Nepal Hazard Risk Assessment - Asia-Pacific Gateway for Disaster ...
Nepal Hazard Risk Assessment - Asia-Pacific Gateway for Disaster ...
Nepal Hazard Risk Assessment - Asia-Pacific Gateway for Disaster ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Nepal</strong> <strong>Hazard</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong><br />
3.2 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT<br />
<strong>Nepal</strong> has witnessed several large scale earthquakes in past centuries. The Department of Mines and<br />
Geology has developed Peak Ground Acceleration map <strong>for</strong> the whole country (Pandey et al., 2002). The<br />
earthquake hazard maps have been developed in MMI scale. The MMI scale is one of the simple<br />
indicators <strong>for</strong> understanding the severity of earthquake hazards.<br />
3.2.1 MAP CONTENT<br />
Earthquake hazard map has been developed in Modified Mercalli Intensity scale (MMI), which shows<br />
distribution of intensity throughout the country. The earthquake hazard maps have been prepared <strong>for</strong><br />
several return periods i.e., 500, 250, 100, and 50 yr.<br />
• Epicentre maps of <strong>Nepal</strong> Himalaya from National Seismological Centre (NSC, 2005)<br />
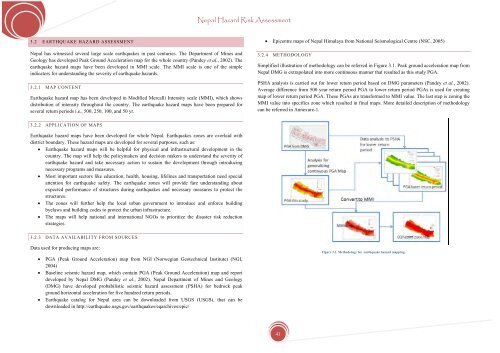
3.2.4 METHODOLOGY<br />
Simplified illustration of methodology can be referred in Figure 3.1. Peak ground acceleration map from<br />
<strong>Nepal</strong> DMG is extrapolated into more continuous manner that resulted as this study PGA.<br />
PSHA analysis is carried out <strong>for</strong> lower return period based on DMG parameters (Pandey et al., 2002).<br />
Average difference from 500 year return period PGA to lower return period PGAs is used <strong>for</strong> creating<br />
map of lower return period PGA. These PGAs are trans<strong>for</strong>med to MMI value. The last step is zoning the<br />
MMI value into specifics zone which resulted in final maps. More detailed description of methodology<br />
can be referred in Annexure-1.<br />
3.2.2 APPLICATION OF MAPS<br />
Earthquake hazard maps have been developed <strong>for</strong> whole <strong>Nepal</strong>. Earthquakes zones are overlaid with<br />
district boundary. These hazard maps are developed <strong>for</strong> several purposes, such as:<br />
• Earthquake hazard maps will be helpful <strong>for</strong> physical and infrastructural development in the<br />
country. The map will help the policymakers and decision makers to understand the severity of<br />
earthquake hazard and take necessary action to sustain the development through introducing<br />
necessary programs and measures.<br />
• Most important sectors like education, health, housing, lifelines and transportation need special<br />
attention <strong>for</strong> earthquake safety. The earthquake zones will provide fare understanding about<br />
expected per<strong>for</strong>mance of structures during earthquakes and necessary measures to protect the<br />
structures.<br />
• The zones will further help the local urban government to introduce and en<strong>for</strong>ce building<br />
byelaws and building codes to protect the urban infrastructure.<br />
• The maps will help national and international NGOs to prioritize the disaster risk reduction<br />
strategies.<br />
3.2.3 DATA AVAILABILITY FROM SOURCES<br />
Data used <strong>for</strong> producing maps are:<br />
• PGA (Peak Ground Acceleration) map from NGI (Norwegian Geotechnical Institute) (NGI,<br />
2004)<br />
• Baseline seismic hazard map, which contain PGA (Peak Ground Acceleration) map and report<br />
developed by <strong>Nepal</strong> DMG (Pandey et al., 2002). <strong>Nepal</strong> Department of Mines and Geology<br />
(DMG) have developed probabilistic seismic hazard assessment (PSHA) <strong>for</strong> bedrock peak<br />
ground horizontal acceleration <strong>for</strong> five hundred return periods.<br />
• Earthquake catalog <strong>for</strong> <strong>Nepal</strong> area can be downloaded from USGS (USGS), that can be<br />
downloaded in http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqarchives/epic/<br />
Figure 3.1. Methodology <strong>for</strong> earthquake hazard mapping.<br />
41