fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Defining IKE negotiation parameters Auto Key phase 1 parameters<br />
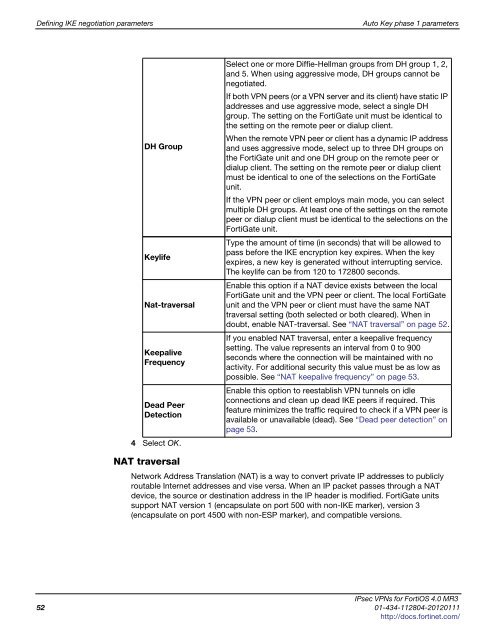
DH Group<br />
Keylife<br />
Nat-traversal<br />
Keepalive<br />
Frequency<br />
Dead Peer<br />
Detection<br />
4 Select OK.<br />
NAT traversal<br />
Select one or more Diffie-Hellman groups from DH group 1, 2,<br />
and 5. When using aggressive mode, DH groups cannot be<br />
negotiated.<br />
If both VPN peers (or a VPN server and its client) have static IP<br />
addresses and use aggressive mode, select a single DH<br />
group. The setting on the FortiGate unit must be identical to<br />
the setting on the remote peer or dialup client.<br />
When the remote VPN peer or client has a dynamic IP address<br />
and uses aggressive mode, select up to three DH groups on<br />
the FortiGate unit and one DH group on the remote peer or<br />
dialup client. The setting on the remote peer or dialup client<br />
must be identical to one of the selections on the FortiGate<br />
unit.<br />
If the VPN peer or client employs main mode, you can select<br />
multiple DH groups. At least one of the settings on the remote<br />
peer or dialup client must be identical to the selections on the<br />
FortiGate unit.<br />
Type the amount of time (in seconds) that will be allowed to<br />
pass before the IKE encryption key expires. When the key<br />
expires, a new key is generated without interrupting service.<br />
The keylife can be from 120 to 172800 seconds.<br />
Enable this option if a NAT device exists between the local<br />
FortiGate unit and the VPN peer or client. The local FortiGate<br />
unit and the VPN peer or client must have the same NAT<br />
traversal setting (both selected or both cleared). When in<br />
doubt, enable NAT-traversal. See “NAT traversal” on page 52.<br />
If you enabled NAT traversal, enter a keepalive frequency<br />
setting. The value represents an interval from 0 to 900<br />
seconds where the connection will be maintained with no<br />
activity. For additional security this value must be as low as<br />
possible. See “NAT keepalive frequency” on page 53.<br />
Enable this option to reestablish VPN tunnels on idle<br />
connections and clean up dead IKE peers if required. This<br />
feature minimizes the traffic required to check if a VPN peer is<br />
available or unavailable (dead). See “Dead peer detection” on<br />
page 53.<br />
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a way to convert private IP addresses to publicly<br />
routable Internet addresses and vise versa. When an IP packet passes through a NAT<br />
device, the source or destination address in the IP header is modified. FortiGate units<br />
support NAT version 1 (encapsulate on port 500 with non-IKE marker), version 3<br />
(encapsulate on port 4500 with non-ESP marker), and compatible versions.<br />
IPsec VPNs for FortiOS 4.0 MR3<br />
52 01-434-112804-20120111<br />
http://docs.fortinet.com/