Fourth Study Conference on BALTEX Scala Cinema Gudhjem
Fourth Study Conference on BALTEX Scala Cinema Gudhjem
Fourth Study Conference on BALTEX Scala Cinema Gudhjem
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
- 30 -<br />
Validati<strong>on</strong> of Boundary Layer Parameters and Extensi<strong>on</strong> of Boundary<br />
C<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s of the Climate Model REMO – Estimati<strong>on</strong> of Leaf Area Index<br />
from NOAA-AVHRR-Data<br />
Birgit Streckenbach und Eberhard Reimer<br />
Institute of Meteorology, Free University of Berlin, Carl-Heinrich-Becker-Weg 6-10, streckba@zedat.fu-berlin.de<br />
1. Introducti<strong>on</strong><br />
At this time the climate model REMO of the Max-Planck-<br />
Institute Hamburg works with fixed regi<strong>on</strong>al vegetati<strong>on</strong><br />
parameters for every m<strong>on</strong>th of the year. To obtain a better<br />
adaptati<strong>on</strong> to real c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s the estimati<strong>on</strong> of the annual<br />
changes in vegetati<strong>on</strong>, especially deciduous forests, which<br />
significantly influence the boundary layer processes and in<br />
particular the moisture budget, is necessary. The Leaf Area<br />
Index (LAI) is a characteristic indicator for the type of<br />
vegetati<strong>on</strong> and its activity.<br />
2. Data and Method<br />
At the Institute of Meteorology of the Free University Berlin<br />
NOAA-AVHRR data for the European regi<strong>on</strong> are available<br />
day by day since 1989. The data are corrected to eliminate<br />
typical errors referring to calibrati<strong>on</strong> and shift in observati<strong>on</strong><br />
time. They are also adjusted to geographic coordinates and<br />
to a land mask.<br />
On the basis of these data from 1995 until 2002 during the<br />
vegetati<strong>on</strong> period (April-September) the LAI in the Baltic<br />
regi<strong>on</strong> was predicted pixelwise from the Normalized<br />
Difference Vegetati<strong>on</strong> Index (NDVI) for 1km x 1km resoluti<strong>on</strong><br />
using an algorithm from Sellers et al. (1996).<br />
At first 10 day composites of the NDVI were created to<br />
eliminate the disturbing influence of cloudiness. Missing or<br />
incorrect pixels were completed in time by harm<strong>on</strong>ic<br />
analysis and regi<strong>on</strong>ally by pixel neighbourhood rec<strong>on</strong>structi<strong>on</strong>.<br />
From these NDVI values the Fracti<strong>on</strong> of Absorbed<br />
Photosynthetic Active Radiati<strong>on</strong> (FAPAR) was predicted<br />
and then the LAI was determined using a modified USGS<br />
land cover classificati<strong>on</strong>. Finally the 1km x 1km, 10 day<br />
averaged LAI data were c<strong>on</strong>verted into the 1/6 degree<br />
resoluti<strong>on</strong> of the REMO climate model.<br />
3. Results<br />
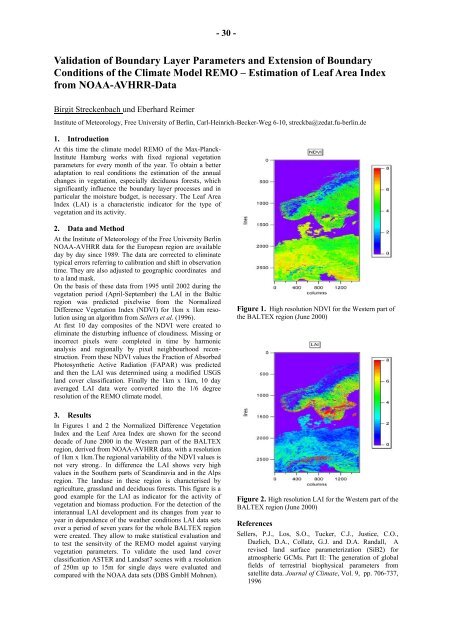
In Figures 1 and 2 the Normalized Difference Vegetati<strong>on</strong><br />
Index and the Leaf Area Index are shown for the sec<strong>on</strong>d<br />
decade of June 2000 in the Western part of the <strong>BALTEX</strong><br />
regi<strong>on</strong>, derived from NOAA-AVHRR data. with a resoluti<strong>on</strong><br />
of 1km x 1km.The regi<strong>on</strong>al variability of the NDVI values is<br />
not very str<strong>on</strong>g.. In difference the LAI shows very high<br />
values in the Southern parts of Scandinavia and in the Alps<br />
regi<strong>on</strong>. The landuse in these regi<strong>on</strong> is characterised by<br />
agriculture, grassland and deciduous forests. This figure is a<br />
good example for the LAI as indicator for the activity of<br />
vegetati<strong>on</strong> and biomass producti<strong>on</strong>. For the detecti<strong>on</strong> of the<br />
interannual LAI development and its changes from year to<br />
year in dependence of the weather c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s LAI data sets<br />
over a period of seven years for the whole <strong>BALTEX</strong> regi<strong>on</strong><br />
were created. They allow to make statistical evaluati<strong>on</strong> and<br />
to test the sensitvity of the REMO model against varying<br />
vegetati<strong>on</strong> parameters. To validate the used land cover<br />
classificati<strong>on</strong> ASTER and Landsat7 scenes with a resoluti<strong>on</strong><br />
of 250m up to 15m for single days were evaluated and<br />
compared with the NOAA data sets (DBS GmbH Mohnen).<br />
Figure 1. High resoluti<strong>on</strong> NDVI for the Western part of<br />
the <strong>BALTEX</strong> regi<strong>on</strong> (June 2000)<br />
Figure 2. High resoluti<strong>on</strong> LAI for the Western part of the<br />
<strong>BALTEX</strong> regi<strong>on</strong> (June 2000)<br />
References<br />
Sellers, P.J., Los, S.O., Tucker, C.J., Justice, C.O.,<br />
Dazlich, D.A., Collatz, G.J. and D.A. Randall, A<br />
revised land surface parameterizati<strong>on</strong> (SiB2) for<br />
atmospheric GCMs. Part II: The generati<strong>on</strong> of global<br />
fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters from<br />
satellite data. Journal of Climate, Vol. 9, pp. 706-737,<br />
1996