Improved Methodology for the Preparation of Chiral Amines
Improved Methodology for the Preparation of Chiral Amines
Improved Methodology for the Preparation of Chiral Amines
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
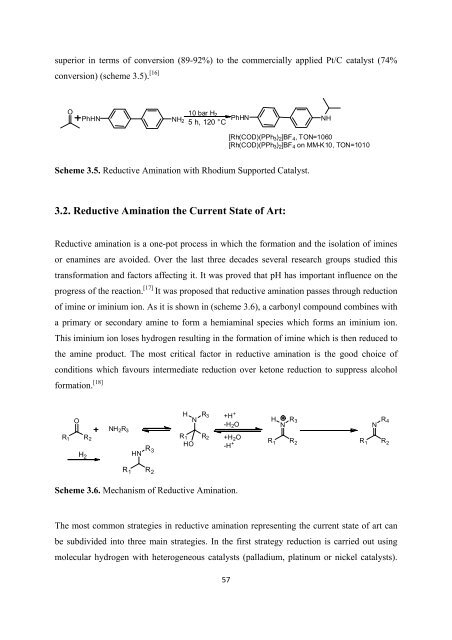
superior in terms <strong>of</strong> conversion (89-92%) to <strong>the</strong> commercially applied Pt/C catalyst (74%<br />
conversion) (scheme 3.5). [16]<br />
O 10 bar H 2<br />
PhHN NH2 PhHN NH<br />
5h,120°C<br />
[Rh(COD)(PPh 3 ) 2 ]BF 4 ,TON=1060<br />
[Rh(COD)(PPh 3 ) 2 ]BF 4 on MM-K10, TON=1010<br />
Scheme 3.5. Reductive Amination with Rhodium Supported Catalyst.<br />
3.2. Reductive Amination <strong>the</strong> Current State <strong>of</strong> Art:<br />
Reductive amination is a one-pot process in which <strong>the</strong> <strong>for</strong>mation and <strong>the</strong> isolation <strong>of</strong> imines<br />
or enamines are avoided. Over <strong>the</strong> last three decades several research groups studied this<br />
trans<strong>for</strong>mation and factors affecting it. It was proved that pH has important influence on <strong>the</strong><br />
progress <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> reaction. [17] It was proposed that reductive amination passes through reduction<br />
<strong>of</strong> imine or iminium ion. As it is shown in (scheme 3.6), a carbonyl compound combines with<br />
a primary or secondary amine to <strong>for</strong>m a hemiaminal species which <strong>for</strong>ms an iminium ion.<br />
This iminium ion loses hydrogen resulting in <strong>the</strong> <strong>for</strong>mation <strong>of</strong> imine which is <strong>the</strong>n reduced to<br />
<strong>the</strong> amine product. The most critical factor in reductive amination is <strong>the</strong> good choice <strong>of</strong><br />
conditions which favours intermediate reduction over ketone reduction to suppress alcohol<br />
<strong>for</strong>mation. [18]<br />
O<br />
R 1 R 2<br />
H<br />
N R 3<br />
NH 2 R 3<br />
HN R 3<br />
H 2<br />
R 1 R 2<br />
R 1<br />
HO<br />
R 2<br />
+H +<br />
-H 2 O<br />
H<br />
N R 3<br />
N R 4<br />
+H 2 O<br />
-H + R 1 R 2<br />
R 1 R 2<br />
Scheme 3.6. Mechanism <strong>of</strong> Reductive Amination.<br />
The most common strategies in reductive amination representing <strong>the</strong> current state <strong>of</strong> art can<br />
be subdivided into three main strategies. In <strong>the</strong> first strategy reduction is carried out using<br />
molecular hydrogen with heterogeneous catalysts (palladium, platinum or nickel catalysts).<br />
57