GTMB 7 - Gene Therapy & Molecular Biology
GTMB 7 - Gene Therapy & Molecular Biology
GTMB 7 - Gene Therapy & Molecular Biology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
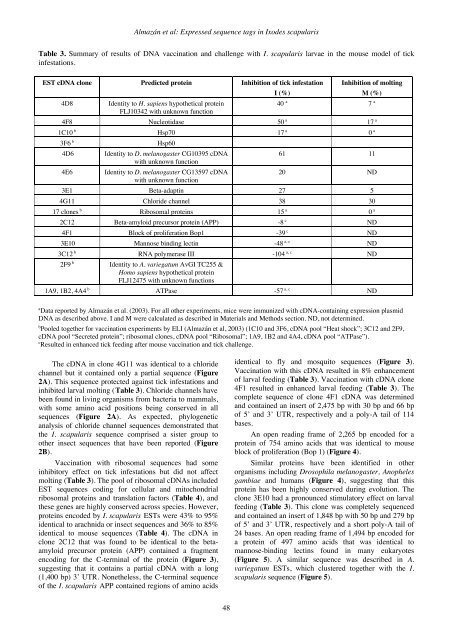
Almazán et al: Expressed sequence tags in Ixodes scapularisTable 3. Summary of results of DNA vaccination and challenge with I. scapularis larvae in the mouse model of tickinfestations.EST cDNA clone Predicted protein Inhibition of tick infestation4D8Identity to H. sapiens hypothetical proteinFLJ10342 with unknown functionI (%)Inhibition of moltingM (%)40 a 7 a4F8 Nucleotidase 50 a 17 a1C10 b Hsp70 17 a 0 a3F6 b4D64E6Hsp60Identity to D. melanogaster CG10395 cDNAwith unknown functionIdentity to D. melanogaster CG13597 cDNAwith unknown function61 1120 ND3E1 Beta-adaptin 27 54G11 Chloride channel 38 3017 clones b Ribosomal proteins 15 a 0 a2C12 Beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) -8 c ND4F1 Block of proliferation Bop1 -39 c ND3E10 Mannose binding lectin -48 a, c ND3C12 b RNA polymerase III -104 a, c ND2F9 bIdentity to A. variegatum AvGI TC255 &Homo sapiens hypothetical proteinFLJ12475 with unknown functions1A9, 1B2, 4A4 b ATPase -57 a, c NDa Data reported by Almazán et al. (2003). For all other experiments, mice were immunized with cDNA-containing expression plasmidDNA as described above. I and M were calculated as described in Materials and Methods section. ND, not determined.b Pooled together for vaccination experiments by ELI (Almazán et al, 2003) (1C10 and 3F6, cDNA pool “Heat shock”; 3C12 and 2F9,cDNA pool “Secreted protein”; ribosomal clones, cDNA pool “Ribosomal”; 1A9, 1B2 and 4A4, cDNA pool “ATPase”).c Resulted in enhanced tick feeding after mouse vaccination and tick challenge.The cDNA in clone 4G11 was identical to a chloridechannel but it contained only a partial sequence (Figure2A). This sequence protected against tick infestations andinhibited larval molting (Table 3). Chloride channels havebeen found in living organisms from bacteria to mammals,with some amino acid positions being conserved in allsequences (Figure 2A). As expected, phylogeneticanalysis of chloride channel sequences demonstrated thatthe I. scapularis sequence comprised a sister group toother insect sequences that have been reported (Figure2B).Vaccination with ribosomal sequences had someinhibitory effect on tick infestations but did not affectmolting (Table 3). The pool of ribosomal cDNAs includedEST sequences coding for cellular and mitochondrialribosomal proteins and translation factors (Table 4), andthese genes are highly conserved across species. However,proteins encoded by I. scapularis ESTs were 43% to 95%identical to arachnida or insect sequences and 36% to 85%identical to mouse sequences (Table 4). The cDNA inclone 2C12 that was found to be identical to the betaamyloidprecursor protein (APP) contained a fragmentencoding for the C-terminal of the protein (Figure 3),suggesting that it contains a partial cDNA with a long(1,400 bp) 3’ UTR. Nonetheless, the C-terminal sequenceof the I. scapularis APP contained regions of amino acidsidentical to fly and mosquito sequences (Figure 3).Vaccination with this cDNA resulted in 8% enhancementof larval feeding (Table 3). Vaccination with cDNA clone4F1 resulted in enhanced larval feeding (Table 3). Thecomplete sequence of clone 4F1 cDNA was determinedand contained an insert of 2,475 bp with 30 bp and 66 bpof 5’ and 3’ UTR, respectively and a poly-A tail of 114bases.An open reading frame of 2,265 bp encoded for aprotein of 754 amino acids that was identical to mouseblock of proliferation (Bop 1) (Figure 4).Similar proteins have been identified in otherorganisms including Drosophila melanogaster, Anophelesgambiae and humans (Figure 4), suggesting that thisprotein has been highly conserved during evolution. Theclone 3E10 had a pronounced stimulatory effect on larvalfeeding (Table 3). This clone was completely sequencedand contained an insert of 1,848 bp with 50 bp and 279 bpof 5’ and 3’ UTR, respectively and a short poly-A tail of24 bases. An open reading frame of 1,494 bp encoded fora protein of 497 amino acids that was identical tomannose-binding lectins found in many eukaryotes(Figure 5). A similar sequence was described in A.variegatum ESTs, which clustered together with the I.scapularis sequence (Figure 5).48