fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Authenticating the FortiGate unit Auto Key phase 1 parameters<br />
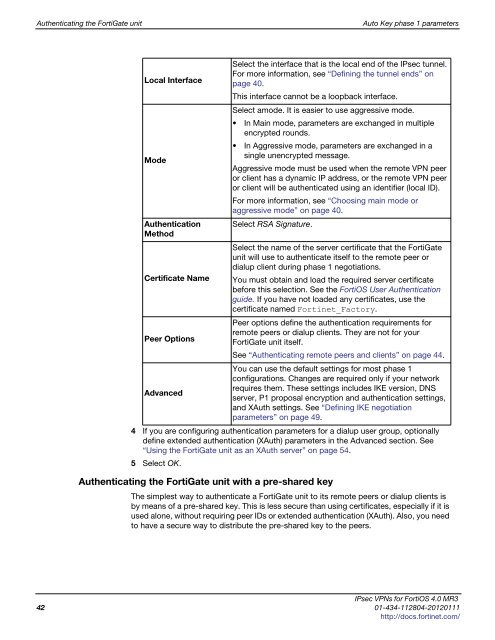
Local Interface<br />
Mode<br />
Authentication<br />
Method<br />
Certificate Name<br />
Peer Options<br />
Advanced<br />
4 If you are configuring authentication parameters for a dialup user group, optionally<br />
define extended authentication (XAuth) parameters in the Advanced section. See<br />
“Using the FortiGate unit as an XAuth server” on page 54.<br />
5 Select OK.<br />
Authenticating the FortiGate unit with a pre-shared key<br />
Select the interface that is the local end of the IPsec tunnel.<br />
For more information, see “Defining the tunnel ends” on<br />
page <strong>40</strong>.<br />
This interface cannot be a loopback interface.<br />
Select amode. It is easier to use aggressive mode.<br />
In Main mode, parameters are exchanged in multiple<br />
encrypted rounds.<br />
In Aggressive mode, parameters are exchanged in a<br />
single unencrypted message.<br />
Aggressive mode must be used when the remote VPN peer<br />
or client has a dynamic IP address, or the remote VPN peer<br />
or client will be authenticated using an identifier (local ID).<br />
For more information, see “Choosing main mode or<br />
aggressive mode” on page <strong>40</strong>.<br />
Select RSA Signature.<br />
Select the name of the server certificate that the FortiGate<br />
unit will use to authenticate itself to the remote peer or<br />
dialup client during phase 1 negotiations.<br />
You must obtain and load the required server certificate<br />
before this selection. See the FortiOS User Authentication<br />
guide. If you have not loaded any certificates, use the<br />
certificate named Fortinet_Factory.<br />
Peer options define the authentication requirements for<br />
remote peers or dialup clients. They are not for your<br />
FortiGate unit itself.<br />
See “Authenticating remote peers and clients” on page 44.<br />
You can use the default settings for most phase 1<br />
configurations. Changes are required only if your network<br />
requires them. These settings includes IKE version, DNS<br />
server, P1 proposal encryption and authentication settings,<br />
and XAuth settings. See “Defining IKE negotiation<br />
parameters” on page 49.<br />
The simplest way to authenticate a FortiGate unit to its remote peers or dialup clients is<br />
by means of a pre-shared key. This is less secure than using certificates, especially if it is<br />
used alone, without requiring peer IDs or extended authentication (XAuth). Also, you need<br />
to have a secure way to distribute the pre-shared key to the peers.<br />
IPsec VPNs for FortiOS 4.0 MR3<br />
42 01-434-112804-20120111<br />
http://docs.fortinet.com/