Thesis - faculty.ait.ac.th - Asian Institute of Technology
Thesis - faculty.ait.ac.th - Asian Institute of Technology
Thesis - faculty.ait.ac.th - Asian Institute of Technology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Colloidal material as well as metal precipitation can cause fouling and clogging in<br />
<strong>th</strong>e membranes. Fouling leads to an increase in osmotic pressure and hydraulic resistance,<br />
<strong>th</strong>us increasing <strong>th</strong>e energy consumption. In order to minimize <strong>th</strong>e fouling effect, <strong>th</strong>e pH<br />
can be adjusted from 4 to 7.5.<br />
Since membranes cannot retain volatile fatty <strong>ac</strong>ids, <strong>ac</strong>idogenic le<strong>ac</strong>hate is poorly<br />
treated using membrane systems. A coupling <strong>of</strong> a membrane and <strong>ac</strong>tivated sludge process<br />
to form a membrane biore<strong>ac</strong>tor may be more viable as <strong>th</strong>e membrane ensures total solids<br />
retention. For moderate to strong me<strong>th</strong>anogenic le<strong>ac</strong>hate, a good removal <strong>of</strong> several<br />
substances, including metals can be <strong>ac</strong>hieved using biore<strong>ac</strong>tors. Hence, a combination <strong>of</strong><br />
an <strong>ac</strong>tivated sludge process wi<strong>th</strong> a membrane system, <strong>th</strong>e membrane biore<strong>ac</strong>tor technology<br />
can <strong>ac</strong>hieve high treatment efficiency wi<strong>th</strong> an excellent effluent quality.<br />
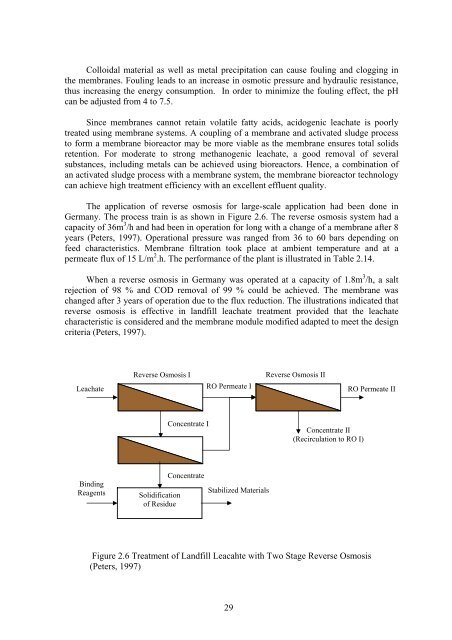
The application <strong>of</strong> reverse osmosis for large-scale application had been done in<br />
Germany. The process train is as shown in Figure 2.6. The reverse osmosis system had a<br />
cap<strong>ac</strong>ity <strong>of</strong> 36m 3 /h and had been in operation for long wi<strong>th</strong> a change <strong>of</strong> a membrane after 8<br />
years (Peters, 1997). Operational pressure was ranged from 36 to 60 bars depending on<br />
feed char<strong>ac</strong>teristics. Membrane filtration took pl<strong>ac</strong>e at ambient temperature and at a<br />
permeate flux <strong>of</strong> 15 L/m 2 .h. The performance <strong>of</strong> <strong>th</strong>e plant is illustrated in Table 2.14.<br />
When a reverse osmosis in Germany was operated at a cap<strong>ac</strong>ity <strong>of</strong> 1.8m 3 /h, a salt<br />
rejection <strong>of</strong> 98 % and COD removal <strong>of</strong> 99 % could be <strong>ac</strong>hieved. The membrane was<br />
changed after 3 years <strong>of</strong> operation due to <strong>th</strong>e flux reduction. The illustrations indicated <strong>th</strong>at<br />
reverse osmosis is effective in landfill le<strong>ac</strong>hate treatment provided <strong>th</strong>at <strong>th</strong>e le<strong>ac</strong>hate<br />
char<strong>ac</strong>teristic is considered and <strong>th</strong>e membrane module modified adapted to meet <strong>th</strong>e design<br />
criteria (Peters, 1997).<br />
Le<strong>ac</strong>hate<br />
Binding<br />
Reagents<br />
Reverse Osmosis I Reverse Osmosis II<br />
RO Permeate I<br />
Solidification<br />
<strong>of</strong> Residue<br />
Concentrate I<br />
Concentrate<br />
Stabilized Materials<br />
Figure 2.6 Treatment <strong>of</strong> Landfill Le<strong>ac</strong>ahte wi<strong>th</strong> Two Stage Reverse Osmosis<br />
(Peters, 1997)<br />
29<br />
Concentrate II<br />
(Recirculation to RO I)<br />
RO Permeate II