fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
General configuration steps Dynamic DNS configuration<br />
Assumptions<br />
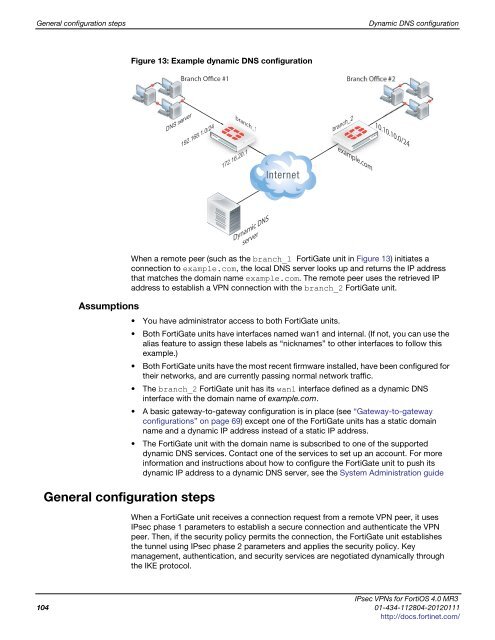
Figure 13: Example dynamic DNS configuration<br />
DNS server<br />
Branch Office #1<br />
192.168.1.0/24<br />
General configuration steps<br />
branch_1 anch_1<br />
172.16.20.1<br />
Dynamic DNS<br />
server<br />
branch_2<br />
Branch Office #2<br />
example.com<br />
10.10.10.0/24<br />
When a remote peer (such as the branch_1 FortiGate unit in Figure 13) initiates a<br />
connection to example.com, the local DNS server looks up and returns the IP address<br />
that matches the domain name example.com. The remote peer uses the retrieved IP<br />
address to establish a VPN connection with the branch_2 FortiGate unit.<br />
You have administrator access to both FortiGate units.<br />
Both FortiGate units have interfaces named wan1 and internal. (If not, you can use the<br />
alias feature to assign these labels as “nicknames” to other interfaces to follow this<br />
example.)<br />
Both FortiGate units have the most recent firmware installed, have been configured for<br />
their networks, and are currently passing normal network traffic.<br />
The branch_2 FortiGate unit has its wan1 interface defined as a dynamic DNS<br />
interface with the domain name of example.com.<br />
A basic gateway-to-gateway configuration is in place (see “Gateway-to-gateway<br />
configurations” on page 69) except one of the FortiGate units has a static domain<br />
name and a dynamic IP address instead of a static IP address.<br />
The FortiGate unit with the domain name is subscribed to one of the supported<br />
dynamic DNS services. Contact one of the services to set up an account. For more<br />
information and instructions about how to configure the FortiGate unit to push its<br />
dynamic IP address to a dynamic DNS server, see the System Administration guide<br />
When a FortiGate unit receives a connection request from a remote VPN peer, it uses<br />
IPsec phase 1 parameters to establish a secure connection and authenticate the VPN<br />
peer. Then, if the security policy permits the connection, the FortiGate unit establishes<br />
the tunnel using IPsec phase 2 parameters and applies the security policy. Key<br />
management, authentication, and security services are negotiated dynamically through<br />
the IKE protocol.<br />
IPsec VPNs for FortiOS 4.0 MR3<br />
104 01-434-112804-20120111<br />
http://docs.fortinet.com/