Docetaxel with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of ...
Docetaxel with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of ...
Docetaxel with prednisone or prednisolone for the treatment of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
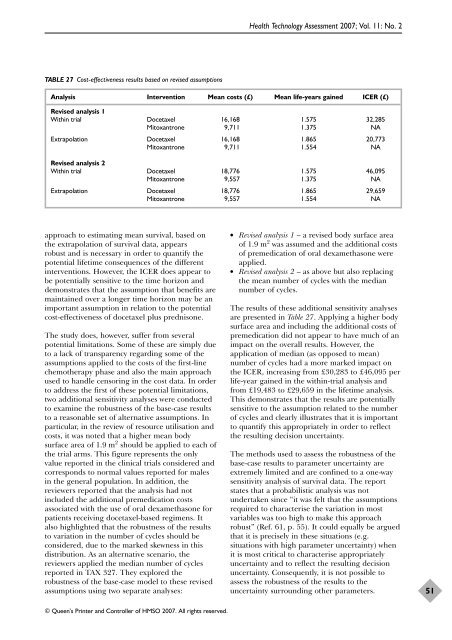
TABLE 27 Cost-effectiveness results based on revised assumptions<br />
approach to estimating mean survival, based on<br />
<strong>the</strong> extrapolation <strong>of</strong> survival data, appears<br />
robust and is necessary in <strong>or</strong>der to quantify <strong>the</strong><br />
potential lifetime consequences <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> different<br />
interventions. However, <strong>the</strong> ICER does appear to<br />
be potentially sensitive to <strong>the</strong> time h<strong>or</strong>izon and<br />
demonstrates that <strong>the</strong> assumption that benefits are<br />
maintained over a longer time h<strong>or</strong>izon may be an<br />
imp<strong>or</strong>tant assumption in relation to <strong>the</strong> potential<br />
cost-effectiveness <strong>of</strong> docetaxel plus <strong>prednisone</strong>.<br />
The study does, however, suffer from several<br />
potential limitations. Some <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se are simply due<br />
to a lack <strong>of</strong> transparency regarding some <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
assumptions applied to <strong>the</strong> costs <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> first-line<br />
chemo<strong>the</strong>rapy phase and also <strong>the</strong> main approach<br />
used to handle cens<strong>or</strong>ing in <strong>the</strong> cost data. In <strong>or</strong>der<br />
to address <strong>the</strong> first <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se potential limitations,<br />
two additional sensitivity analyses were conducted<br />
to examine <strong>the</strong> robustness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> base-case results<br />
to a reasonable set <strong>of</strong> alternative assumptions. In<br />
particular, in <strong>the</strong> review <strong>of</strong> resource utilisation and<br />
costs, it was noted that a higher mean body<br />
surface area <strong>of</strong> 1.9 m 2 should be applied to each <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> trial arms. This figure represents <strong>the</strong> only<br />
value rep<strong>or</strong>ted in <strong>the</strong> clinical trials considered and<br />
c<strong>or</strong>responds to n<strong>or</strong>mal values rep<strong>or</strong>ted f<strong>or</strong> males<br />
in <strong>the</strong> general population. In addition, <strong>the</strong><br />
reviewers rep<strong>or</strong>ted that <strong>the</strong> analysis had not<br />
included <strong>the</strong> additional premedication costs<br />
associated <strong>with</strong> <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> <strong>or</strong>al dexamethasone f<strong>or</strong><br />
patients receiving docetaxel-based regimens. It<br />
also highlighted that <strong>the</strong> robustness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> results<br />
to variation in <strong>the</strong> number <strong>of</strong> cycles should be<br />
considered, due to <strong>the</strong> marked skewness in this<br />
distribution. As an alternative scenario, <strong>the</strong><br />
reviewers applied <strong>the</strong> median number <strong>of</strong> cycles<br />
rep<strong>or</strong>ted in TAX 327. They expl<strong>or</strong>ed <strong>the</strong><br />
robustness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> base-case model to <strong>the</strong>se revised<br />
assumptions using two separate analyses:<br />
Health Technology Assessment 2007; Vol. 11: No. 2<br />
Analysis Intervention Mean costs (£) Mean life-years gained ICER (£)<br />
Revised analysis 1<br />
Within trial <strong>Docetaxel</strong> 16,168 1.575 32,285<br />
Mitoxantrone 9,711 1.375 NA<br />
Extrapolation <strong>Docetaxel</strong> 16,168 1.865 20,773<br />
Mitoxantrone 9,711 1.554 NA<br />
Revised analysis 2<br />
Within trial <strong>Docetaxel</strong> 18,776 1.575 46,095<br />
Mitoxantrone 9,557 1.375 NA<br />
Extrapolation <strong>Docetaxel</strong> 18,776 1.865 29,659<br />
Mitoxantrone 9,557 1.554 NA<br />
© Queen’s Printer and Controller <strong>of</strong> HMSO 2007. All rights reserved.<br />
● Revised analysis 1 – a revised body surface area<br />
<strong>of</strong> 1.9 m 2 was assumed and <strong>the</strong> additional costs<br />
<strong>of</strong> premedication <strong>of</strong> <strong>or</strong>al dexamethasone were<br />
applied.<br />
● Revised analysis 2 – as above but also replacing<br />
<strong>the</strong> mean number <strong>of</strong> cycles <strong>with</strong> <strong>the</strong> median<br />
number <strong>of</strong> cycles.<br />
The results <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se additional sensitivity analyses<br />
are presented in Table 27. Applying a higher body<br />
surface area and including <strong>the</strong> additional costs <strong>of</strong><br />
premedication did not appear to have much <strong>of</strong> an<br />
impact on <strong>the</strong> overall results. However, <strong>the</strong><br />
application <strong>of</strong> median (as opposed to mean)<br />
number <strong>of</strong> cycles had a m<strong>or</strong>e marked impact on<br />
<strong>the</strong> ICER, increasing from £30,283 to £46,095 per<br />
life-year gained in <strong>the</strong> <strong>with</strong>in-trial analysis and<br />
from £19,483 to £29,659 in <strong>the</strong> lifetime analysis.<br />
This demonstrates that <strong>the</strong> results are potentially<br />
sensitive to <strong>the</strong> assumption related to <strong>the</strong> number<br />
<strong>of</strong> cycles and clearly illustrates that it is imp<strong>or</strong>tant<br />
to quantify this appropriately in <strong>or</strong>der to reflect<br />
<strong>the</strong> resulting decision uncertainty.<br />
The methods used to assess <strong>the</strong> robustness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
base-case results to parameter uncertainty are<br />
extremely limited and are confined to a one-way<br />
sensitivity analysis <strong>of</strong> survival data. The rep<strong>or</strong>t<br />
states that a probabilistic analysis was not<br />
undertaken since “it was felt that <strong>the</strong> assumptions<br />
required to characterise <strong>the</strong> variation in most<br />
variables was too high to make this approach<br />
robust” (Ref. 61, p. 55). It could equally be argued<br />
that it is precisely in <strong>the</strong>se situations (e.g.<br />
situations <strong>with</strong> high parameter uncertainty) when<br />
it is most critical to characterise appropriately<br />
uncertainty and to reflect <strong>the</strong> resulting decision<br />
uncertainty. Consequently, it is not possible to<br />
assess <strong>the</strong> robustness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> results to <strong>the</strong><br />
uncertainty surrounding o<strong>the</strong>r parameters.<br />
51