fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
FortiGate dialup-client configurations Configuration overview<br />
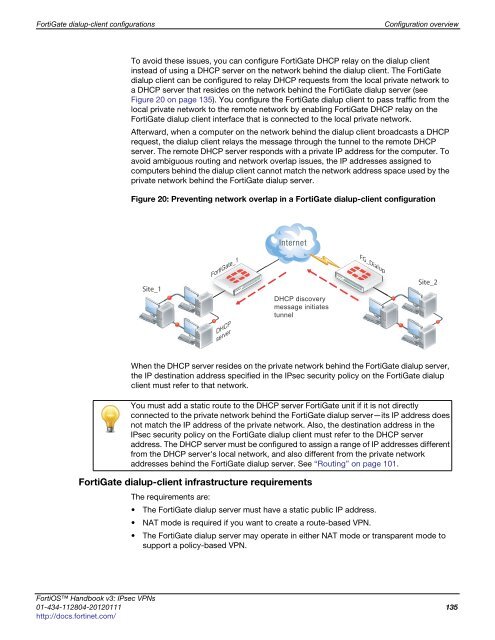
To avoid these issues, you can configure FortiGate DHCP relay on the dialup client<br />
instead of using a DHCP server on the network behind the dialup client. The FortiGate<br />
dialup client can be configured to relay DHCP requests from the local private network to<br />
a DHCP server that resides on the network behind the FortiGate dialup server (see<br />
Figure 20 on page 135). You configure the FortiGate dialup client to pass traffic from the<br />
local private network to the remote network by enabling FortiGate DHCP relay on the<br />
FortiGate dialup client interface that is connected to the local private network.<br />
Afterward, when a computer on the network behind the dialup client broadcasts a DHCP<br />
request, the dialup client relays the message through the tunnel to the remote DHCP<br />
server. The remote DHCP server responds with a private IP address for the computer. To<br />
avoid ambiguous routing and network overlap issues, the IP addresses assigned to<br />
computers behind the dialup client cannot match the network address space used by the<br />
private network behind the FortiGate dialup server.<br />
Figure 20: Preventing network overlap in a FortiGate dialup-client configuration<br />
Site_1<br />
FortiGate_1<br />
FortiGate_<br />
DHCP<br />
server<br />
DHCP discovery<br />
message initiates<br />
tunnel<br />
When the DHCP server resides on the private network behind the FortiGate dialup server,<br />
the IP destination address specified in the IPsec security policy on the FortiGate dialup<br />
client must refer to that network.<br />
FortiGate dialup-client infrastructure requirements<br />
FG_Dialup<br />
The requirements are:<br />
The FortiGate dialup server must have a static public IP address.<br />
NAT mode is required if you want to create a route-based VPN.<br />
The FortiGate dialup server may operate in either NAT mode or transparent mode to<br />
support a policy-based VPN.<br />
FortiOS Handbook v3: IPsec VPNs<br />
01-434-112804-20120111 135<br />
http://docs.fortinet.com/<br />
Site_2<br />
You must add a static route to the DHCP server FortiGate unit if it is not directly<br />
connected to the private network behind the FortiGate dialup server—its IP address does<br />
not match the IP address of the private network. Also, the destination address in the<br />
IPsec security policy on the FortiGate dialup client must refer to the DHCP server<br />
address. The DHCP server must be configured to assign a range of IP addresses different<br />
from the DHCP server's local network, and also different from the private network<br />
addresses behind the FortiGate dialup server. See “Routing” on page 101.