fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
fortigate-ipsec-40-mr3
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Concentrator<br />
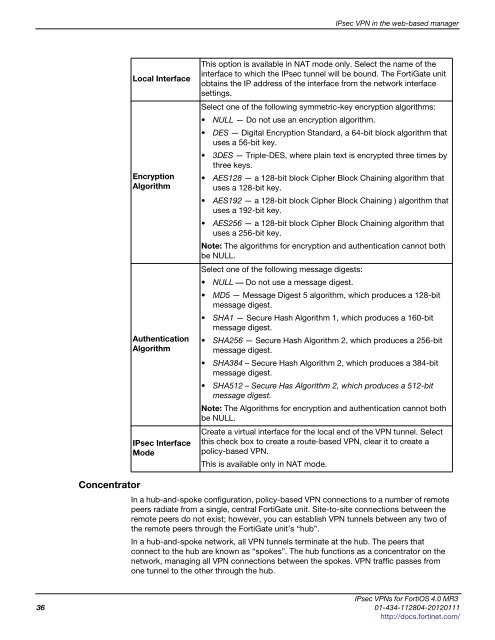
Local Interface<br />
Encryption<br />
Algorithm<br />
Authentication<br />
Algorithm<br />
IPsec Interface<br />
Mode<br />
IPsec VPN in the web-based manager<br />
This option is available in NAT mode only. Select the name of the<br />
interface to which the IPsec tunnel will be bound. The FortiGate unit<br />
obtains the IP address of the interface from the network interface<br />
settings.<br />
Select one of the following symmetric-key encryption algorithms:<br />
NULL — Do not use an encryption algorithm.<br />
DES — Digital Encryption Standard, a 64-bit block algorithm that<br />
uses a 56-bit key.<br />
3DES — Triple-DES, where plain text is encrypted three times by<br />
three keys.<br />
AES128 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining algorithm that<br />
uses a 128-bit key.<br />
AES192 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining ) algorithm that<br />
uses a 192-bit key.<br />
AES256 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining algorithm that<br />
uses a 256-bit key.<br />
Note: The algorithms for encryption and authentication cannot both<br />
be NULL.<br />
Select one of the following message digests:<br />
NULL –– Do not use a message digest.<br />
MD5 — Message Digest 5 algorithm, which produces a 128-bit<br />
message digest.<br />
SHA1 — Secure Hash Algorithm 1, which produces a 160-bit<br />
message digest.<br />
SHA256 — Secure Hash Algorithm 2, which produces a 256-bit<br />
message digest.<br />
SHA384 – Secure Hash Algorithm 2, which produces a 384-bit<br />
message digest.<br />
SHA512 – Secure Has Algorithm 2, which produces a 512-bit<br />
message digest.<br />
Note: The Algorithms for encryption and authentication cannot both<br />
be NULL.<br />
Create a virtual interface for the local end of the VPN tunnel. Select<br />
this check box to create a route-based VPN, clear it to create a<br />
policy-based VPN.<br />
This is available only in NAT mode.<br />
In a hub-and-spoke configuration, policy-based VPN connections to a number of remote<br />
peers radiate from a single, central FortiGate unit. Site-to-site connections between the<br />
remote peers do not exist; however, you can establish VPN tunnels between any two of<br />
the remote peers through the FortiGate unit’s “hub”.<br />
In a hub-and-spoke network, all VPN tunnels terminate at the hub. The peers that<br />
connect to the hub are known as “spokes”. The hub functions as a concentrator on the<br />
network, managing all VPN connections between the spokes. VPN traffic passes from<br />
one tunnel to the other through the hub.<br />
IPsec VPNs for FortiOS 4.0 MR3<br />
36 01-434-112804-20120111<br />
http://docs.fortinet.com/