- Page 2 and 3:
Europeanisation, National Identitie
- Page 4 and 5:
Europeanisation, National Identitie
- Page 6:
To Evgenios and Dionisio
- Page 9 and 10:
viii Contents PART II Europeanisati
- Page 11 and 12:
x Contributors zmiany systemowej (W
- Page 14:
Acknowledgements Most of the contri
- Page 17 and 18:
2 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfrie
- Page 19 and 20:
4 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfrie
- Page 21 and 22:
6 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfrie
- Page 23 and 24:
8 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfrie
- Page 25 and 26:
10 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfri
- Page 27 and 28:
12 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfri
- Page 29 and 30:
14 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfri
- Page 31 and 32:
16 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfri
- Page 33 and 34:
18 Anna Triandafyllidou and Willfri
- Page 36 and 37:
2 The collective identity of Europe
- Page 38 and 39:
The collective identity of Europe 2
- Page 40 and 41:
The collective identity of Europe 2
- Page 42 and 43:
Europe as translation The collectiv
- Page 44 and 45:
The collective identity of Europe 2
- Page 46 and 47:
The collective identity of Europe 3
- Page 48 and 49:
A European heritage? The collective
- Page 50 and 51:
The collective identity of Europe 3
- Page 52 and 53:
The enduring character of nations I
- Page 54 and 55:
Illusions of European integration 3
- Page 56 and 57:
Illusions of European integration 4
- Page 58 and 59:
Illusions of European integration 4
- Page 60 and 61:
Illusions of European integration 4
- Page 62 and 63:
Illusions of European integration 4
- Page 64 and 65:
Illusions of European integration 4
- Page 66 and 67:
Illusions of European integration 5
- Page 68 and 69:
Democracy without demos 53 standard
- Page 70 and 71:
De-limitation of markets and solida
- Page 72 and 73:
Democracy without demos 57 Correspo
- Page 74 and 75:
Democracy without demos 59 direct i
- Page 76 and 77:
Democracy without demos 61 justice,
- Page 78 and 79:
Democracy without demos 63 The repr
- Page 80 and 81:
Democracy without demos 65 however,
- Page 82 and 83:
Democracy without demos 67 differen
- Page 84 and 85:
Democracy without demos 69 between
- Page 86 and 87:
Democracy without demos 71 overtime
- Page 88 and 89:
Democracy without demos 73 This is
- Page 90 and 91:
Democracy without demos 75 matters,
- Page 92 and 93:
Democracy without demos 77 however,
- Page 94 and 95:
the European democratic formation o
- Page 96 and 97:
Democracy without demos 81 Kowalsky
- Page 98 and 99:
5 Integrating immigrants and minori
- Page 100 and 101:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 102 and 103:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 104 and 105:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 106 and 107:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 108 and 109:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 110 and 111:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 112 and 113:
Integrating immigrants and minoriti
- Page 114 and 115:
6 Migration, cultural diversificati
- Page 116 and 117:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 118 and 119:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 120 and 121:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 122 and 123:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 124 and 125:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 126 and 127:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 128 and 129:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 130 and 131:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 132 and 133:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 134 and 135:
Migration and cultural diversificat
- Page 136:
Part II Europeanisation, nations an
- Page 139 and 140:
124 Willfried Spohn populations on
- Page 141 and 142:
126 Willfried Spohn ‘small-Polish
- Page 143 and 144:
128 Willfried Spohn Protestant-secu
- Page 145 and 146:
130 Willfried Spohn about 6 million
- Page 147 and 148:
132 Willfried Spohn The reconstruct
- Page 149 and 150:
134 Willfried Spohn created an open
- Page 151 and 152:
136 Willfried Spohn and core-periph
- Page 153 and 154:
138 Willfried Spohn with nationalis
- Page 155 and 156:
140 Willfried Spohn The consequence
- Page 157 and 158:
142 Willfried Spohn Evans, R. (1982
- Page 159 and 160:
8 Polish identity in the process of
- Page 161 and 162:
146 Miroslava Marody at the time of
- Page 163 and 164:
148 Miroslava Marody Table 8.4 Chan
- Page 165 and 166:
150 Miroslava Marody years, in publ
- Page 167 and 168:
152 Miroslava Marody One could say,
- Page 169 and 170:
154 Erhard Stölting thought since
- Page 171 and 172:
156 Erhard Stölting encompassed th
- Page 173 and 174:
158 Erhard Stölting violations in
- Page 175 and 176:
160 Erhard Stölting remained a top
- Page 177 and 178:
162 Erhard Stölting In general, th
- Page 179 and 180:
164 Erhard Stölting Even before th
- Page 181 and 182:
166 Erhard Stölting Berdiaev, N. (
- Page 184:
Part III Europeanisation, national
- Page 187 and 188:
172 Ewa Morawska 2001; Rajkiewicz 2
- Page 189 and 190:
174 Ewa Morawska These are sociolog
- Page 191 and 192:
176 Ewa Morawska experienced some o
- Page 193 and 194:
178 Ewa Morawska not a particular f
- Page 195 and 196:
180 Ewa Morawska in Düsseldorf in
- Page 197 and 198: 182 Ewa Morawska immigrant business
- Page 199 and 200: 184 Ewa Morawska Appendix I Factors
- Page 201 and 202: 186 Ewa Morawska savings and about
- Page 203 and 204: 188 Ewa Morawska —— (1996) Nati
- Page 205 and 206: 190 Ewa Morawska —— (2001b) ‘
- Page 207 and 208: 11 Changing rhetoric and narratives
- Page 209 and 210: 194 Norbert Cyrus which are most af
- Page 211 and 212: 196 Norbert Cyrus 8 Another trend d
- Page 213 and 214: 198 Norbert Cyrus The differentiati
- Page 215 and 216: 200 Norbert Cyrus 3 Most of all, se
- Page 217 and 218: 202 Norbert Cyrus demands of our ex
- Page 219 and 220: 204 Norbert Cyrus employment of wor
- Page 221 and 222: 206 Norbert Cyrus number of contrac
- Page 223 and 224: 208 Norbert Cyrus enacted that enab
- Page 225 and 226: 210 Norbert Cyrus He really cannot
- Page 227 and 228: 212 Norbert Cyrus collective memory
- Page 229 and 230: 214 Norbert Cyrus increasing xenoph
- Page 231 and 232: 216 Norbert Cyrus would fit the tra
- Page 233 and 234: 218 Norbert Cyrus while in reality
- Page 235 and 236: 220 Norbert Cyrus —— (2001a)
- Page 237 and 238: 222 Norbert Cyrus Meister, H.-P. (1
- Page 239 and 240: 224 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik • c
- Page 241 and 242: 226 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik The q
- Page 243 and 244: 228 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik The u
- Page 245 and 246: 230 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik The i
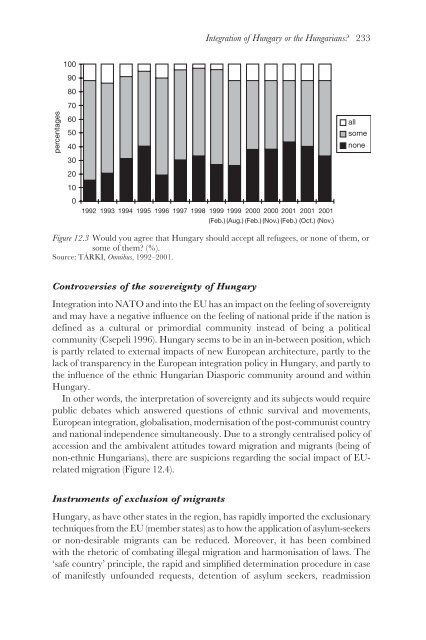
- Page 247: 232 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik 200 1
- Page 251 and 252: 236 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik natio
- Page 253 and 254: 238 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik commi
- Page 255 and 256: 240 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik On th
- Page 257 and 258: 242 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik studi
- Page 259 and 260: 244 Judit Tóth and Endre Sik —
- Page 261 and 262: 246 Index constitutional regime, id
- Page 263 and 264: 248 Index Krawat, K. 176, 178 Kried
- Page 265: 250 Index theoretical framework, th