- Page 1 and 2:
Copyright/WarrantyEnd User License
- Page 3 and 4:
Copyright/WarrantyTerm and Terminat
- Page 7:
Appendix A: Electronic Imaging Theo
- Page 14 and 15:
Installation GuidelinesEquipment St
- Page 16 and 17:
Installation GuidelinesWhat is in t
- Page 18 and 19:
Installation GuidelinesVideo Card R
- Page 20 and 21:
Installation GuidelinesMultiple Cam
- Page 22:
Taking Your First PictureQuick Star
- Page 27 and 28:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program Mode• The F
- Page 29 and 30:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeShow Imag
- Page 31 and 32:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeSetupThe
- Page 33 and 34:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeBusMiscel
- Page 35 and 36:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeBrightfie
- Page 37 and 38:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeChip Imag
- Page 39 and 40:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModePerform t
- Page 41 and 42:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeNoise Fil
- Page 43 and 44:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program Mode• There
- Page 45 and 46:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeViewing,
- Page 47 and 48:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program Mode2. Positi
- Page 49 and 50:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeCropCut o
- Page 51 and 52:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program Mode−−−
- Page 53 and 54:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeCreating
- Page 55 and 56:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeDefining
- Page 57 and 58:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeDefining
- Page 59 and 60:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModeThe Edit
- Page 61 and 62:
Ch. 3 - Basic Program ModePrinting
- Page 63 and 64:
Ch. 4 - The Advanced Program ModeTh
- Page 65 and 66:
Ch. 4 - The Advanced Program ModeRe
- Page 67 and 68:
Ch. 4 - The Advanced Program ModeOp
- Page 69 and 70:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModeSetupT
- Page 71 and 72:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModePeriph
- Page 73 and 74:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModeNaming
- Page 75 and 76:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModePush t
- Page 77 and 78:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModeNote:
- Page 79 and 80:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModeIn a T
- Page 81 and 82:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModeFile N
- Page 83 and 84:
Ch. 4 - Advanced Program ModeToolba
- Page 85 and 86:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 87 and 88:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 89 and 90:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 91 and 92:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 93 and 94:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 95 and 96:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 97 and 98:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 99 and 100:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 101 and 102:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 103 and 104:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 105 and 106:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 107 and 108:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 109 and 110:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 111 and 112:
Ch. 6 - Using Live ImagesCh. 6 - Us
- Page 113 and 114:
Ch. 6 - Using Live ImagesThe Live I
- Page 115 and 116:
Ch. 6 - Using Live Images• Red -
- Page 117 and 118:
Ch. 6 - Using Live ImagesLive Image
- Page 119 and 120:
Ch. 7 - Taking a PictureCh. 7 - Tak
- Page 121 and 122:
Ch. 7 - Taking a PictureGet Image (
- Page 123 and 124:
Ch. 7 - Taking a Picture1. Select t
- Page 125 and 126:
Ch. 7 - Taking a Picture(image sequ
- Page 127 and 128:
Ch. 7 - Taking a Picture6. Save the
- Page 129 and 130:
Ch. 7 - Taking a Picture3. The Get
- Page 131 and 132:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 133 and 134:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 135 and 136:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 137 and 138:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 139 and 140:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 141 and 142:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 143 and 144:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 145 and 146:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 147 and 148:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 149 and 150:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 151 and 152:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 153 and 154:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 155 and 156:
Ch. 5 - Preparing to Take a Picture
- Page 157 and 158:
Ch. 6 - Using Live ImagesCh. 6 - Us
- Page 159 and 160:
Ch. 6 - Using Live ImagesThe Live I
- Page 161 and 162:
Ch. 6 - Using Live Images• Red -
- Page 163 and 164:
Ch. 6 - Using Live ImagesLive Image
- Page 165 and 166:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesCh. 9 -
- Page 167 and 168:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesOpen th
- Page 169 and 170:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesSave an
- Page 171 and 172:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesLocatio
- Page 173 and 174:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesText/Nu
- Page 175 and 176:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT Databasesphysici
- Page 177 and 178:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT Databasesa) Open
- Page 179 and 180:
To do so, follow these steps:1. Sea
- Page 181 and 182:
5. Click on OK to save the search p
- Page 183 and 184:
Send Results to: Exported FileDispl
- Page 185 and 186:
User Guide to the SPOT Insight Came
- Page 187 and 188:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 189 and 190:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 191 and 192:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 193 and 194:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 195 and 196:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 197 and 198:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 199 and 200:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 201 and 202:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 203 and 204:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 205 and 206:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 207 and 208:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 209 and 210:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 211 and 212:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 213 and 214:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 215 and 216:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 217 and 218:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 219 and 220:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 221 and 222:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 223 and 224:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 225 and 226:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 227 and 228:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 229 and 230:
Ch. 8 - Viewing, Editing, and Annot
- Page 231 and 232:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesIntrodu
- Page 233 and 234:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesView Da
- Page 235 and 236:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT Databases3. Defi
- Page 237 and 238:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesImage F
- Page 239 and 240:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT Databases1. Ente
- Page 241 and 242:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesEditing
- Page 243 and 244:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT Databasesf) Clic
- Page 245 and 246:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesDefinin
- Page 247 and 248:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesSend Re
- Page 249 and 250:
Ch. 9 - Using SPOT DatabasesAccesse
- Page 251 and 252:
Ch. 10 - ReportingIntroductionThe S
- Page 253 and 254:
Ch. 10 - ReportingRun the SPOT Samp
- Page 255 and 256:
Ch. 10 - Reporting• To size objec
- Page 257 and 258:
Ch. 10 - ReportingShow ToolsClick o
- Page 259 and 260:
Ch. 10 - ReportingText Border, Just
- Page 261 and 262:
Ch. 10 - ReportingImagesStatic Imag
- Page 263 and 264:
Ch. 10 - ReportingImages(cont.)Sele
- Page 265 and 266:
Ch. 10 - ReportingText(cont.)Image
- Page 267 and 268:
Ch. 10 - ReportingThe Edit MenuThe
- Page 269 and 270:
Ch. 10 - Reporting3. Specify the Al
- Page 271 and 272:
Ch. 10 - ReportingInstant ReportsTo
- Page 273 and 274:
Ch. 11 - Printing ImagesCh. 11 - Pr
- Page 275 and 276:
Ch. 11 - Printing Images• From a
- Page 277 and 278:
Ch. 12 - TaskbarsCh. 12 - TaskbarsI
- Page 279 and 280:
Ch. 12 - TaskbarsAlmost simultaneou
- Page 281 and 282:
Ch. 12 - TaskbarsContinue to add bu
- Page 283 and 284:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingChapter 13
- Page 285 and 286:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingAccessing a
- Page 287 and 288:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingTopicComman
- Page 289 and 290:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingThe menu sc
- Page 291 and 292:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingYou will al
- Page 293 and 294:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingMacro Windo
- Page 295 and 296:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingEditThis co
- Page 297 and 298:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingNew Macro-s
- Page 299 and 300:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingName of the
- Page 301 and 302:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingGeneric Exa
- Page 303 and 304:
Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingWindow spec
- Page 305 and 306: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingBegin Macro
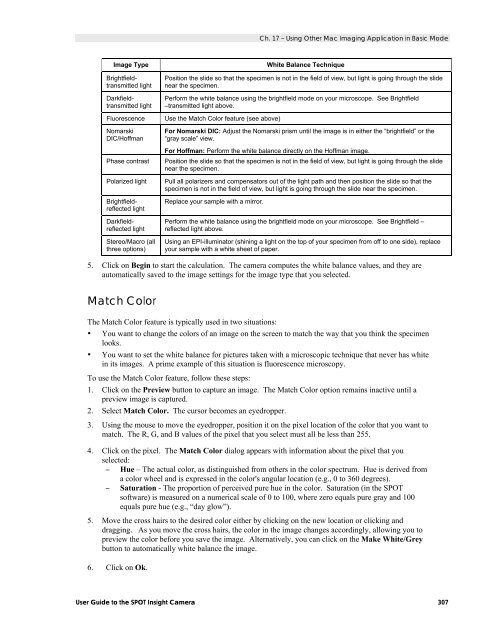
- Page 307 and 308: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingIn the gene
- Page 309 and 310: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingGeneric Exa
- Page 311 and 312: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingThe date fo
- Page 313 and 314: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingWindow spec
- Page 315 and 316: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingTable B. Pr
- Page 317 and 318: Ch. 13 - Macro ScriptingWhen this c
- Page 319 and 320: Preparing to Take a PictureCh. 14 -
- Page 321 and 322: Ch. 14 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 323 and 324: Ch. 14 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 325 and 326: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 327 and 328: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 329 and 330: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 331 and 332: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 333 and 334: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 335 and 336: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 337 and 338: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 339 and 340: Ch. 15 - Using Other Windows Imagin
- Page 341 and 342: Ch. 16 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 343 and 344: Ch. 16 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 345 and 346: Ch. 16 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 347 and 348: Ch. 16 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 349 and 350: Ch. 17 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 351 and 352: Ch. 17 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 353 and 354: Ch. 17 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 355: Ch. 17 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 359 and 360: Ch. 17 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 361 and 362: Ch. 17 - Using Other Mac Imaging Ap
- Page 363 and 364: Appendix AColor ImagesBecause a CCD
- Page 365 and 366: Appendix AAn 80 second exposure at
- Page 367 and 368: Appendix BCamera DimensionsPower Su
- Page 369 and 370: Appendix CAppendix C: Keyboard and
- Page 371 and 372: Appendix DAppendix D: Converting Pr