Helicobacter pylori: - Österreichische Gesellschaft für ...
Helicobacter pylori: - Österreichische Gesellschaft für ...
Helicobacter pylori: - Österreichische Gesellschaft für ...
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
GASTROENTEROLOGIE<br />
Guidelines<br />
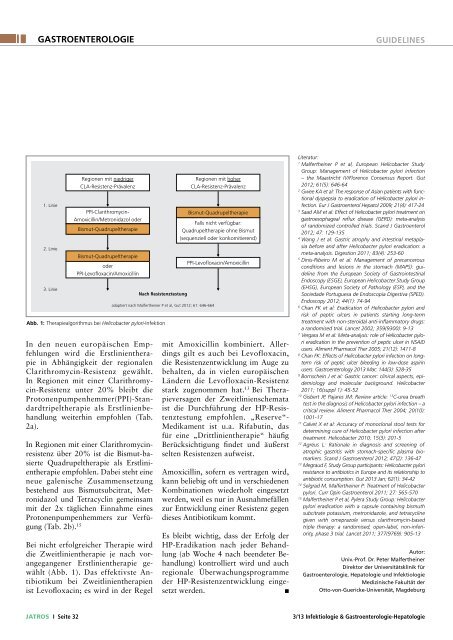
1. Linie<br />
2. Linie<br />
3. Linie<br />
Regionen mit niedriger<br />
CLA-Resistenz-Prävalenz<br />
PPI-Clarithromycin-<br />
Amoxicillin/Metronidazol oder<br />
Bismut-Quadrupeltherapie<br />
Bismut-Quadrupeltherapie<br />
oder<br />
PPI-Levofloxacin/Amoxicillin<br />
In den neuen europäischen Empfehlungen<br />
wird die Erstlinientherapie<br />
in Abhängigkeit der regionalen<br />
Clarithromycin-Resistenz gewählt.<br />
In Regionen mit einer Clarithromycin-Resistenz<br />
unter 20% bleibt die<br />
Protonenpumpenhemmer(PPI)-Standardtripeltherapie<br />
als Erstlinienbehandlung<br />
weiterhin empfohlen (Tab.<br />
2a).<br />
In Regionen mit einer Clarithromycinresistenz<br />
über 20% ist die Bismut-basierte<br />
Quadrupeltherapie als Erstlinientherapie<br />
empfohlen. Dabei steht eine<br />
neue galenische Zusammensetzung<br />
bestehend aus Bismutsubcitrat, Metronidazol<br />
und Tetracyclin gemeinsam<br />
mit der 2x täglichen Einnahme eines<br />
Protonenpumpenhemmers zur Verfügung<br />
(Tab. 2b). 15<br />
Bei nicht erfolgreicher Therapie wird<br />
die Zweitlinientherapie je nach vorangegangener<br />
Erstlinientherapie gewählt<br />
(Abb. 1). Das effektivste Antibiotikum<br />
bei Zweitlinientherapien<br />
ist Levofloxacin; es wird in der Regel<br />
Nach Resistenztestung<br />
adaptiert nach Malfertheiner P et al, Gut 2012; 61: 646-664<br />
Abb. 1: Therapiealgorithmus bei <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong>-Infektion<br />
Regionen mit hoher<br />
CLA-Resistenz-Prävalenz<br />
Bismut-Quadrupeltherapie<br />
Falls nicht verfügbar:<br />
Quadrupeltherapie ohne Bismut<br />
(sequenziell oder konkomitierend)<br />
PPI-Levofloxacin/Amoxicillin<br />
mit Amoxicillin kombiniert. Allerdings<br />
gilt es auch bei Levofloxacin,<br />
die Resistenzentwicklung im Auge zu<br />
behalten, da in vielen europäischen<br />
Ländern die Levofloxacin-Resistenz<br />
stark zugenommen hat. 13 Bei Therapieversagen<br />
der Zweitlinienschemata<br />
ist die Durchführung der HP-Resistenztestung<br />
empfohlen. „Reserve“-<br />
Medikament ist u.a. Rifabutin, das<br />
für eine „Drittlinientherapie“ häufig<br />
Berücksichtigung findet und äußerst<br />
selten Resistenzen aufweist.<br />
Amoxicillin, sofern es vertragen wird,<br />
kann beliebig oft und in verschiedenen<br />
Kombinationen wiederholt eingesetzt<br />
werden, weil es nur in Ausnahmefällen<br />
zur Entwicklung einer Resistenz gegen<br />
dieses Antibiotikum kommt.<br />
Es bleibt wichtig, dass der Erfolg der<br />
HP-Eradikation nach jeder Behandlung<br />
(ab Woche 4 nach beendeter Behandlung)<br />
kontrolliert wird und auch<br />
regionale Überwachungsprogramme<br />
der HP-Resistenzentwicklung eingesetzt<br />
werden.<br />
n<br />
Literatur:<br />
1<br />
Malfertheiner P et al, European <strong>Helicobacter</strong> Study<br />
Group: Management of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> infection<br />
– the Maastricht IV/Florence Consensus Report. Gut<br />
2012; 61(5): 646-64<br />
2<br />
Gwee KA et al: The response of Asian patients with functional<br />
dyspepsia to eradication of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> infection.<br />
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 21(4): 417-24<br />
3<br />
Saad AM et al: Effect of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> treatment on<br />
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): meta-analysis<br />
of randomized controlled trials. Scand J Gastroenterol<br />
2012; 47: 129-135<br />
4<br />
Wang J et al: Gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia<br />
before and after <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> eradication: a<br />
meta-analysis. Digestion 2011; 83(4): 253-60<br />
5<br />
Dinis-Ribeiro M et al: Management of precancerous<br />
conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS): guideline<br />
from the European Society of Gastrointestinal<br />
Endoscopy (ESGE), European <strong>Helicobacter</strong> Study Group<br />
(EHSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and the<br />
Sociedade Portuguesa de Endoscopia Digestiva (SPED).<br />
Endoscopy 2012; 44(1): 74-94<br />
6<br />
Chan FK et al: Eradication of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> and<br />
risk of peptic ulcers in patients starting long-term<br />
treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:<br />
a randomised trial. Lancet 2002; 359(9300): 9-13<br />
7<br />
Vergara M et al: Meta-analysis: role of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong><br />
eradication in the prevention of peptic ulcer in NSAID<br />
users. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 21(12): 1411-8<br />
8<br />
Chan FK: Effects of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> infection on longterm<br />
risk of peptic ulcer bleeding in low-dose aspirin<br />
users. Gastroenterology 2013 Mar; 144(3): 528-35<br />
9<br />
Bornschein J et al: Gastric cancer: clinical aspects, epidemiology<br />
and molecular background. <strong>Helicobacter</strong><br />
2011; 16(suppl 1): 45-52<br />
10<br />
Gisbert JP, Pajares JM: Review article: 13 C-urea breath<br />
test in the diagnosis of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> infection – a<br />
critical review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 20(10):<br />
1001-17<br />
11<br />
Calvet X et al: Accuracy of monoclonal stool tests for<br />
determining cure of <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong> infection after<br />
treatment. <strong>Helicobacter</strong> 2010; 15(3): 201-5<br />
12<br />
Agréus L: Rationale in diagnosis and screening of<br />
atroph ic gastritis with stomach-specific plasma biomarkers.<br />
Scand J Gastroenterol 2012; 47(2): 136-47<br />
13<br />
Megraud F, Study Group participants: <strong>Helicobacter</strong> <strong>pylori</strong><br />
resistance to antibiotics in Europe and its relationship to<br />
antibiotic consumption. Gut 2013 Jan; 62(1): 34-42<br />
14<br />
Selgrad M, Malfertheiner P: Treatment of <strong>Helicobacter</strong><br />
<strong>pylori</strong>. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2011; 27: 565-570<br />
15<br />
Malfertheiner P et al, Pylera Study Group: <strong>Helicobacter</strong><br />
<strong>pylori</strong> eradication with a capsule containing bismuth<br />
subcitrate potassium, metronidazole, and tetracycline<br />
given with omeprazole versus clarithromycin-based<br />
triple therapy: a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority,<br />
phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011; 377(9769): 905-13<br />
Autor:<br />
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Peter Malfertheiner<br />
Direktor der Universitätsklinik für<br />
Gastroenterologie, Hepatologie und Infektiologie<br />
Medizinische Fakultät der<br />
Otto-von-Guericke-Universität, Magdeburg<br />
jatros I Seite 32<br />
3/13 Infektiologie & Gastroenterologie-Hepatologie