II International Symposium on Carbon for Catalysis ABSTRACTS
II International Symposium on Carbon for Catalysis ABSTRACTS
II International Symposium on Carbon for Catalysis ABSTRACTS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
OP-I-12<br />
The carb<strong>on</strong> matrix avoids the <strong>for</strong>mati<strong>on</strong> of large Al 2 O 3 or TiO 2 crystallite in the<br />
composite, as shown by XRD. XPS show that both organic and inorganic phases were nearly<br />
independent, no significant interacti<strong>on</strong>s between them were observed. The carb<strong>on</strong> matrix, as<br />
well Al 2 O 3 or TiO 2 oxides present similar XPS patterns than their pure phases. Their acidity,<br />
determined by isopropanol decompositi<strong>on</strong> depended <strong>on</strong> the nature of the metal oxide present<br />
(TiO 2 ≥Al 2 O 3 ) while the organic fracti<strong>on</strong> was not active.<br />
Regarding to the hydrophilic character of the samples, two types of active sites were<br />
determined by water adsorpti<strong>on</strong> at room temperature. The str<strong>on</strong>g primary centres corresp<strong>on</strong>d<br />
to the micropore filling or water adsorpti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> acidic centres and weak sec<strong>on</strong>dary centres<br />
corresp<strong>on</strong>d to adsorpti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> hydrophilic (C=O) groups (2). Primary centres were more<br />
abundant and str<strong>on</strong>ger <strong>on</strong> composites than in carb<strong>on</strong> aerogels according with their more acid<br />
character and smaller microporosity.<br />
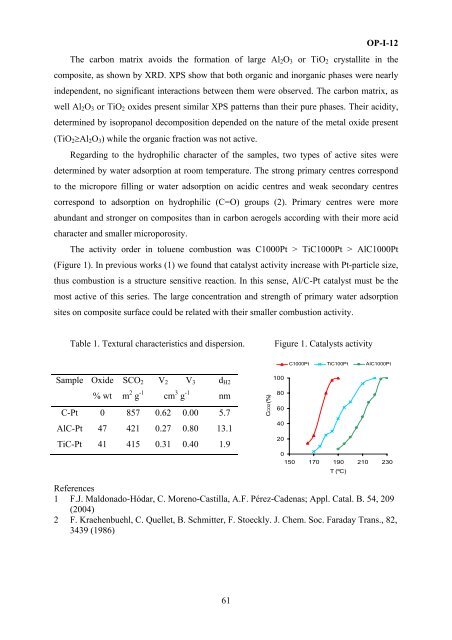
The activity order in toluene combusti<strong>on</strong> was C1000Pt > TiC1000Pt > AlC1000Pt<br />
(Figure 1). In previous works (1) we found that catalyst activity increase with Pt-particle size,<br />
thus combusti<strong>on</strong> is a structure sensitive reacti<strong>on</strong>. In this sense, Al/C-Pt catalyst must be the<br />
most active of this series. The large c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> and strength of primary water adsorpti<strong>on</strong><br />
sites <strong>on</strong> composite surface could be related with their smaller combusti<strong>on</strong> activity.<br />
Table 1. Textural characteristics and dispersi<strong>on</strong>.<br />
Figure 1. Catalysts activity<br />
C1000Pt TiC100Pt AlC1000Pt<br />
Sample Oxide SCO 2 V 2 V 3 d H2<br />
% wt m 2 g -1 cm 3 g -1 nm<br />
C-Pt 0 857 0.62 0.00 5.7<br />
AlC-Pt 47 421 0.27 0.80 13.1<br />
TiC-Pt 41 415 0.31 0.40 1.9<br />
CCO2 (%)<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
150 170 190 210 230<br />
T (ºC)<br />
References<br />
1 F.J. Mald<strong>on</strong>ado-Hódar, C. Moreno-Castilla, A.F. Pérez-Cadenas; Appl. Catal. B. 54, 209<br />
(2004)<br />
2 F. Kraehenbuehl, C. Quellet, B. Schmitter, F. Stoeckly. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans., 82,<br />
3439 (1986)<br />
61