OP-755 Part 2 Pages 197-401 - Personal Page of GENE SLOVER
OP-755 Part 2 Pages 197-401 - Personal Page of GENE SLOVER
OP-755 Part 2 Pages 197-401 - Personal Page of GENE SLOVER
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
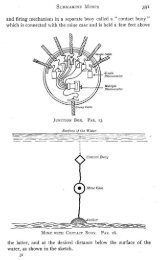
282<br />
striction. The limits <strong>of</strong> adjustment permit hoist acceleration<br />
and deceleration greater than the rates as determined by the<br />
B-end cams but not in excess <strong>of</strong> one-half gravity. Dashpot<br />
reservoir 70 supplies oil to take care <strong>of</strong> the differential<br />
area <strong>of</strong> the piston and to replace seepage loss.<br />
56. Power failure - Servo Electrical. - The diagram <strong>of</strong><br />
plate 10 shows the circuit during power failure whenoperating<br />
with servo electrical control. If power should fail during<br />
servo operation, both solenoids 1 and 28 wil,l be de-energized,<br />
which vents the brake cylinder and applies the brake, and also<br />
positions valve 2 to by-pass the main circuit lines. However,<br />
with the pump in hoi.st Lng position, line 24 is open to line<br />
25 only through restriction 49 until the pumpis near its centered<br />
position. Restriction 49 is small enough to prevent a<br />
pressure drop in line 23 which would permit the car to drop<br />
due to a slack cable (power failure when.hoisting) ,but is<br />
sufficiently large to prevent hoisting when the car is at the<br />
lower unloading station with door open. At occurrence <strong>of</strong> power<br />
failure the pumpcontinues to drive the B-end carried on by<br />
electric. motor inertia. The brake under these conditions is<br />
engaged, but the free wheeling device 11 allows over-r-un.<strong>of</strong> the<br />
drum and .the B-end. Thus the car gradually decelerates, without<br />
cable whl.p , and as it comes to rest the ·load is taken by<br />
the brake. Simultaneously pressure falls <strong>of</strong>f in line 23 and<br />
centering plunger 22 restores the pumpyoke to its center posi<br />
tion. The electric motor cannot be started until the pump<br />
yoke has been returned to near the center position. At this<br />
position neutral switch 13 (in the motor starting circuit) is<br />
closed.<br />
57. If power failure should occur during a lowering<br />
cycle (servo electrical control), solenoids 1 and 28 will be<br />
de-energized to by-pass and vent the main circuit, and to vent<br />
the control circuit. Venting the latter applies the brake to<br />
decelerate and stop the hoist. Centering plunger 21 is vented<br />
and moves to return the yoke to centered position.<br />
58. St op pos it ion - Servo Meehan i c a l. - The diagram <strong>of</strong><br />
pLate 11 showsthe circuit in the stop position with the controls<br />
set for servo mechanical operation. The arrangement shown<br />
provides for hoist control and operation in event that the electrical<br />
control circuit is inoperative. The controls are set<br />
:for servo mechanical operation by shifting the selector control<br />
lever 12 to "Servo Mechanical" position. This movement<br />
shifts the brake release valve 14, the venting valve 2 and releases<br />
latch 52. The latter drops into the notch on cam 53<br />
(provided lever 31 is at neutral). This allows latch valve 54<br />
to shift to vent the main circuit and the control circuit to<br />
the tank. Main circuit lines 23 and 41 are vented to the tank<br />
through check valves 62. and 64 and thence around the power