Nepal Hazard Risk Assessment - Asia-Pacific Gateway for Disaster ...
Nepal Hazard Risk Assessment - Asia-Pacific Gateway for Disaster ...
Nepal Hazard Risk Assessment - Asia-Pacific Gateway for Disaster ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Nepal</strong> <strong>Hazard</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong><br />
2.1.4 LANDSLIDES<br />
ICMOD 1996 has published landslide studies and management in <strong>Nepal</strong>. The publication provides<br />
evidence of severs landslide in the country. In 1953, at least five earthquakes rocked Far-western <strong>Nepal</strong>.<br />
The epicentres were located either in <strong>Nepal</strong> or the adjoining Indian Himalayas. Most of the secondary<br />
epicentres were near the Main Boundary Thrust or in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Also in the same volume<br />
it was reported that a landslide dam was <strong>for</strong>med at Labu Besi, Central <strong>Nepal</strong>, on August 1 1968, and it<br />
blocked the entire Budhi Gandaki River and created a 60m deep lake <strong>for</strong> 29 hours. After the breaching of<br />
the dam, the debris flow and flood washed away most of the houses and bridges in the low lying areas<br />
the earthquake of 1969 in Far-western <strong>Nepal</strong> which took a heavy toll of life and property in the Bajhang<br />
area. The dam on the Pardi Khola, at the southern end of Phewa Lake, Pokhara, collapsed in 1970 owing<br />
to severed piping on the right abutment (Sharma, 1981). The Tansen area of Western <strong>Nepal</strong> suffered<br />
from heavy rainfall in 1971. The rainfall measured 450mm in 24 hours (Sharma 1981) and the Tinau<br />
Khola flood washed away Khaseuli (Butwal) Bazaar. In 1975, a part of Tahamalla Tolof Bhaktapur<br />
municipality was damaged by slumping. In the same year, several houses in Humat Toi, Kathmandu,<br />
which were built on soft soil the solid waste of the city, were also destroyed or damaged by slumps. On<br />
the morning of June 5, 1976, a huge landslide occurred in Bhagabati Tar Panchayat of Kaski district in<br />
Western <strong>Nepal</strong>, burying the entire village and killing about 75 people. The slide occurred after 50mm of<br />
rainfall.<br />
The Department of Mines and Geology has compiled landslide catalog, however due to paucity of<br />
resources, dataset is restricted to smaller region.<br />
2.1.5 EPIDEMICS<br />
<strong>Nepal</strong> is prone to wide range of outbreaks and diseases. Several deaths have been reported due to water,<br />
vector and infection bond diseases. Few of the frequently reported diseases are Diarrhea, Kalazaar,<br />
Chickenpox, Hepatitis, Influenza, Typhoid, Acute Respiratory Infection, Malaria, Sexual Transmitted<br />
Infection, Tuberculosis, and Leprosy. The reports are available from various database sources. Official<br />
data is available with Department of Health Service (EHA, 2007). Apart from this, DesInventar<br />
(DesInventar) has also compiled data <strong>for</strong> epidemics <strong>for</strong> more than two decades. The root cause <strong>for</strong> water<br />
and vector bond diseases are linked to existing socio-economic condition, hygiene and health<br />
infrastructure. There is a cross linkage of these diseases with floods and other hydro-meteorological<br />
conditions.<br />
Apart from above stated five major hydro meteorological, geographical and health hazards. the country<br />
in also susceptible to other hazards like GLOF, <strong>for</strong>est fire, Thunder lighting, hailstorm, high wind, heavy<br />
metal in ground water, fire and terrorism. If these hazards are analyzed with respect to exposure of<br />
human life, economic & physical sector, more losses are attributed due to earthquake, flood landslide,<br />
drought and health hazard. This project is scoping only five main hazards <strong>for</strong> future study.<br />
2.2 TREND ANALYSIS OF DISASTERS<br />
<strong>Nepal</strong> is prone to several classes of hazards ranging from hydro-meteorological, geological, biological,<br />
industrial and accident related disasters. Several disasters have been reported in past. In view of<br />
youngest mountain, Himalaya, the region is hotspot <strong>for</strong> geological <strong>for</strong>mation and activities. This leads to<br />
frequent large earthquakes, landslide, floods and other collateral hazards. Apart from these activities, the<br />
country is prone to cloud burst, hailstorm, high winds and heat strokes in central and Terai Region. The<br />
climate change has accelerated the frequency of hazards occurrence. Table 2.1 shows the severity of<br />
hazards and impacts. Ministry of Home Affairs (MOHA, 2004) has compiled the hazard profile of<br />
<strong>Nepal</strong>. This comprehensive compilation records are existing <strong>for</strong> more than a decade.<br />
Figure 2.1 shows the trend line <strong>for</strong> disasters in <strong>Nepal</strong>. As per MOHA report, the disasters are broadly<br />
categorized into various types including Floods, landslide, earthquake, hailstorm, Thunder bolt, wind<br />
storm, fire and epidemic. The disasters have significantly contributed <strong>for</strong> loss of human, livestock and<br />
economic losses.<br />
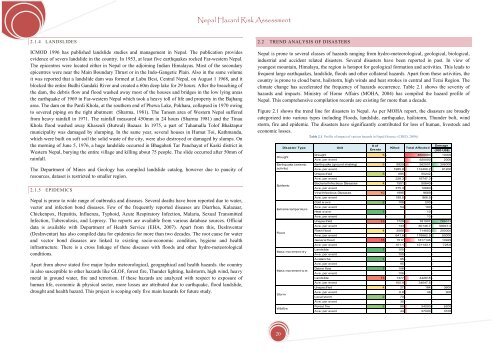
Table 2.1. Profile of impact of various hazards in <strong>Nepal</strong> (Source: (CRED, 2009))<br />
<strong>Disaster</strong> Type<br />
Drought<br />
Earthquake (seismic<br />
activity)<br />
Epidemic<br />
Extreme temperature<br />
Flood<br />
Mass movement dry<br />
Mass movement w et<br />
Storm<br />
Wildfire<br />
Unit<br />
# of<br />
Dam age<br />
Killed Total Affected<br />
Eve nts<br />
(000 US$)<br />
Drought 5 - 4600000 10000<br />
Ave. per event - 920000 2000<br />
Earthquake (ground shaking) 5 9929 562001 306000<br />
Ave. per event 1985.8 112400.2 61200<br />
Unspecified 3 685 50242 -<br />
Ave. per event 228.3 16747.3 -<br />
Bacterial Infectious Diseases 4 1501 50640 -<br />
Ave. per event 375.3 12660 -<br />
Viral Infectious Diseases 10 1995 9669 -<br />
Ave. per event 199.5 966.9 -<br />
Cold w ave 2 108 200 -<br />
Ave. per event 54 100 -<br />
Heat w ave 1 - 10 -<br />
Ave. per event - 10 -<br />
Unspecified 13 1729 781907 766313<br />
Ave. per event 133 60146.7 58947.2<br />
Flash flood 4 2566 714650 200000<br />
Ave. per event 641.5 178662.5 50000<br />
General flood 15 1517 1817146 10929<br />
Ave. per event 101.1 121143.1 728.6<br />
Landslide 1 150 - -<br />
Ave. per event 150 - -<br />
Avalanche 1 95 - -<br />
Ave. per event 95 - -<br />
Debris flow 1 106 - -<br />
Ave. per event 106 - -<br />
Landslide 13 1377 442618 -<br />
Ave. per event 105.9 34047.5 -<br />
Unspecified 4 27 184 3600<br />
Ave. per event 6.8 46 900<br />
Local storm 2 70 - -<br />
Ave. per event 35 - -<br />
Forest fire 2 88 54000 6200<br />
Ave. per event 44 27000 3100<br />
20