- Page 1: INTERNATIONAL ENERGY AGENCY RENEWAB
- Page 4 and 5: INTERNATIONAL ENERGY AGENCY 9, rue
- Page 7: ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This publication d
- Page 10 and 11: 8 Prospects for Wind Power 158 Issu
- Page 12 and 13: 10 4. Turbine Efficiency Over Time
- Page 15 and 16: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Renewables are th
- Page 17 and 18: Technology and Technological Develo
- Page 19 and 20: Table 1 Focal Points for Policy Int
- Page 21 and 22: Table 2 Ranges of Investment and Ge
- Page 23 and 24: Table 3 Current and Forecast Instal
- Page 25 and 26: generation. Better power quality re
- Page 27: per kWh from plants with proven con
- Page 30 and 31: 28 Renewables for Power Generation
- Page 32 and 33: 30 ● basic features: characterist
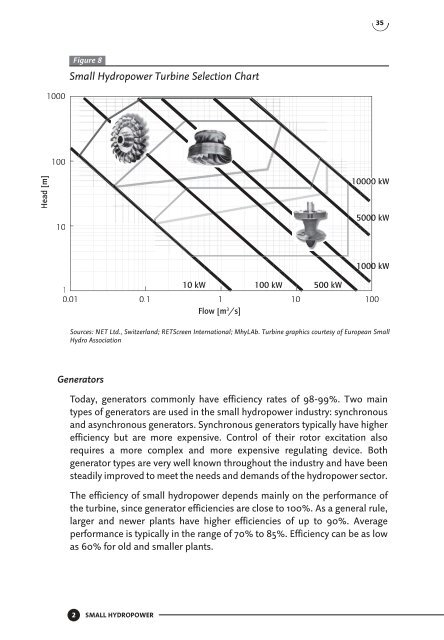
- Page 34 and 35: 32 The natural factors which affect
- Page 38 and 39: 36 ● Costs Investment costs for S
- Page 40 and 41: Installation costs [€/kW] 10000 8
- Page 42 and 43: Electricity generation cost in USD
- Page 44 and 45: ● Market Installed capacity [MW]
- Page 46 and 47: 44 Nevertheless, hydropower project
- Page 48 and 49: Worldwide hydro production [TWh/yr]
- Page 50 and 51: 48 Table 5 Key Factors for SHP Pote
- Page 52 and 53: 50 Materials Low-cost materials lik
- Page 55 and 56: SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER A Brief Hi
- Page 57 and 58: to the alternating current (AC) req
- Page 59 and 60: from USD 10 to 18 per W. Off-grid s
- Page 61 and 62: companies like Sharp, Kyocera and S
- Page 63 and 64: sells customised module manufacturi
- Page 65 and 66: germane, and toxic metals like cadm
- Page 67 and 68: Efficiency [%] 20 15 10 5 0 R&D is
- Page 69 and 70: Generation costs in €/kWh 1.1 1 0
- Page 71 and 72: This is seen most often in Japan, a
- Page 73 and 74: System DC/AC unit costs (individual
- Page 75 and 76: issue as production levels increase
- Page 77: chemistry. Such developments - ulti
- Page 80 and 81: 78 delivered to the receiver. The r
- Page 82 and 83: 80 ● Thermal Storage Like hybridi
- Page 84 and 85: Electricity generation cost USD cen
- Page 86 and 87:
84 An example of a CSP industry is
- Page 88 and 89:
86 If CSP plants are hybridised wit
- Page 90 and 91:
88 reduces the capital cost by 12-1
- Page 92 and 93:
90 innovations have influenced all
- Page 94 and 95:
92 receiver technology is entering
- Page 96 and 97:
94 energy storage) and higher solar
- Page 98 and 99:
96 but solar-field maintenance cost
- Page 100 and 101:
98 Further cost reductions will be
- Page 102 and 103:
100 Global Renewable Energy Resourc
- Page 105 and 106:
BIOPOWER A Brief History of Biopowe
- Page 107 and 108:
transport, emissions, etc.) of fast
- Page 109 and 110:
100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% Figure 38 T
- Page 111 and 112:
● Swedish forestry harvesting sys
- Page 113 and 114:
Gross electricty generation in GWh
- Page 115 and 116:
Specific investement costs in € p
- Page 117 and 118:
Table 30 Generation Costs for 2-MW
- Page 119 and 120:
€/MWh 16 12 8 4 0 for reductions
- Page 121 and 122:
coal at the inlet to the mill, b) f
- Page 123 and 124:
Table 33 Cost Reduction Opportuniti
- Page 125 and 126:
GEOTHERMAL POWER A Brief History of
- Page 127 and 128:
eached relatively shallow depths (5
- Page 129 and 130:
Capital cost in 1993 USD per kW 300
- Page 131 and 132:
An example of a large scale power p
- Page 133 and 134:
● Industry The international geot
- Page 135 and 136:
Cumulative global geothermal power
- Page 137 and 138:
Wastewater: Discharge of wastewater
- Page 139 and 140:
The following are areas where R&D c
- Page 141 and 142:
● Market Opportunities Market Pot
- Page 143 and 144:
the simplest form of local distribu
- Page 145 and 146:
Based on country update papers for
- Page 147:
Power Generation Technology Combine
- Page 150 and 151:
148 Commercial and technological de
- Page 152 and 153:
150 Table 45 Average Investment Cos
- Page 154 and 155:
152 Generation Costs Generating cap
- Page 156 and 157:
154 Table 47 Top Ten Suppliers, 200
- Page 158 and 159:
156 Table 49 Installed Capacity (in
- Page 160 and 161:
158 On the positive side, no direct
- Page 162 and 163:
DKK (1999)/kWh/Year Productivity 3
- Page 164 and 165:
Productivity in kWh per m 2 per yea
- Page 166 and 167:
164 before the intermittent nature
- Page 168 and 169:
166 The 2 to 3 MW power class will
- Page 170 and 171:
168 Grid Integration and Intermitte
- Page 172 and 173:
170 Internationally accepted requir
- Page 174 and 175:
172 EPRI: Electrical Power Research
- Page 177 and 178:
SOURCES AND FURTHER READING Chapter
- Page 179 and 180:
European Commission (1997), Energy
- Page 181 and 182:
Sellers, R. (1996), PV Diffusion Re
- Page 183 and 184:
Morse, F. H. (2000), The Commercial
- Page 185 and 186:
Veringa, H. (2001), Biomass Paper,
- Page 187 and 188:
CADDET (2001), Renewable Energy New
- Page 189 and 190:
WEBSITES Australian Greenhouse offi
- Page 191:
RETScreen International: http://www