- Page 1 and 2:
COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN, ENGINEERING,
- Page 3 and 4:
Library of Congress Cataloging-in-P
- Page 5 and 6:
Editor Cornelius T. Leondes, B.S.,
- Page 7 and 8:
Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapt
- Page 9 and 10:
the implementation of the IPD syste
- Page 11 and 12:
In our IPD system implementations,
- Page 13 and 14:
2. Specification of analysis-specif
- Page 15 and 16:
FIGURE 1.2 base or the design insta
- Page 17 and 18:
FIGURE 1.4 System architecture of t
- Page 19 and 20:
of a beam is considered for FEA. Th
- Page 21 and 22:
FIGURE 1.7 through the control expe
- Page 23 and 24:
2. machining facility (e.g., gang m
- Page 25 and 26:
from the FBDS. The user also specif
- Page 27 and 28:
Depending on the type of feature to
- Page 29 and 30:
TABLE 1.6 Tolerance synthesis is de
- Page 31 and 32:
FIGURE 1.12 Display of the NC tool
- Page 33 and 34:
component geometric entities and va
- Page 35 and 36:
FIGURE 1.14 The system architecture
- Page 37 and 38:
TABLE 1.10 User Input for the Toler
- Page 39 and 40:
TABLE 1.11 Tolerance Specifications
- Page 41 and 42:
7. Z. Young and I. R. Groose. A rul
- Page 43 and 44:
FIGURE 2.1 Tool paths generated for
- Page 45 and 46:
FIGURE 2.2 sented by instances of f
- Page 47 and 48:
TABLE 2.1 A CAD-Generated Hole Conf
- Page 49 and 50:
FIGURE 2.6 mounted on the rotary ta
- Page 51 and 52:
FIGURE 2.8 fixture for the machinin
- Page 53 and 54:
FIGURE 2.10 or best-fit, or the cur
- Page 55 and 56:
FIGURE 2.11 Linear approximation of
- Page 57 and 58:
FIGURE 2.13 Circular approximation
- Page 59 and 60:
FIGURE 2.14(b) Circular approximati
- Page 61 and 62:
FIGURE 2.16 Types of biarcs. FIGURE
- Page 63 and 64:
FIGURE 2.18 Approximation of scanne
- Page 65 and 66:
FIGURE 2.20 A touch trigger probe c
- Page 67 and 68:
TABLE 2.4 Substitute Elements in CM
- Page 69 and 70:
FIGURE 2.21 CMM planning requiremen
- Page 71 and 72: Product Model Representation for Co
- Page 73 and 74: © 2001 by CRC Press LLC TABLE 2.5
- Page 75 and 76: TABLE 2.7 Partial Listing of Dimens
- Page 77 and 78: 24. Makinouchi, S., Okamoto, M., an
- Page 79 and 80: Bijan Shirinzadeh Monash University
- Page 81 and 82: FIGURE 3.1 Trends in flexible manuf
- Page 83 and 84: FIGURE 3.3 and constrain different
- Page 85 and 86: Other Fixturing Techniques There ar
- Page 87 and 88: FIGURE 3.6 contact point. The geome
- Page 89 and 90: FIGURE 3.8 The vertical support fix
- Page 91 and 92: and moments about the contact point
- Page 93 and 94: een identified, the normals are use
- Page 95 and 96: one of choosing the variables: such
- Page 97 and 98: Fixture Module Location An importan
- Page 99 and 100: FIGURE 3.15 Illustration of functio
- Page 101 and 102: FIGURE 3.18 Minimum separation test
- Page 103 and 104: direction) the face, respectively.
- Page 105 and 106: FIGURE 3.21 Software structure for
- Page 107 and 108: 3.8 Conclusion A reconfigurable fix
- Page 109 and 110: Heui Jae Pahk Seoul National Univer
- Page 111 and 112: FIGURE 4.1(b) Conceptual framework
- Page 113 and 114: 4.3 Measurement Points Sampling and
- Page 115 and 116: Surface S2 Measurement Path FIGURE
- Page 117 and 118: FIGURE 4.4 Rough phase alignment ba
- Page 119 and 120: deviation between the nominal CAD d
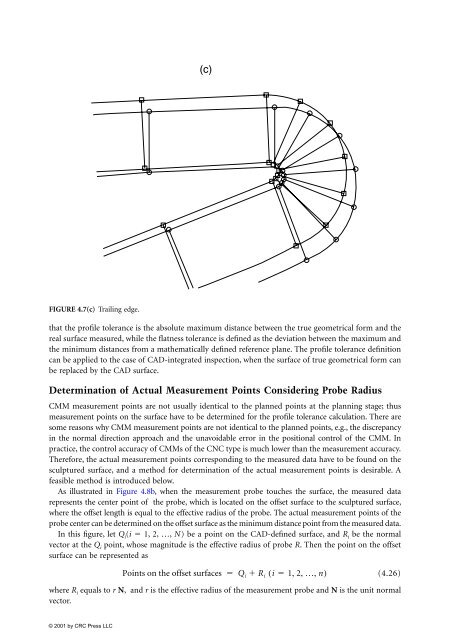
- Page 121: FIGURE 4.6(a) Sum of squares distan
- Page 125 and 126: FIGURE 4.8(a) Profile tolerance of
- Page 127 and 128: The calculated minimum form error i
- Page 129 and 130: FIGURE 4.11(a) A typical mold havin
- Page 131 and 132: FIGURE 4.11(d) Inspection results f
- Page 133 and 134: FIGURE 4.12(c) Maximum deviation (p
- Page 135 and 136: 5.1 Introduction Developments in th
- Page 137 and 138: process plan for a part (Figure 5.3
- Page 139 and 140: FIGURE 5.5 leading to the developme
- Page 141 and 142: the previously stored process plan
- Page 143 and 144: FIGURE 5.7 Techniques of defining a
- Page 145 and 146: Feature Recognition and Extraction
- Page 147 and 148: in relation to another feature (e.g
- Page 149 and 150: FIGURE 5.9 Framework for building a
- Page 151 and 152: FIGURE 5.10 Process plan content.
- Page 153 and 154: FIGURE 5.12 Schematic sketch of the
- Page 155 and 156: Several techniques of defining a fe
- Page 157 and 158: TABLE 5.1 Data Structure for Repres
- Page 159 and 160: FIGURE 5.16 Classification of the t
- Page 161 and 162: system to ensure that the part bein
- Page 163 and 164: FIGURE 5.19 Graphical model of the
- Page 165 and 166: TABLE 5.4 Data Structure for Repres
- Page 167 and 168: FIGURE 5.20 Mapping between machini
- Page 169 and 170: algorithms. (Some details of the pr
- Page 171 and 172: FIGURE 5.24 An example rotational p
- Page 173 and 174:
FIGURE 5.26 Down_face-turn-up_face
- Page 175 and 176:
FIGURE 5.27 Procedure for machine t
- Page 177 and 178:
FIGURE 5.28 Determining the number
- Page 179 and 180:
DL is needed to be set only if the
- Page 181 and 182:
FIGURE 5.31 Operation sequencing co
- Page 183 and 184:
Cutting Tool Selection Selection of
- Page 185 and 186:
1. A tool is searched for in the da
- Page 187 and 188:
FIGURE 5.32 Inputs to optimization
- Page 189 and 190:
When these values are substituted,
- Page 191 and 192:
Usually, maximum and minimum speed
- Page 193 and 194:
FIGURE 5.33 Solution methodology.
- Page 195 and 196:
TABLE 5.6 Process Plan Internal Rep
- Page 197 and 198:
In a strict theoretical perspective
- Page 199 and 200:
18. Domazet, D. S. and Lu, S. C. Y,
- Page 201 and 202:
63. Prasad, A. V. S. R. K., Rao, P.
- Page 203 and 204:
CAD systems. The sample consists of
- Page 205 and 206:
learn to master the new system. An
- Page 207 and 208:
Although researchers appear to agre
- Page 209 and 210:
Link and Zmud28 found that organic
- Page 211 and 212:
Informal Training Informal CAD trai
- Page 213 and 214:
informal training programs, felt th
- Page 215 and 216:
6. C. A. Beatty, Tall Tales and Rea
- Page 217 and 218:
A.Y.C. Nee National University of S
- Page 219 and 220:
FIGURE 7.1 Planning, design, and ma
- Page 221 and 222:
A metal stamping can have the follo
- Page 223 and 224:
FIGURE 7.3 Strips used to notch out
- Page 225 and 226:
A Skeletal Approach for the Recogni
- Page 227 and 228:
These findings can be used to devel
- Page 229 and 230:
Semi-Direct Piloting In cases where
- Page 231 and 232:
a larger value, the die operations
- Page 233 and 234:
FIGURE 7.9 Symbolic relationship be
- Page 235 and 236:
FIGURE 7.11 The shape of the envelo
- Page 237 and 238:
TABLE 7.1 Schema for the Generation
- Page 239 and 240:
strong reasons to support a move to
- Page 241 and 242:
FIGURE 7.16 3-D CAD model of a part
- Page 243 and 244:
References Cheok, B.T. et al. (1994
- Page 245 and 246:
include the once forbidden generati
- Page 247 and 248:
A temporal matrix (T-Matrix) is pro
- Page 249 and 250:
FIGURE 8.1 A basic process. (From R
- Page 251 and 252:
FIGURE 8.4(a) Generate a new IG usi
- Page 253 and 254:
Note if the pair of nodes are both
- Page 255 and 256:
TABLE 8.1 Summary of the Rules Cond
- Page 257 and 258:
The correctness of these rules is e
- Page 259 and 260:
needs to show that after each full
- Page 261 and 262:
ule is violated, a warning should b
- Page 263 and 264:
Π1 Π3 Π4 FIGURE 8.8(a) After add
- Page 265 and 266:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
- Page 267 and 268:
A ik � ‘U’ and is in a cycle
- Page 269 and 270:
FIGURE 8.12(a) Add [p2 t7 p7 t8 p4]
- Page 271 and 272:
FIGURE 8.12(c) Add a token to p8 vi
- Page 273 and 274:
FIGURE 8.12(e) Add [p8 t9 p14 t10 p
- Page 275 and 276:
FIGURE 8.13 An example of rule TT.0
- Page 277 and 278:
FIGURE 8.14 A GPN model of a machin
- Page 279 and 280:
FIGURE 8.15(b) The first exclusive
- Page 281 and 282:
FIGURE 8.15(d) The last exclusive T
- Page 283 and 284:
FIGURE 8.15(f) After entering the a
- Page 285 and 286:
FIGURE 8.15(h) Completion of Compon
- Page 287 and 288:
FIGURE 8.15(j) Two PP-generations:
- Page 289 and 290:
FIGURE 8.15(l) The last exclusive T
- Page 291 and 292:
t1 t5 p1 p5 t6 (a) t2 t3 t4 2 2 p2
- Page 293 and 294:
FIGURE 8.17 An example of partial f
- Page 295 and 296:
Theorem 10: If pi → pk in a synth
- Page 297 and 298:
Note that control transitions are o
- Page 299 and 300:
t j than the lower at , it indicate
- Page 301 and 302:
• Programming logic and VLSI arra
- Page 303 and 304:
7. Chao, D. Y. and D. T. Wang, Appl
- Page 305 and 306:
53. Villaroel, J. L., J. Martinez,
- Page 307 and 308:
q u : the numerator of the least ra
- Page 309 and 310:
geometric modeling, engineering ana
- Page 311 and 312:
In dimension driven or parametric d
- Page 313 and 314:
FIGURE 9.3 configuration of bodies
- Page 315 and 316:
FIGURE 9.6 FIGURE 9.7 Geometric Int
- Page 317 and 318:
FIGURE 9.8 Intersection of degrees
- Page 319 and 320:
will introduce a way to propagate p
- Page 321 and 322:
Completeness of Dimensions Complete
- Page 323 and 324:
FIGURE 9.12 3-D constraints. © 200
- Page 325 and 326:
The distance constraint from pt �
- Page 327 and 328:
therefore: Now merge the lists and
- Page 329 and 330:
Quantity analysis methods have the
- Page 331 and 332:
y a revolute joint. By selecting al