Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors - ideals ...
Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors - ideals ...
Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors - ideals ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1.8715 x10 5 #ofdatablocks<br />
1.871<br />
meas urement 1<br />
measurement 2<br />
Time (sec)<br />
1.8705<br />
1.87<br />
1.8695<br />
1.869<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250<br />
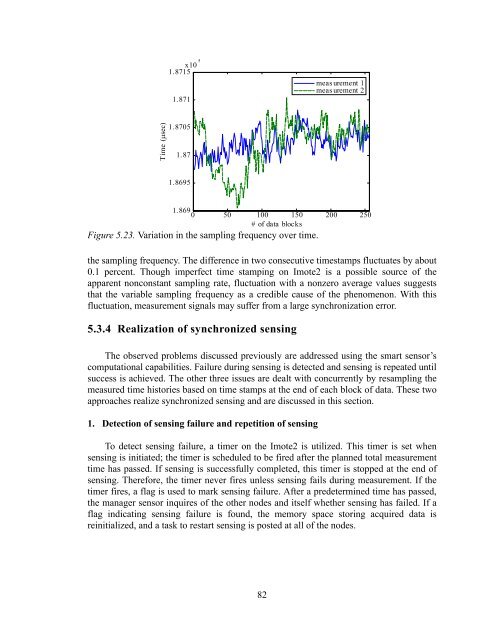
Figure 5.23. Variation in the sampling frequency over time.<br />
the sampling frequency. The difference in two consecutive timestamps fluctuates by about<br />
0.1 percent. Though imperfect time stamping on Imote2 is a possible source of the<br />
apparent nonconstant sampling rate, fluctuation with a nonzero average values suggests<br />
that the variable sampling frequency as a credible cause of the phenomenon. With this<br />
fluctuation, measurement signals may suffer from a large synchronization error.<br />
5.3.4 Realization of synchronized sensing<br />
The observed problems discussed previously are addressed using the smart sensor’s<br />
computational capabilities. Failure during sensing is detected and sensing is repeated until<br />
success is achieved. The other three issues are dealt with concurrently by resampling the<br />
measured time histories based on time stamps at the end of each block of data. These two<br />
approaches realize synchronized sensing and are discussed in this section.<br />
1. Detection of sensing failure and repetition of sensing<br />
To detect sensing failure, a timer on the Imote2 is utilized. This timer is set when<br />
sensing is initiated; the timer is scheduled to be fired after the planned total measurement<br />
time has passed. If sensing is successfully completed, this timer is stopped at the end of<br />
sensing. Therefore, the timer never fires unless sensing fails during measurement. If the<br />
timer fires, a flag is used to mark sensing failure. After a predetermined time has passed,<br />
the manager sensor inquires of the other nodes and itself whether sensing has failed. If a<br />
flag indicating sensing failure is found, the memory space storing acquired data is<br />
reinitialized, and a task to restart sensing is posted at all of the nodes.<br />
82