fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
IPsec VPN in the web-based manager<br />
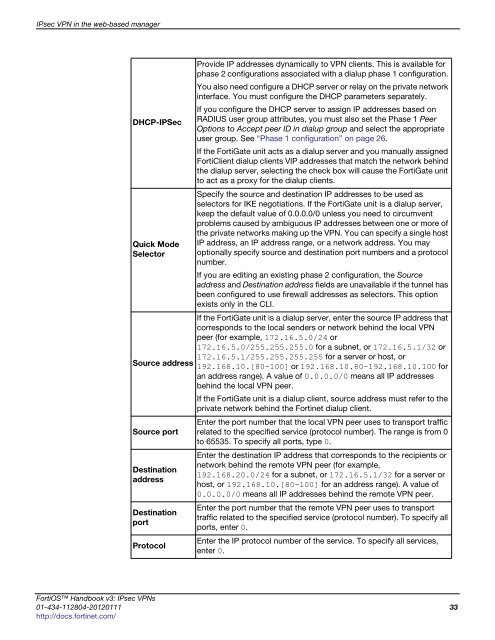
DHCP-IPSec<br />
Quick Mode<br />
Selector<br />
Source address<br />
Source port<br />
Destination<br />
address<br />
Destination<br />
port<br />
Protocol<br />
Provide IP addresses dynamically to VPN clients. This is available for<br />
phase 2 configurations associated with a dialup phase 1 configuration.<br />
You also need configure a DHCP server or relay on the private network<br />
interface. You must configure the DHCP parameters separately.<br />
If you configure the DHCP server to assign IP addresses based on<br />
RADIUS user group attributes, you must also set the Phase 1 Peer<br />
Options to Accept peer ID in dialup group and select the appropriate<br />
user group. See “Phase 1 configuration” on page 26.<br />
If the FortiGate unit acts as a dialup server and you manually assigned<br />
FortiClient dialup clients VIP addresses that match the network behind<br />
the dialup server, selecting the check box will cause the FortiGate unit<br />
to act as a proxy for the dialup clients.<br />
Specify the source and destination IP addresses to be used as<br />
selectors for IKE negotiations. If the FortiGate unit is a dialup server,<br />
keep the default value of 0.0.0.0/0 unless you need to circumvent<br />
problems caused by ambiguous IP addresses between one or more of<br />
the private networks making up the VPN. You can specify a single host<br />
IP address, an IP address range, or a network address. You may<br />
optionally specify source and destination port numbers and a protocol<br />
number.<br />
If you are editing an existing phase 2 configuration, the Source<br />
address and Destination address fields are unavailable if the tunnel has<br />
been configured to use firewall addresses as selectors. This option<br />
exists only in the CLI.<br />
If the FortiGate unit is a dialup server, enter the source IP address that<br />
corresponds to the local senders or network behind the local VPN<br />
peer (for example, 172.16.5.0/24 or<br />
172.16.5.0/255.255.255.0 for a subnet, or 172.16.5.1/32 or<br />
172.16.5.1/255.255.255.255 for a server or host, or<br />
192.168.10.[80-100] or 192.168.10.80-192.168.10.100 for<br />
an address range). A value of 0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses<br />
behind the local VPN peer.<br />
If the FortiGate unit is a dialup client, source address must refer to the<br />
private network behind the Fortinet dialup client.<br />
Enter the port number that the local VPN peer uses to transport traffic<br />
related to the specified service (protocol number). The range is from 0<br />
to 65535. To specify all ports, type 0.<br />
Enter the destination IP address that corresponds to the recipients or<br />
network behind the remote VPN peer (for example,<br />
192.168.20.0/24 for a subnet, or 172.16.5.1/32 for a server or<br />
host, or 192.168.10.[80-100] for an address range). A value of<br />
0.0.0.0/0 means all IP addresses behind the remote VPN peer.<br />
Enter the port number that the remote VPN peer uses to transport<br />
traffic related to the specified service (protocol number). To specify all<br />
ports, enter 0.<br />
Enter the IP protocol number of the service. To specify all services,<br />
enter 0.<br />
FortiOS Handbook v3: IPsec VPNs<br />
01-434-112804-20120111 33<br />
http://docs.fortinet.com/