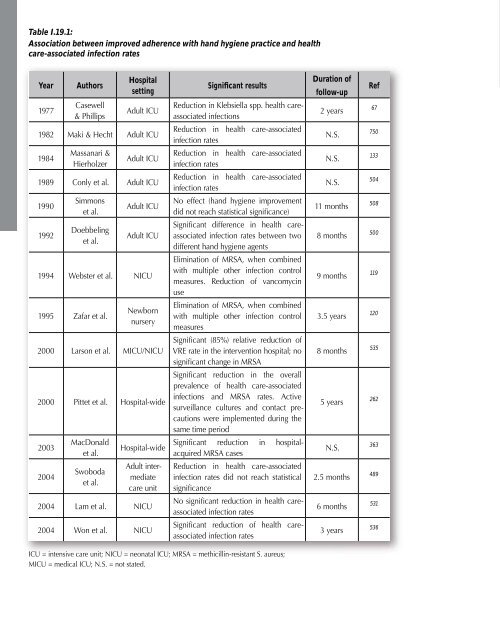
Table I.19.1:<br />
Association between improved adherence with hand <strong>hygiene</strong> practice and health<br />
care-associated infection rates<br />
Year<br />
1977<br />
Authors<br />
Casewell<br />
& Phillips<br />
Hospital<br />
setting<br />
Adult ICU<br />
1982 Maki & Hecht Adult ICU<br />
1984<br />
Massanari &<br />
Hierholzer<br />
Adult ICU<br />
1989 Conly et al. Adult ICU<br />
1990<br />
1992<br />
Simmons<br />
et al.<br />
Doebbeling<br />
et al.<br />
Adult ICU<br />
Adult ICU<br />
1994 Webster et al. NICU<br />
1995 Zafar et al.<br />
Newborn<br />
nursery<br />
2000 Larson et al. MICU/NICU<br />
2000 Pittet et al. Hospital-wide<br />
2003<br />
2004<br />
MacDonald<br />
et al.<br />
Swoboda<br />
et al.<br />
Hospital-wide<br />
Adult intermediate<br />
care unit<br />
2004 Lam et al. NICU<br />
2004 Won et al. NICU<br />
Significant results<br />
Reduction in Klebsiella spp. health careassociated<br />
infections<br />
Reduction in health care-associated<br />
infection rates<br />
Reduction in health care-associated<br />
infection rates<br />
Reduction in health care-associated<br />
infection rates<br />
No effect (hand <strong>hygiene</strong> improvement<br />
did not reach statistical significance)<br />
Significant difference in health careassociated<br />
infection rates between two<br />
different hand <strong>hygiene</strong> agents<br />
Elimination of MRSA, when combined<br />
with multiple other infection control<br />
measures. Reduction of vancomycin<br />
use<br />
Elimination of MRSA, when combined<br />
with multiple other infection control<br />
measures<br />
Significant (85%) relative reduction of<br />
VRE rate in the intervention hospital; no<br />
significant change in MRSA<br />
Significant reduction in the overall<br />
prevalence of health care-associated<br />
infections and MRSA rates. Active<br />
surveillance cultures and contact precautions<br />
were implemented during the<br />
same time period<br />
Significant reduction in hospitalacquired<br />
MRSA cases<br />
Reduction in health care-associated<br />
infection rates did not reach statistical<br />
significance<br />
No significant reduction in health careassociated<br />
infection rates<br />
Significant reduction of health careassociated<br />
infection rates<br />
Duration of<br />
follow-up<br />
2 years<br />
N.S.<br />
N.S.<br />
N.S.<br />
11 months<br />
8 months<br />
9 months<br />
3.5 years<br />
8 months<br />
5 years<br />
N.S.<br />
2.5 months<br />
6 months<br />
3 years<br />
Ref<br />
67<br />
750<br />
133<br />
504<br />
508<br />
500<br />
119<br />
120<br />
535<br />
262<br />
363<br />
489<br />
531<br />
536<br />
ICU = intensive care unit; NICU = neonatal ICU; MRSA = methicillin-resistant S. aureus;<br />
MICU = medical ICU; N.S. = not stated.