Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors - ideals ...
Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors - ideals ...
Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors - ideals ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
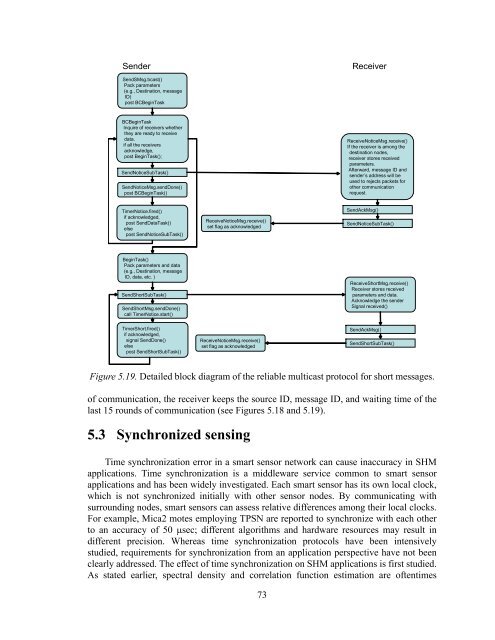
Sender<br />
Receiver<br />
SendSMsg.bcast()<br />
Pack parameters<br />
(e.g., Destination, message<br />
ID)<br />
post BCBeginTask<br />
BCBeginTask<br />
Inquire of receivers whether<br />
they are ready to receive<br />
data.<br />
if all the receivers<br />
acknowledge,<br />
post BeginTask();<br />
SendNoticeSubTask()<br />
SendNoticeMsg.sendDone()<br />
post BCBeginTask()<br />
ReceiveNoticeMsg.receive()<br />
If the receiver is among the<br />
destination nodes,<br />
receiver stores received<br />
parameters.<br />
Afterward, message ID and<br />
sender’s address will be<br />
used to rejects packets for<br />
other communication<br />
request.<br />
TimerNotice.fired()<br />
if acknowledged,<br />
post SendDataTask()<br />
else<br />
post SendNoticeSubTask()<br />
ReceiveNoticeMsg.receive()<br />
set flag as acknowledged<br />
SendAckMsg()<br />
SendNoticeSubTask()<br />
BeginTask()<br />
Pack parameters and data<br />
(e.g., Destination, message<br />
ID, data, etc. )<br />
SendShortSubTask()<br />
SendShortMsg.sendDone()<br />
call TimerNotice.start()<br />
ReceiveShortMsg.receive()<br />
Receiver stores received<br />
parameters and data.<br />
Acknowledge the sender<br />
Signal received()<br />
TimerShort.fired()<br />
if acknowledged,<br />
signal SendDone()<br />
else<br />
post SendShortSubTask()<br />
ReceiveNoticeMsg.receive()<br />
set flag as acknowledged<br />
SendAckMsg()<br />
SendShortSubTask()<br />
Figure 5.19. Detailed block diagram of the reliable multicast protocol for short messages.<br />
of communication, the receiver keeps the source ID, message ID, and waiting time of the<br />
last 15 rounds of communication (see Figures 5.18 and 5.19).<br />
5.3 Synchronized sensing<br />
Time synchronization error in a smart sensor network can cause inaccuracy in SHM<br />
applications. Time synchronization is a middleware service common to smart sensor<br />
applications and has been widely investigated. Each smart sensor has its own local clock,<br />
which is not synchronized initially with other sensor nodes. By communicating with<br />
surrounding nodes, smart sensors can assess relative differences among their local clocks.<br />
For example, Mica2 motes employing TPSN are reported to synchronize with each other<br />
to an accuracy of 50 sec; different algorithms and hardware resources may result in<br />
different precision. Whereas time synchronization protocols have been intensively<br />
studied, requirements for synchronization from an application perspective have not been<br />
clearly addressed. The effect of time synchronization on SHM applications is first studied.<br />
As stated earlier, spectral density and correlation function estimation are oftentimes<br />
73