II International Symposium on Carbon for Catalysis ABSTRACTS
II International Symposium on Carbon for Catalysis ABSTRACTS
II International Symposium on Carbon for Catalysis ABSTRACTS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
OP-I-9<br />
Hydrogenati<strong>on</strong>s were carried out in a batch stainless steel reactor equipped with a heating<br />
jacket and a hydrogen supply system at temperatures of 293-323K and hydrogen pressures<br />
between 0.4-1.7 MPa. The structured Pd/ACF catalyst was placed between two metal grids.<br />
As the reacti<strong>on</strong> products, 1-hexene, n-hexane, 2-trans-hexene and 2-cis-hexene were found by<br />
GC. n-Heptane was used as a solvent.<br />
Results and discussi<strong>on</strong><br />
Catalysts with different Pd loading (0.4 wt.%, 0.6 wt.%, 1.2 wt.%) and the same<br />
dispersi<strong>on</strong> showed an identical initial activity of 0.140 ±0.004 kmolH 2·kgPd -1·s -1 (at 303 K,<br />
1.3 MPa), indicating the absence of mass transfer limitati<strong>on</strong>s. Selectivity to 1-hexene was<br />
97±0.4% up to 80% c<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong>, and 96±0.4% at 90% c<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong> was obtained.<br />
The catalyst activity and selectivity were observed to be stable from the sec<strong>on</strong>d run and<br />
no Pd leaching occurred during repeated catalyst reuse. The catalyst does not require any<br />
c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>ing between runs. Both fresh and used Pd/ACF catalysts showed better catalytic<br />
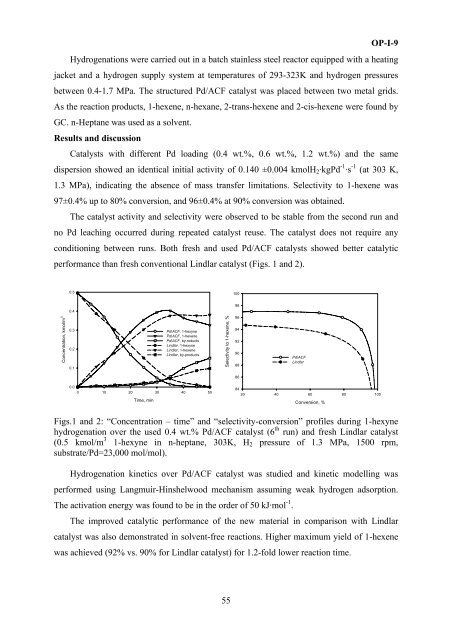
per<strong>for</strong>mance than fresh c<strong>on</strong>venti<strong>on</strong>al Lindlar catalyst (Figs. 1 and 2).<br />
0.5<br />
0.5100<br />
0.4<br />
98<br />
0.4<br />
C<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>, kmol/m 3<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
Pd/ACF, 1-hexyne<br />
Pd/ACF, 1-hexene<br />
Pd/ACF, by-roducts<br />
Lindlar, 1-hexyne<br />
Lindlar, 1-hexene<br />
Lindlar, by-products<br />
C<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>, kmol/m 3<br />
Selectivity to 1-hexene, %<br />
96<br />
0.3 94<br />
92<br />
0.2<br />
90<br />
88<br />
0.1<br />
Pd/ACF<br />
Lindlar<br />
Pd/ACF, 1-hexyne<br />
Pd/ACF, 1-hexene<br />
Pd/ACF, by-roducts<br />
Lindlar, 1-hexyne<br />
Lindlar, 1-hexene<br />
Lindlar, by-products<br />
86<br />
0.0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50<br />
Time, min<br />
0.0<br />
84<br />
0<br />
20<br />
10<br />
40<br />
20 30<br />
60<br />
40<br />
80<br />
50<br />
100<br />
Time,<br />
C<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong>,<br />
min<br />
%<br />
Figs.1 and 2: “C<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> – time” and “selectivity-c<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong>” profiles during 1-hexyne<br />
hydrogenati<strong>on</strong> over the used 0.4 wt.% Pd/ACF catalyst (6 th run) and fresh Lindlar catalyst<br />
(0.5 kmol/m 3 1-hexyne in n-heptane, 303K, H 2 pressure of 1.3 MPa, 1500 rpm,<br />
substrate/Pd=23,000 mol/mol).<br />
Hydrogenati<strong>on</strong> kinetics over Pd/ACF catalyst was studied and kinetic modelling was<br />
per<strong>for</strong>med using Langmuir-Hinshelwood mechanism assuming weak hydrogen adsorpti<strong>on</strong>.<br />
The activati<strong>on</strong> energy was found to be in the order of 50 kJ·mol -1 .<br />
The improved catalytic per<strong>for</strong>mance of the new material in comparis<strong>on</strong> with Lindlar<br />
catalyst was also dem<strong>on</strong>strated in solvent-free reacti<strong>on</strong>s. Higher maximum yield of 1-hexene<br />
was achieved (92% vs. 90% <strong>for</strong> Lindlar catalyst) <strong>for</strong> 1.2-fold lower reacti<strong>on</strong> time.<br />
55