- Page 1: Law Commission Scottish Law Commiss
- Page 4 and 5: CODE OF PRACTICE ON CONSULTATION Th
- Page 6 and 7: The default powers of the Privy Cou
- Page 8 and 9: Review hearings 187 Should regulato
- Page 10 and 11: FOREWORD BY THE CHAIRMEN OF THE LAW
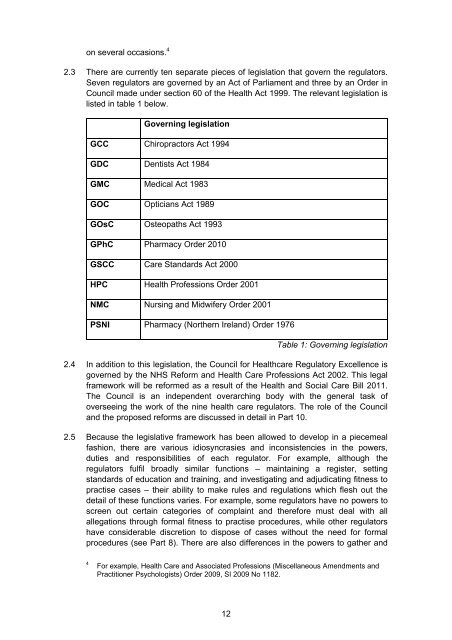
- Page 12 and 13: TABLE OF ABBREVIATIONS CHRE Council
- Page 14 and 15: approval imposes burdens on the Dep
- Page 16 and 17: 1.14 Second, recent times have witn
- Page 18 and 19: constrain the costs of the current
- Page 20 and 21: 1.26 The regulation of social care
- Page 22 and 23: 1.34 We will be undertaking a wide
- Page 26 and 27: workers), some are largely self-emp
- Page 28 and 29: (2) to guarantee minimum procedural
- Page 30 and 31: (8) the instrument is scrutinised b
- Page 32 and 33: subject to scrutiny by the Joint Co
- Page 34 and 35: PUBLIC CONSULTATION 2.37 Consultati
- Page 36 and 37: (1) that which is binding (such as
- Page 38 and 39: 2.54 The role of the Privy Council
- Page 40 and 41: Parliament”. 34 It is likely that
- Page 42 and 43: (1) a report on the exercise of its
- Page 44 and 45: earlier in this Part, Orders in Cou
- Page 46 and 47: 2.87 But the retention of section 6
- Page 48 and 49: safety and well-being of the public
- Page 50 and 51: Provisional Proposal 2-18: The Gove
- Page 52 and 53: 2.119 But we also consider it impor
- Page 54 and 55: PART 3 MAIN DUTY AND GENERAL FUNCTI
- Page 56 and 57: asset”. 10 The courts have also r
- Page 58 and 59: practise is impaired. Thus, in maki
- Page 60 and 61: interests of its members. Under our
- Page 62 and 63: 3.36 In our view, the need for gene
- Page 64 and 65: PART 4 GOVERNANCE 4.1 All of the re
- Page 66 and 67: egulators would be placed directly
- Page 68 and 69: powers to investigate and intervene
- Page 70 and 71: 4.30 A regulator not included in ta
- Page 72 and 73: Education and training 4.39 Most co
- Page 74 and 75:
must be lay or that there should be
- Page 76 and 77:
4.57 The General Medical Council ha
- Page 78 and 79:
4.66 Moreover, it is not evident th
- Page 80 and 81:
PART 5 REGISTERS 5.1 A key statutor
- Page 82 and 83:
5.9 However, the significance of re
- Page 84 and 85:
5.18 In effect, statutory powers wo
- Page 86 and 87:
5.25 Finally, a small number of the
- Page 88 and 89:
Voluntary registers 5.33 Our provis
- Page 90 and 91:
Council may register a person (or g
- Page 92 and 93:
through negligence on the part of a
- Page 94 and 95:
5.61 We propose that the statute sh
- Page 96 and 97:
communicated, which have no formal
- Page 98 and 99:
the statute should impose the same
- Page 100 and 101:
5.90 In some cases, the right to ap
- Page 102 and 103:
not complied with continuing profes
- Page 104 and 105:
could be made to provide better inf
- Page 106 and 107:
and provide links to information ab
- Page 108 and 109:
which practitioners have undertaken
- Page 110 and 111:
the Government in its guidance to d
- Page 112 and 113:
eing met by the local education pro
- Page 114 and 115:
6.13 Second, our legal framework wo
- Page 116 and 117:
Medical Council must satisfy the re
- Page 118 and 119:
6.31 The Health Professions Council
- Page 120 and 121:
(1) which qualifications are approv
- Page 122 and 123:
6.48 Finally, there are a number of
- Page 124 and 125:
Good Medical Practice which covers
- Page 126 and 127:
and other optical appliances, such
- Page 128 and 129:
6.72 We also believe that the new l
- Page 130 and 131:
looked at in detail only when conce
- Page 132 and 133:
professionals to remain registered
- Page 134 and 135:
Misconduct 7.6 Most of the governin
- Page 136 and 137:
(1) an order under section 246(2) o
- Page 138 and 139:
THE FITNESS TO PRACTISE FINDINGS 7.
- Page 140 and 141:
Option 2: consolidation of the exis
- Page 142 and 143:
(a) has in the past acted and/or is
- Page 144 and 145:
that many of the regulators have de
- Page 146 and 147:
PART 8 FITNESS TO PRACTISE: INVESTI
- Page 148 and 149:
language is not English. 7 However,
- Page 150 and 151:
of working around their legislative
- Page 152 and 153:
8.22 Some of the regulators, such a
- Page 154 and 155:
undertake this task, for example, i
- Page 156 and 157:
Assessments 8.37 Most regulators ha
- Page 158 and 159:
(1) an Investigation Committee whic
- Page 160 and 161:
THRESHOLD TEST 8.52 Having undertak
- Page 162 and 163:
egulators accept undertakings given
- Page 164 and 165:
hearings or other safeguards, espec
- Page 166 and 167:
epeated. Second, following an inves
- Page 168 and 169:
Provisional view 8.84 The current p
- Page 170 and 171:
PART 9 FITNESS TO PRACTISE: ADJUDIC
- Page 172 and 173:
of the individual circumstances of
- Page 174 and 175:
practise process to be considered i
- Page 176 and 177:
to set up and the new arrangements
- Page 178 and 179:
oversee their Panel appointment pro
- Page 180 and 181:
the regulators to ensure that Panel
- Page 182 and 183:
9.50 For most regulators the fitnes
- Page 184 and 185:
enable the regulators to deliver ma
- Page 186 and 187:
(3) a private hearing is necessary
- Page 188 and 189:
Question 9-16: Should the statute p
- Page 190 and 191:
and final sanction”. 63 We theref
- Page 192 and 193:
Question 9-22: Should the statute g
- Page 194 and 195:
found to be unfit to practise. 73 W
- Page 196 and 197:
accountable, consistent, transparen
- Page 198 and 199:
above. The Council for Healthcare R
- Page 200 and 201:
Provisional Proposal 9-32: The stat
- Page 202 and 203:
that the sanction is clearly inappr
- Page 204 and 205:
away from self-regulation in health
- Page 206 and 207:
may appoint employees and has a wid
- Page 208 and 209:
Provisional Proposal 10-3: Appointm
- Page 210 and 211:
general functions should be retaine
- Page 212 and 213:
the imposition of a relevant sancti
- Page 214 and 215:
independence of the new Medical Pra
- Page 216 and 217:
11.5 However, it may be that the co
- Page 218 and 219:
Act 1972. For example, the Medicine
- Page 220 and 221:
is fit to carry on such a business
- Page 222 and 223:
extend to all businesses or to all
- Page 224 and 225:
Council and Care Quality Commission
- Page 226 and 227:
in the 2011 White Paper Enabling Ex
- Page 228 and 229:
12.13 The Council for Healthcare Re
- Page 230 and 231:
12.23 We welcome views on the examp
- Page 232 and 233:
places a general duty to cooperate
- Page 234 and 235:
equired to give due consideration t
- Page 236 and 237:
professions are not subject to the
- Page 238 and 239:
attach to systemic failures to impl
- Page 240 and 241:
Order 1976. The definition of the U
- Page 242 and 243:
oute to UK registration. 30 The Gen
- Page 244 and 245:
13.39 The potential advantages of t
- Page 246 and 247:
(6) professional bodies that repres
- Page 248 and 249:
Provisional Proposal 4-2: The statu
- Page 250 and 251:
Provisional Proposal 5-15: The stat
- Page 252 and 253:
(5) the appointment of visitors and
- Page 254 and 255:
Provisional Proposal 8-13: The powe
- Page 256 and 257:
Provisional Proposal 9-13: The stat
- Page 258 and 259:
Provisional Proposal 10-3: Appointm
- Page 260 and 261:
PART 13: CROSS BORDER ISSUES Provis
- Page 262 and 263:
GENERAL SOCIAL CARE COUNCIL It shal
- Page 264 and 265:
(8) Standards Committee GENERAL OST
- Page 266 and 267:
(22) Licentiate in medicine and sur
- Page 268 and 269:
(68) Speech therapist NURSING AND M