history of mathematics - National STEM Centre
history of mathematics - National STEM Centre
history of mathematics - National STEM Centre
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The Arabs<br />
Activity 5.2<br />
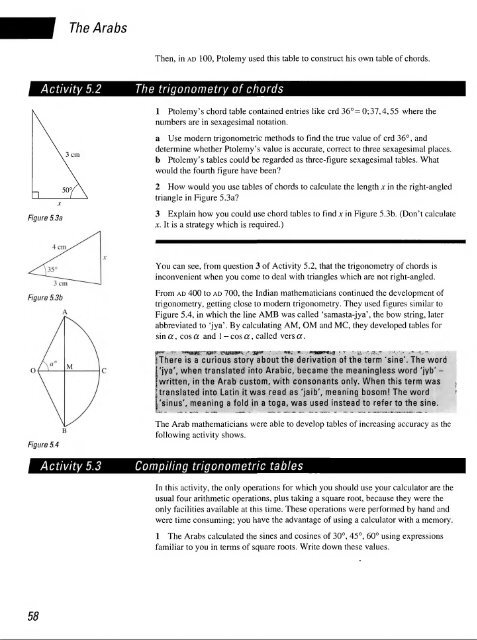
Figure 5.3a<br />
O<br />
Figure 5,4<br />
58<br />
3 cm<br />
50°,<br />
Then, in AD 100, Ptolemy used this table to construct his own table <strong>of</strong> chords.<br />
The trigonometry <strong>of</strong> chords<br />
1 Ptolemy's chord table contained entries like crd 36°= 0;37,4,55 where the<br />
numbers are in sexagesimal notation.<br />
a Use modern trigonometric methods to find the true value <strong>of</strong> crd 36°, and<br />
determine whether Ptolemy's value is accurate, correct to three sexagesimal places.<br />
b Ptolemy's tables could be regarded as three-figure sexagesimal tables. What<br />
would the fourth figure have been?<br />
2 How would you use tables <strong>of</strong> chords to calculate the length x in the right-angled<br />
triangle in Figure 5.3a?<br />
3 Explain how you could use chord tables to find x in Figure 5.3b. (Don't calculate<br />
x. It is a strategy which is required.)<br />
You can see, from question 3 <strong>of</strong> Activity 5.2, that the trigonometry <strong>of</strong> chords is<br />
inconvenient when you come to deal with triangles which are not right-angled.<br />
From AD 400 to AD 700, the Indian mathematicians continued the development <strong>of</strong><br />
trigonometry, getting close to modern trigonometry. They used figures similar to<br />
Figure 5.4, in which the line AMB was called 'samasta-jya', the bow string, later<br />
abbreviated to 'jya'. By calculating AM, OM and MC, they developed tables for<br />
sin a, cos a and 1 - cos a, called vers a.<br />
'There is a curious story about the derivation <strong>of</strong> the term 'sine'. The word'!<br />
'jya', when translated into Arabic, became the meaningless word 'jyb' - ;<br />
written, in the Arab custom, with consonants only. When this term was<br />
translated into Latin it was read as 'jaib', meaning bosom! The word<br />
'sinus', meaning a fold in a toga, was used instead to refer to the sine. as<br />
'••S!<br />
The Arab mathematicians were able to develop tables <strong>of</strong> increasing accuracy as the<br />
following activity shows.<br />
Activity 5.3 Compiling trigonometric tables<br />
In this activity, the only operations for which you should use your calculator are the<br />
usual four arithmetic operations, plus taking a square root, because they were the<br />
only facilities available at this time. These operations were performed by hand and<br />
were time consuming; you have the advantage <strong>of</strong> using a calculator with a memory.<br />
1 The Arabs calculated the sines and cosines <strong>of</strong> 30°, 45°, 60° using expressions<br />
familiar to you in terms <strong>of</strong> square roots. Write down these values.