Improved Methodology for the Preparation of Chiral Amines
Improved Methodology for the Preparation of Chiral Amines
Improved Methodology for the Preparation of Chiral Amines
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
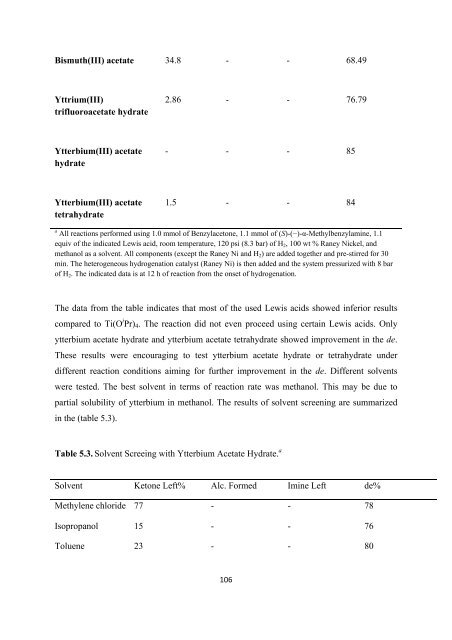
Bismuth(III) acetate 34.8 - - 68.49<br />
Yttrium(III)<br />
trifluoroacetate hydrate<br />
2.86 - - 76.79<br />
Ytterbium(III) acetate<br />
hydrate<br />
- - - 85<br />
Ytterbium(III) acetate<br />
tetrahydrate<br />
1.5 - - 84<br />
a All reactions per<strong>for</strong>med using 1.0 mmol <strong>of</strong> Benzylacetone, 1.1 mmol <strong>of</strong> (S)-(−)-α-Methylbenzylamine, 1.1<br />
equiv <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> indicated Lewis acid, room temperature, 120 psi (8.3 bar) <strong>of</strong> H 2 , 100 wt % Raney Nickel, and<br />
methanol as a solvent. All components (except <strong>the</strong> Raney Ni and H 2 ) are added toge<strong>the</strong>r and pre-stirred <strong>for</strong> 30<br />
min. The heterogeneous hydrogenation catalyst (Raney Ni) is <strong>the</strong>n added and <strong>the</strong> system pressurized with 8 bar<br />
<strong>of</strong> H 2 . The indicated data is at 12 h <strong>of</strong> reaction from <strong>the</strong> onset <strong>of</strong> hydrogenation.<br />
The data from <strong>the</strong> table indicates that most <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> used Lewis acids showed inferior results<br />
compared to Ti(O i Pr) 4 . The reaction did not even proceed using certain Lewis acids. Only<br />
ytterbium acetate hydrate and ytterbium acetate tetrahydrate showed improvement in <strong>the</strong> de.<br />
These results were encouraging to test ytterbium acetate hydrate or tetrahydrate under<br />
different reaction conditions aiming <strong>for</strong> fur<strong>the</strong>r improvement in <strong>the</strong> de. Different solvents<br />
were tested. The best solvent in terms <strong>of</strong> reaction rate was methanol. This may be due to<br />
partial solubility <strong>of</strong> ytterbium in methanol. The results <strong>of</strong> solvent screening are summarized<br />
in <strong>the</strong> (table 5.3).<br />
Table 5.3. Solvent Screeing with Ytterbium Acetate Hydrate. a<br />
Solvent Ketone Left% Alc. Formed Imine Left de%<br />
Methylene chloride 77 - - 78<br />
Isopropanol 15 - - 76<br />
Toluene 23 - - 80<br />
106