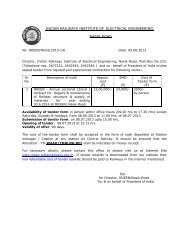
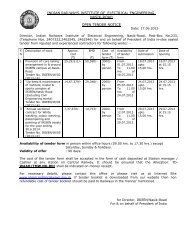
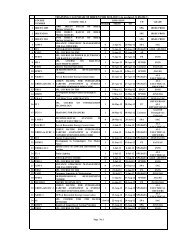
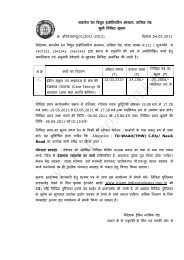
remote control equipment - Indian Railways Institute of Electrical ...
remote control equipment - Indian Railways Institute of Electrical ...
remote control equipment - Indian Railways Institute of Electrical ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
i) Three post, centre post rotating double break type and<br />
ii) Two post single break type.<br />
These isolators are <strong>of</strong> horizontal break type on the secondary side i.e. 25 KV side, the<br />
isolators used are <strong>of</strong> vertical break type. The rated normal current <strong>of</strong> these isolators is fixed to<br />
match the rated current <strong>of</strong> circuit breakers and bus bars etc. The standard values <strong>of</strong> rated<br />
normal current as specified in the IEC and IS specifications are the same as shown in para<br />
5.5 for breakers.<br />
4.7 CURRENT & POTENTIAL TRANSFORMERS<br />
4.7.1 Bushing type CTs have been provided on primary and secondary side <strong>of</strong> the<br />
traction transformers and are exclusively meant for differential protection. Separately mounted<br />
132 KV and 25 KV CT and 25 KV PTs are <strong>of</strong> conventional type.<br />
4.8 BUS BARS<br />
4.8.1 Two types <strong>of</strong> bus bar have been used for traction substation viz. strung type<br />
bus bar on the HV side and rigid type bus bar on LV side i.e. 25 KV side. The strung bus<br />
used in the earlier electrification schemes was consisting <strong>of</strong> All Aluminium ‘spider’ conductor<br />
<strong>of</strong> size 19/3 99 mm. The capacity <strong>of</strong> this conductor is adequate only to meet the maximum<br />
fault current <strong>of</strong> above 17KA, but due to increase in the fault/level <strong>of</strong> grid system, the value<br />
<strong>of</strong> fault current has exceeded 25KA. Therefore, to meet the higher requirement <strong>of</strong> fault<br />
current in the system, use <strong>of</strong> ‘Zebra’ Acsr conductor has been adopted in the ongoing<br />
electrification schemes, (size 61/3.18, dia 28.62 mm). This conductor is capable to withstand<br />
fault currents <strong>of</strong> the order <strong>of</strong> 31.5 KA. The tension in the strung bus is kept between 500 to<br />
900 kgf. To keep corona losses within limits, the minimum diameter <strong>of</strong> conductors (strung<br />
bus) and jumpers shall not be less than 28 mm in case <strong>of</strong> 220 KV system.<br />
4.8.2 Similarly the rigid type bus used in earlier electrification schemes was <strong>of</strong><br />
Aluminium Alloy <strong>of</strong> 36 mm O.D. (36/28 mm). This bus was capable to carry the normal<br />
rated current <strong>of</strong> 960 Amps. But with the use <strong>of</strong> 20 MVA, transformers the requirement <strong>of</strong><br />
rated normal current has increased to 1500 Amps (for short duration). Therefore, the size <strong>of</strong><br />
the rigid bus bar has also been increased to 50 mm O.D. (50/39 mm). This bus is capable<br />
to carry continuos current <strong>of</strong> 1530 Amps. The rigid type bus is supported on the support<br />
insulators provided at a distance not exceeding 3 m. The minimum height <strong>of</strong> the 25 KV bus<br />
bar has been kept as 3800 mm. Chances <strong>of</strong> failure <strong>of</strong> rigid bus are very <strong>remote</strong>, but its<br />
installation is costlier than the strung bus.<br />
4.9 LIGHTNING ARRESTERS<br />
4.9.1 Lightning arrestors ar also called surge diverters. The primary purpose <strong>of</strong> a<br />
lightning arrester is to protect the system from getting damaged by the over-voltages caused<br />
due to lightning strokes and switching surges. Lightning arresters absorb the energy and<br />
reduce the over voltage in the system. The ideal arrester is one which draws negligible<br />
current at operating voltage by <strong>of</strong>fering very high impedance and negligible impedance<br />
84